c语言单向链表
看如下代码,这是一个完整的可运行的c源文件,要注意的点:
- c语言程序运行不一定需要头文件
- NULL其实是 (void*)0,把指针赋值成(void*)0,就是防止程序员不想该指针被引用的时候被引用,引用地址为0的值程序会引起系统中断,程序会异常终止
- 可能会有人觉得,别人讲链表都是malloc,怎么这里没有malloc,malloc是用来申请内存的,比较灵活,可以自由改变链表长度,这里用赋值的方法是因为从最简单的开始讲,更能讲清楚原理
#define NULL (void*)0
struct list{int num;/*单向链表需要一个结构体指针指向下一个节点的地址,如果是尾巴节点,则是NULL*/struct list *next;
};
int main()
{struct list n0 = {100, NULL};struct list n1 = {29, NULL};struct list n2 = {78, NULL};struct list n3 = {24, NULL};n0.next = &n1;n1.next = &n2; // 等价 n0.next->next = &n2n2.next = &n3; // 等价 n0.next->next->next = &n3return 0;
}
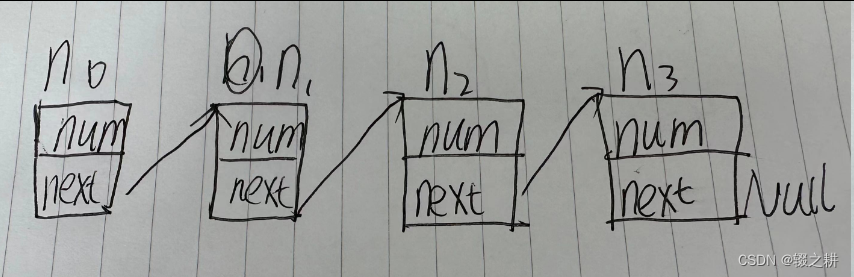
我们先执行完main函数里面前四句赋值语句,
用gdb查看n0, n1, n2, n3的地址,如下,他们的地址都是不一样的,因为他们在内存的不同的地方,他们也没有什么关系(你们运行出来的内存地址应该和我的不一样,无需产生疑惑)
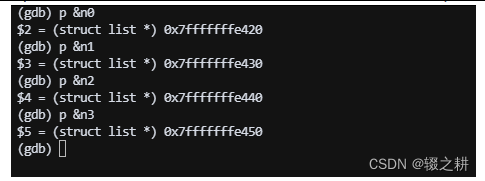
他们在你的内存条里像这样分布,没什么特点,就是四个结构体,他们占用的大小一样,都是sizeof(struct list)

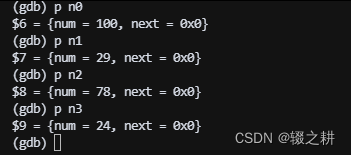
我们再查看他们的值,都是初始化的值,没错
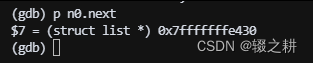
执行 n0.next = &n1;
就是把n1的地址挂在n0的尾巴上(next指针),这样就可以通过n0.next来表示&n1,查看n0.next,发现变成了n1的地址
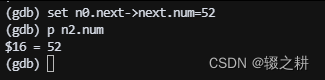
执行 n1.next = &n2;和 n2.next = &n3
经过上面的解释,这两句应该很好理解,就是把n2的地址挂在n1的next上,n3的地址挂在n2的next上,现在,就组成了一个简单的链表,就可以通过结构体n0(通常称之为头节点)访问这个链表上的任何数据

使用malloc申请内存的方式创建链表
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list{int num;struct list *next;
};
int main()
{struct list *tmp_node;struct list *head = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));head->num = 10;head->next = NULL;/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 3;tmp_node->next = NULL;head->next = tmp_node;/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 5;tmp_node->next = NULL;head->next->next = tmp_node;/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 80;tmp_node->next = NULL;head->next->next->next = tmp_node;return 0;
}
这段代码并不难看懂,就是创建一个节点,然后挂在head的尾巴上,可是这里有缺陷,就是每次都要自己记住有几个节点,然后用 head->next->next->next = tmp_node;的语句去接上节点,这样太麻烦了,我们可以再创建一个尾节点,来表示这个链表的尾巴节点。
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list{int num;struct list *next;
};
int main()
{struct list *tmp_node;struct list *head = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));head->num = 10;head->next = NULL;/*刚开始头就是尾,这个能理解吧*/struct list *tail = head;/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 3;tmp_node->next = NULL;tail->next = tmp_node; //接到尾巴上tail = tail->next; //因为后面有新的节点,尾巴要更新位置了,移到新节点了/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 5;tmp_node->next = NULL;tail->next = tmp_node;tail = tail->next;/*添加节点*/tmp_node = (struct list*)malloc(sizeof(struct list));tmp_node->num = 80;tmp_node->next = NULL;tail->next = tmp_node;tail = tail->next;return 0;
}
记住两点:
- 头节点一般不移动
- 每一次操作完毕后,尾节点都是指向最后一个节点的地址
取下/删除链表节点
增加链表节点
插入链表节点
待更新
