数据结构与算法系列之单链表

💗 💗 博客:小怡同学
💗 💗 个人简介:编程小萌新
💗 💗 如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏 🌞
这里写目录标题
- test.h
- SList.h
- 注意事项
- 一级指针与二级指针的使用
- assert的使用
- 空链表与顺序表的区别及优缺点
- 详解各接口函数的功能
test.h
#include "SList.h"
void Test()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SLPrint(plist);SLPushBack(&plist, 7);SLPushBack(&plist, 8);SLPushBack(&plist, 9);SLPushBack(&plist, 10);SLPrint(plist);//SLTNode* ret = SListFind(plist, 8);//SLPrint(plist);//SLisTEraseAfter(ret);//SLPrint(plist);//SListInsert(&plist, ret, 3);//SListInsertAfter(ret, 4);//SlistErase(&plist , ret);//SLisTEraseAfter(ret);//SLPrint(plist);
}int main()
{Test();
}
SList.h
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDataType data;struct SList* next;
}SLTNode;void SLPrint(SLTNode* phead);//打印
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//尾插
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);//尾删
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);//头删
SLTNode* BuySLTode(SLTDataType x);//开辟一个节点
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);//找到x这个节点
void SListInsert(SLTNode** phead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);//在pos之前增加data为x这个节点
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);//在pos之后增加data为x这个节点
void SlistErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);//删除在pos之前,删除这个节点
void SLisTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);//删除pos之后的节点
# SList.c```c
#include "SList.h"
SLTNode* BuySLTode(SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SLPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->",cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail ->next= newnode;}
}void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;}
}void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);if ( (*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;SLTNode* prev = NULL;while (tail->next != NULL){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
}void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;*pphead = (*pphead)->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;}SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){SLTPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* cur = pphead;while (cur->next != pos){cur = cur->next;}SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);cur->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}}void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}void SlistErase(SLTNode**pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);//assert(*pphead);if (*pphead == pos){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != pos){cur = cur->next;}cur->next= pos->next;free(pos);}}void SLisTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);SLTNode* cur = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}
注意事项
一级指针与二级指针的使用
可以看得出来,接口函数传参时有的需要而二级指针,有的需要一级指针
总结为一句话,改变结构体地址需要二级指针,改变结构体(SLTNode)成员需要一级指针。
解析如下
1.根据c语言,实参传址调用与传值调用知识我们可以知道,改变元素大小需要传入地址。而改变地址,则需要传入地址的地址。因为形参只是实参的拷贝 函数销毁之后形参将不存在
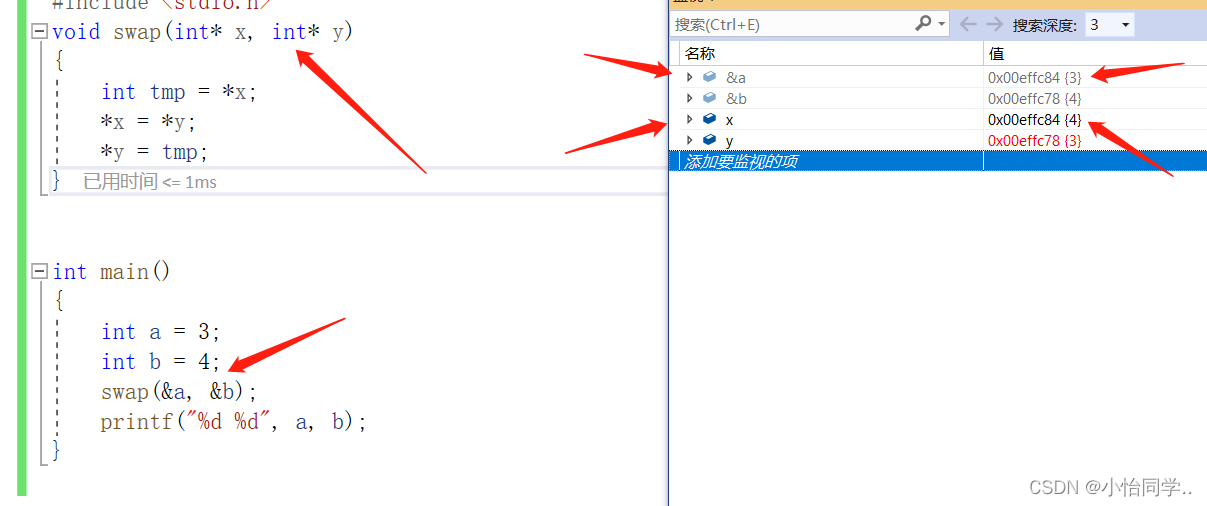
2.改变结构体的地址,具体是如何改变呢
通过头指针的地址(pphead这个是二级指针),再解引用得到头指针(headnoe),就可以使用且改变了。
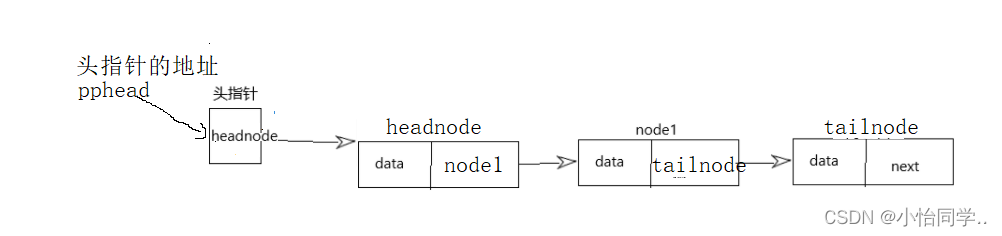
3.通过结构体(headnode),headnode->next可以得到下一个结构体node1
assert的使用
从SList.c可以看出 有时assert(pphead(二级指针)),有时assert(*pphead(一级指针)),
1.当有二级指针传入时,必须使用assert(pphead)断言因为 pphead是头指针的地址 ,虽然头指针 为NULL但是,头指针的地址是真实存在的(也就是地址中的地址)。
2.assert(*pphead)是当链表中已经没有节点存在了,不能进行删除结点的行为。
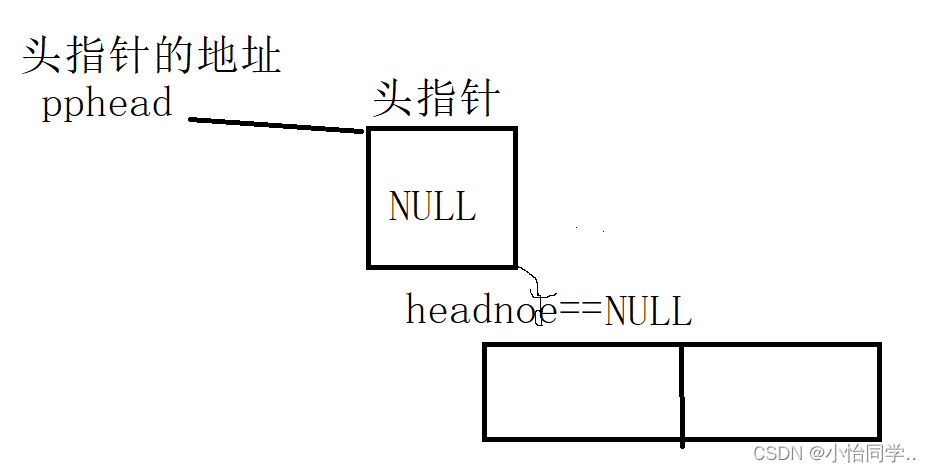
空链表与顺序表的区别及优缺点
区别
1.顺序表为空时 因为结构体不为NULL,只是 size ==0 链表 phead 为空时,没有节点则头指针为NULL。
2,为什么链表不能和顺序表一样直接size++就可以存入数据呢
因为链表每个节点的地址位置都是malloc函数开辟,每个起点位置可能都不一样。而顺序表相当是开辟一段连续内存空间。
优缺点
一.顺序表存储
优点:顺序表存储是将数据元素放到一块连续的内存存储空间,通过下标 访问高效,直接存储与删除
缺点:1.插入和删除比较慢,需要移动大量元素,
2.开辟空间是不可减少的,不可以动态增加长度,容易造成内存浪费
二 .链表存储
原理:没有空间限制,不会溢出,节省空间内存
优点:插入和删除速度快,只需要改变指针指向即可
缺点:不可通过下标访问,需要遍历节点
详解各接口函数的功能
void SLPrint(SLTNode* phead)
void SLPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
//不改变结构体地址,只是循环打印数据所以传一级指针SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->",cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\n");
}
void SLPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
assert(pphead);//因为二级指针,肯定存在,所以需要断言SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);//判断第一个节点是否为空,改变头节点if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL)//寻找最后一个元素{tail = tail->next;}tail ->next= newnode;//在最后的元素添加节点}
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
assert(pphead);//因为头插改变了头节点,所以传二级指针SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);//当没有节点时,增加节点if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{newnode->next = *pphead;//增加首节点*pphead = newnode;}
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
assert(pphead);//二级指针必须断言assert(*pphead);//因为当头节点为空时,不能删除//当只有一个节点时,释放头节点的空间if ( (*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}//当有两个或两个以上的节点时else{SLTNode* tail = *pphead;SLTNode* prev = NULL;while (tail->next != NULL)//找到最后一个元素,以及倒数第二个,所以定义了两个指针,因为只找到最后一个并释放后需要把倒数第二个节点(的next)设为NULL{prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
assert(pphead);//二级指针必定不为空assert(*pphead);//因为链表必须有节点才可以删除,所以需要断言SLTNode* cur = *pphead;*pphead = (*pphead)->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;
SLTNode* BuySLTode(SLTDataType x)
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//开辟一个新节点if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return NULL;}//初始化newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x)return cur;//找到返回此节点坐标cur = cur->next;}return NULL;//找不到返回NULL
void SListInsert(SLTNode** phead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
assert(pphead);//二级指针必不为空assert(pos);//判断pos是否为有效地址//判断头节点是否可以插入if (*pphead == pos){SLTPushFront(pphead, x);}else{SLTNode* cur = pphead;while (cur->next != pos)//找到pos之前的位置{cur = cur->next;}SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);cur->next = newnode;//链接新的节点newnode->next = pos;}void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
assert(pos);//判断pos位置SLTNode* newnode = BuySLTode(x);//链接新的节点newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
void SlistErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
assert(pphead);//二级指针必不为空assert(pos);//pos位置是否合理assert(*pphead);/删除一个节点,所以链表必不为空//改变了头指针,地址改变需要二级指针if (*pphead == pos){SLTPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur->next != pos){cur = cur->next;}cur->next= pos->next;free(pos);}
void SLisTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
assert(pos);//判断pos位置是否合理assert(pos->next);//因为要删除pos的下一个位置的节点,所以只有一个节点不能删除SLTNode* cur = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(cur);cur = NULL;

