HTML---定位
目录
文章目录
一.定位属性概述
二.position
基础数值
三.z-index属性
网页元素透明度
练习
一.定位属性概述
HTML中的定位属性指的是用来控制HTML元素在页面中的位置和布局的属性,包括position、top、bottom、left和right等。
- position属性指定了元素的定位方式,常用的取值有static、relative、absolute和fixed。通过设置不同的position值,可以实现元素的不同定位方式。
- top、bottom、left和right属性用于精确地定位元素的位置。当position属性的值为relative时,这些属性参照的是元素自身的位置进行调整;当position属性的值为absolute或fixed时,这些属性参照的是最近的具有定位属性的父元素进行调整。
二.position
基础数值
| static | 默认值,没有定位 |
| relative | 相对定位 |
| absolute | 绝对定位 |
| fixed | 固定定位 |
演示案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><style type="text/css">div{margin: 10px; padding: 5px; font-size: 15px; line-height: 25px;}#father{border: 1px solid red;padding: 0px;}#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;}#second{background-color: aqua;border: 1px gray dashed;}#third{background-color: aquamarine;border: 1px green solid;}</style></head><body><div id="father"><div id="first">第一个盒子</div><div id="second">第二个盒子</div><div id="third">第三个盒子</div></body>
</html>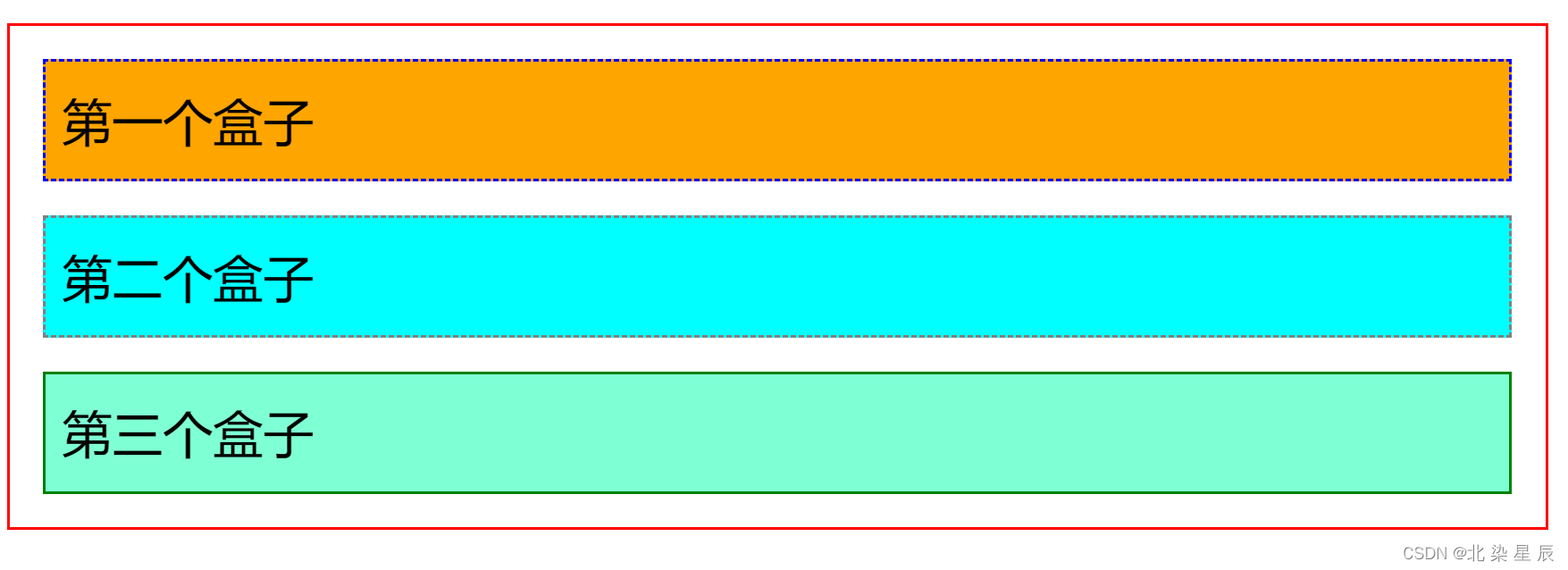
- static
默认值,无定位
- relative
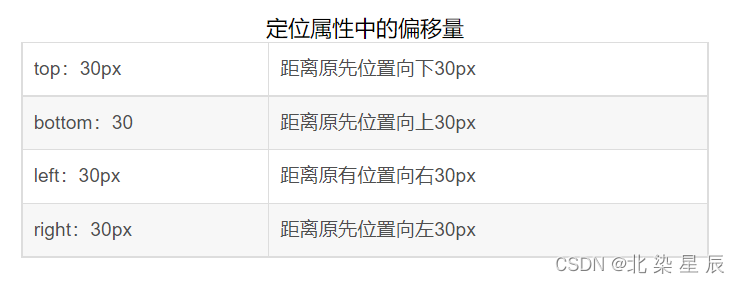
相对定位:元素相对于其正常位置进行定位,可以通过top、right、bottom、left属性调整位置。
- 案例:
#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;position: relative;top: 100px;/**设置偏移量**/
}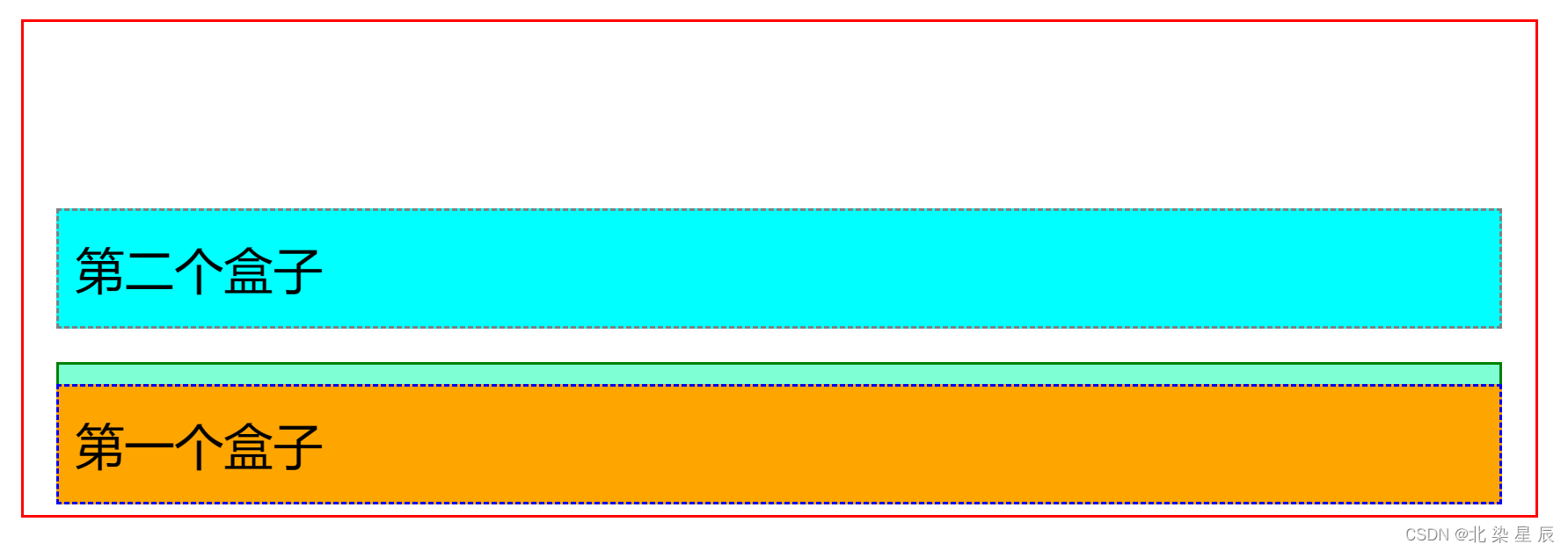
相对定位中元素的原有位置会被保留,父级边框不会塌陷。 相对定位中top:0px left:0px的坐标轴为元素本身。
- absolute
绝对定位:设置绝对定位后的元素将处于悬浮状态。
- 案例:
#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;position: absolute; }
结论:
绝对定位的元素会触发浮动:悬浮,剩余元素将自动补齐浮动元素的位置。
- 停留在浏览器的左上角
#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;position: absolute; top: 0px;left: 0px;}
- 停留在上一级元素边框的左上角
#father{border: 1px solid red;padding: 0px;position: relative;}
#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;position: absolute; top: 0px;left: 0px;}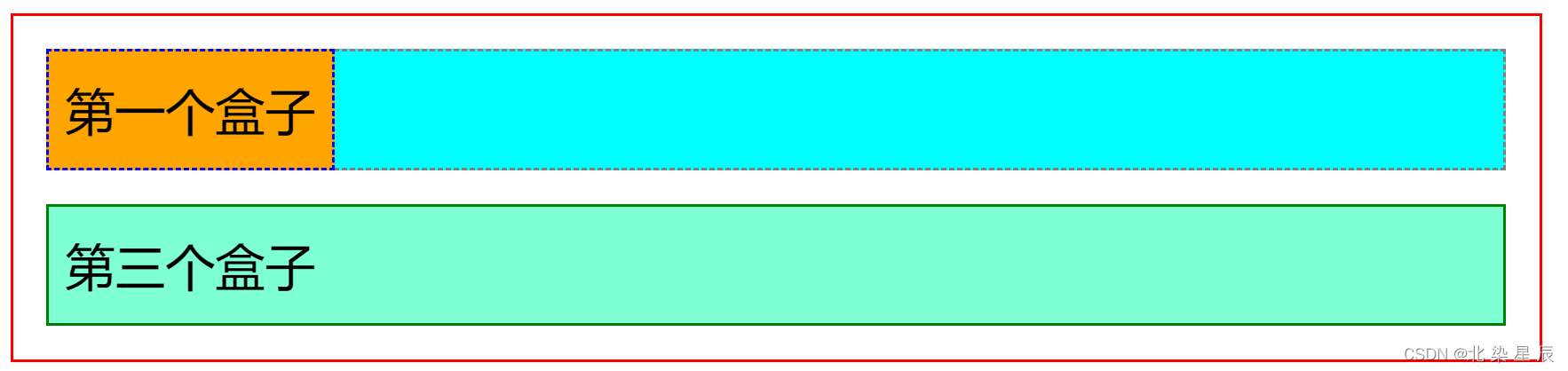
结论:
绝对定位的top:0px left:0px 的坐标轴在上一级设置过元素的左上角,若没有则停留在浏览器左上角。
- fixed
固定定位:
固定定位的元素不会随着浏览器的滚动而改变位置,但会脱离标准文档流,产生悬浮
案例:
#father{border: 1px solid red;padding: 0px;height: 1000px;}
#first{background-color: orange;border: 1px blue dashed;position: absolute; }
#second{background-color: aqua;border: 1px gray dashed;}
#third{background-color: aqua;border: 1px gray dashed; position: fixed;}
- 停留在浏览器左上角
#third{background-color: aqua;border: 1px gray dashed; position: fixed;top: 0px;left: 0px;}
三.z-index属性
在CSS中,z-index属性用于控制元素的堆叠顺序。它指定了一个元素在Z轴上的顺序,即元素在层叠元素堆里的垂直位置。
当两个或多个元素重叠时,z-index属性决定了哪个元素会显示在顶部。默认情况下,元素的堆叠顺序由它们在HTML中的出现顺序决定。后出现的元素会覆盖先出现的元素。
z-index属性的值可以是整数或auto。较高的值表示元素将显示在较低的值上面。
例如,如果一个元素A具有z-index值为2,而另一个元素B具有z-index值为1,那么元素A将显示在元素B上面。
网页元素透明度
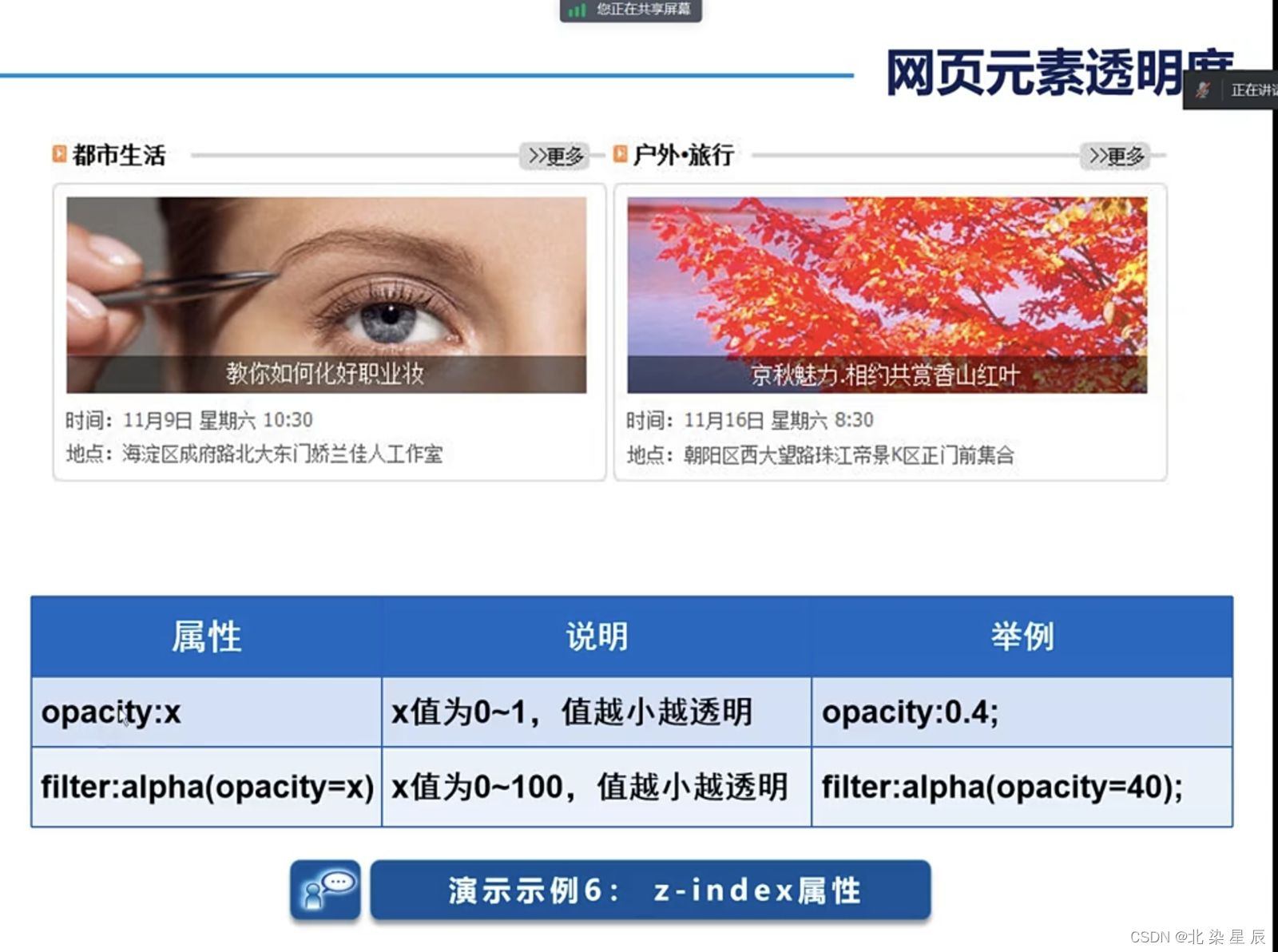
案例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><title></title><style type="text/css">*{margin: 0px;padding: 0px; }ul{list-style: none;position: relative;}#content{width: 330px;overflow: hidden;padding: 5px;font-size: 12px;line-height: 25px;border: 1px red solid; margin: 0 auto;/***设置边框居中*/}#l2,#l3{ /**id="l2"作为空列表属于块状元素需要设置高度否则会被下级元素覆盖**/position: absolute;width: 330px;height: 25px;top:100px}#l2{color: aliceblue;text-align: center;z-index: 0;}#13{}#l3{background-color: black;opacity:0.5;z-index: 1;}</style></head><body><div id=content><ul><li><img src="picture1.png"/></li><li id="l2">金秋魅力.相约共享香山红叶</li><li id="l3"></li><!--设置一个空列表作为id="12"的背景列表--><li>时间:2023年12月20日20:28:10</li><li>地点:朝阳区西大望江路珠江帝景K区正门前集合</li></ul></div></body>
</html>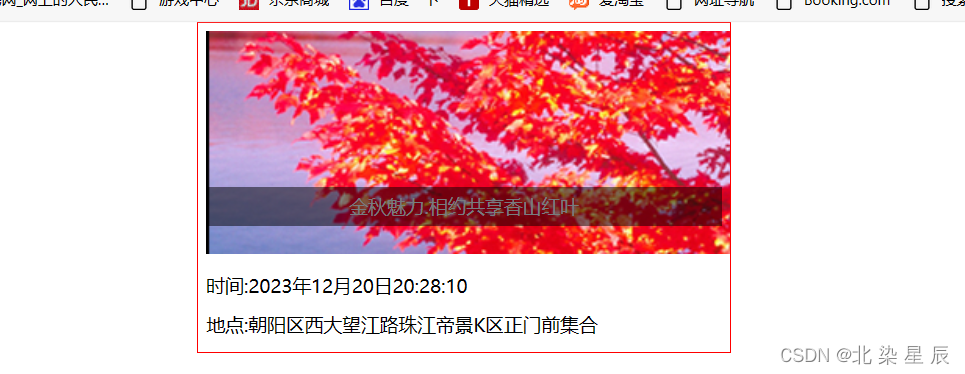
练习