理解io/nio/netty
一、io
io即input/output,输入和输出
1.1 分类
输入流、输出流(按数据流向)
字节流(InputStream/OutputStream(细分File/Buffered))、字符流(Reader/Writer(细分File/Buffered/put))(按数据处理方式)
字节缓存流:避免频繁的io操作,缓冲区的大小默认为 8192 字节
二、字节
- 字节:存储数据的单元
1byte=8bit
一个英文字母=1byte,一个汉字=2byte - 字符:1字符=2byte
三、nio
3.1 基本概念
- 同步:当前任务完成前,不能做其他操作(单线程)
- 异步:当前任务完成前,可以做其他操作(多线程)
- 阻塞:当前任务挂起,不能做其他操作的状态(等待)
- 非阻塞:当前任务进行中,无需挂起,可以做其他操作的状态(一心二用)
3.2 定义
bio为同步阻塞模式
nio为同步非阻塞模式,一个线程管理多个输入输出通道,涉及轮询、多路复用(一个线程不断轮询多个socket的状态,当socket有读写事件时调用io事件)
核心:channel(双向)、buffer、selector(监听通道事件)
3.3 流程
服务器端(pool)
属性:线程池、选择器selector
- 创建一个PoolServer,
- 初始化,并指定端口
开通渠道ServerSocketChannel
设置非阻塞
绑定端口
开通选择器
将渠道注册到选择器- 监听事件
轮询访问选择器
处理对应的通道事件
如果事件key状态为可接收:注册通道到选择器,设置状态为可读
如果事件key状态为可读:将key对应通道设置为可读,线程池执行key对应的继承Thread的handler方法,重写run方法(通过key拿到通道;分配缓冲区,分配输出流;将通道读取的缓冲区内容写入输出流;将服务端回执写入通道;将通道设置可读;唤醒选择器)
3.4 应用
客户端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Socket s = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8888);s.getOutputStream().write("HelloServer".getBytes());s.getOutputStream().flush();System.out.println("write over, waiting for msg back...");byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = s.getInputStream().read(bytes);System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));s.close();}
}
服务端:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8888));ssc.configureBlocking(false);System.out.println("server started, listening on :" + ssc.getLocalAddress());Selector selector = Selector.open();ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);while(true) {selector.select();Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator();while(it.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = it.next();it.remove();handle(key);}}}private static void handle(SelectionKey key) {if(key.isAcceptable()) {try {ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();sc.configureBlocking(false);sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ );} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {}} else if (key.isReadable()) { //flipSocketChannel sc = null;try {sc = (SocketChannel)key.channel();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);buffer.clear();int len = sc.read(buffer);if(len != -1) {System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));}ByteBuffer bufferToWrite = ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes());sc.write(bufferToWrite);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if(sc != null) {try {sc.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}
}服务端:pool
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class PoolServer {ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(50);private Selector selector;/**** @throws IOException*/public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {PoolServer server = new PoolServer();server.initServer(8000);server.listen();}/**** @param port* @throws IOException*/public void initServer(int port) throws IOException {//ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();//serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);//serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));//this.selector = Selector.open();serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);System.out.println("服务端启动成功!");}/**** @throws IOException*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public void listen() throws IOException {// 轮询访问selector while (true) {//selector.select();//Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();while (ite.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();//ite.remove();//if (key.isAcceptable()) {ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();//SocketChannel channel = server.accept();//channel.configureBlocking(false);//channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);//} else if (key.isReadable()) {//key.interestOps(key.interestOps()&(~SelectionKey.OP_READ));//pool.execute(new ThreadHandlerChannel(key));}}}}
}/**** @param* @throws IOException*/
class ThreadHandlerChannel extends Thread{private SelectionKey key;ThreadHandlerChannel(SelectionKey key){this.key=key;}@Overridepublic void run() {//SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();//ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();try {int size = 0;while ((size = channel.read(buffer)) > 0) {buffer.flip();baos.write(buffer.array(),0,size);buffer.clear();}baos.close();//byte[] content=baos.toByteArray();ByteBuffer writeBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(content.length);writeBuf.put(content);writeBuf.flip();channel.write(writeBuf);//if(size==-1){channel.close();}else{//key.interestOps(key.interestOps()|SelectionKey.OP_READ);key.selector().wakeup();}}catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());}}
}
四、netty
netty是JBoss提供的开源网络编程框架,提供异步的、基于事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具。
架构
三层网络架构,Reactor 通信调度层 -> 职责链 PipeLine -> 业务逻辑处理层
为什么选择netty
- API使用简单,开发门槛低
- 功能强大,预置了多种编解码功能,支持多种主流协议
- 定制能力强,可以通过ChannelHandler对通信框架进行灵活的扩展
- 性能高,通过与其他业界主流的nio框架对比,netty的综合性能最优
- 成熟、稳定,netty修复了已经发现的所有的JDK NIO BUG,业务开发人员不需要再为NIO的BUG而烦恼
- 社区活跃,版本迭代周期短,发现的BUGkey倍及时修复,同时更多的新功能会被加入
- 经历了大规模的商业应用考验,质量已经得到验证。在互联网、大数据、网络游戏、企业应用、电信软件等众多行业得到成功商用,证明了它可以完全满足不同行业的商业应用。
4.1 流程
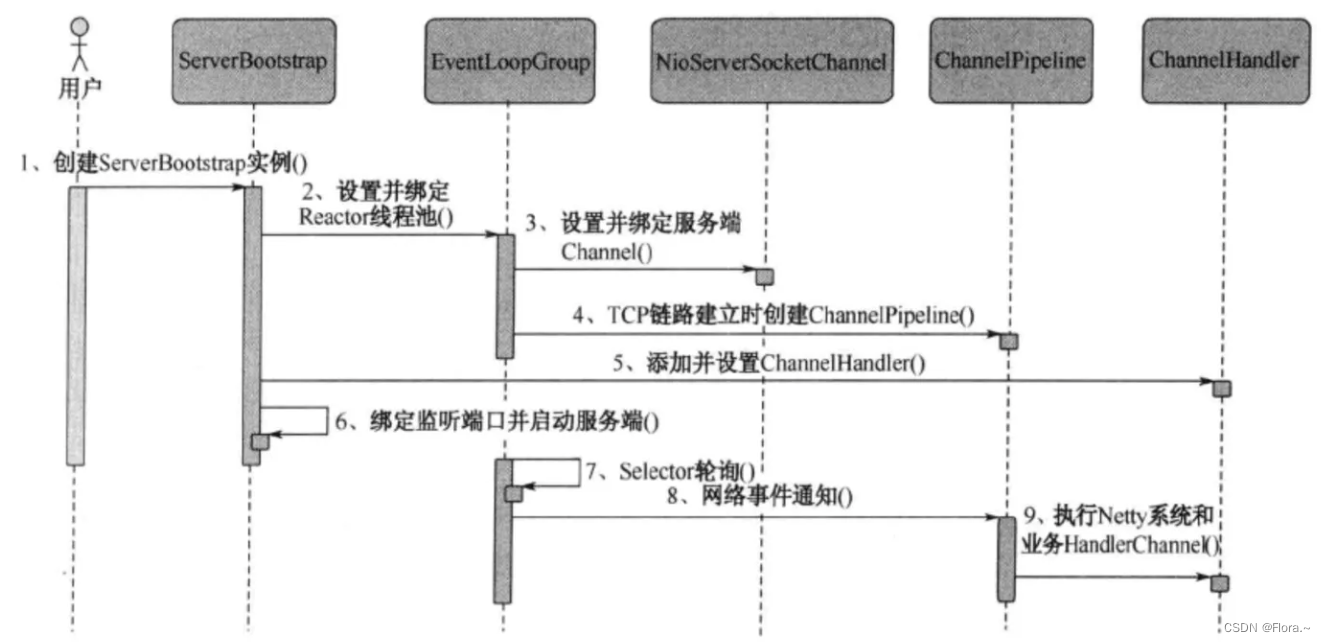
netty的接收和发送ByteBuffer采用direct buffers,使用堆外直接内存进行socket读写,不需要进行字节缓冲区的二次拷贝。(如果使用传统的堆内存进行socket读写,JVM会将堆内存buffer拷贝一份到直接内存中,然后才写入socket中。相比于堆外直接内存,消息在发送过程中多了一次缓冲区的内存拷贝。)
- 服务端:
创建服务端并指定端口,启动服务端
创建boss和worker事件组
绑定事件组到通道,并指定子处理器,初始化通道,将处理器(继承ChannelHandlerContext,重写读方法(获取信息,将信息写入上下文,关闭上下文)以及异常捕获方法(关闭上下文))加到管道的最后
绑定端口获取future
- 客户端:
创建客户端,启动客户端
创建workers事件组
绑定事件组到通道,并指定处理器,初始化通道,将定义的客户端处理器(继承ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter,重写通道激活方法(将信息写入上下文,获取future,添加监听器,当服务端收到信息时输出提示信息)以及读方法(读取信息,最后释放信息))添加到管道的后面
绑定端口,获取future
4.2 应用
服务端
import com.mashibing.io.aio.Server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil;public class HelloNetty {public static void main(String[] args) {new NettyServer(8888).serverStart();}
}class NettyServer {int port = 8888;public NettyServer(int port) {this.port = port;}public void serverStart() {EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ch.pipeline().addLast(new Handler());}});try {ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync();f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}
}class Handler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {//super.channelRead(ctx, msg);System.out.println("server: channel read");// ByteBuf是netty的一个字节容器ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg;System.out.println(buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));ctx.writeAndFlush(msg);ctx.close();//buf.release();}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {//super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);cause.printStackTrace();ctx.close();}
}客户端
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil;public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {new Client().clientStart();}private void clientStart() {EventLoopGroup workers = new NioEventLoopGroup();Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();b.group(workers).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overrideprotected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {System.out.println("channel initialized!");ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());}});try {System.out.println("start to connect...");ChannelFuture f = b.connect("127.0.0.1", 8888).sync();f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {workers.shutdownGracefully();}}}class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {@Overridepublic void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {System.out.println("channel is activated.");final ChannelFuture f = ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("HelloNetty".getBytes()));f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {System.out.println("msg send!");//ctx.close();}});}@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {try {ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg;System.out.println(buf.toString());} finally {ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);}}
}
场景
- 构建高性能、低时延的各种Java中间件,
例如MQ、分布式服务框架、ESB消息总线,netty主要作为基础框架提供高性能、低时延的通信服务 - 共有或者私有协议栈的基础通信框架,
例如可以基于netty构建异步、高性能的websocket协议栈 - 各领域应用,netty作为高性能的通信框架用于内部各模块的数据分发、传输和汇总等,实现模块之间高性能通信
例如大数据、游戏等
4.3 拆包器
TCP拆包粘包
发送的数据出现断开接收或者多个包数据发生粘连
- 要发送的数据大于TCP发送
缓冲区剩余空间大小,将会发生拆包 - 待发送数据大于MSS
最大报文长度,TCP在传输前将进行拆包 - 要发送的数据小于TCP发送缓冲区的大小,TCP将
多次写入缓冲区的数据一次发送出去,将会发生粘包 - 接收数据端的应用层
没有及时读取接收缓冲区中的数据,将发生粘包
解决方法
- 发送端给每个数据包添加
包首部,首部中应该至少包含数据包的长度,这样接收端在接收到数据后,通过读取包首部的长度字段,便知道每一个数据包的实际长度 了 - 发送端将每个数据包封装为
固定长度,这样接收端每次从接收缓冲区中读取固定长度的数据就自然而然的把每个数据包拆分开 - 可以在数据包之间
设置边界,如添加特殊符号,这样接收端通过这个边界就可以将不同的数据包拆分开
netty提供了封装的拆包器:
- 固定长度
- 行
- 分隔符
- 基于长度域(最通用)
4.4 零拷贝
传统拷贝:需要4次数据拷贝和4次上下文切换
磁盘->内核缓冲区的read buffer->用户缓冲区->内核的socket buffer->网卡接口(硬件)的缓冲区
零拷贝:省略中间的2步,不需要CPU的参与
磁盘->内核缓冲区的read buffer->网卡接口(硬件)的缓冲区
零拷贝是指计算机操作的过程中,CPU不需要为数据在内存之间的拷贝消耗资源。而它通常是指计算机在网络上发送文件时,不需要将文件内容拷贝到用户空间,而直接在内核空间中传输到网络的方式。
