生产环境_移动目标轨迹压缩应用和算法处理-Douglas-Peucker轨迹压缩算法
场景:
我目前设计到的场景是:即在地图应用中,对GPS轨迹数据进行压缩,减少数据传输和存储开销,因为轨迹点太频繁了,占用空间太大,运行节点太慢了,经过小组讨论需要上这个算法,。
涉及到的算法
- Douglas-Peucker算法:该算法通过递归地将轨迹分割为线段,并丢弃那些与整体轨迹偏差较小的线段,从而实现轨迹的压缩。
- Visvalingam-Whyatt算法:该算法基于三角形面积的概念,通过不断移除面积最小的点来达到轨迹压缩的目的
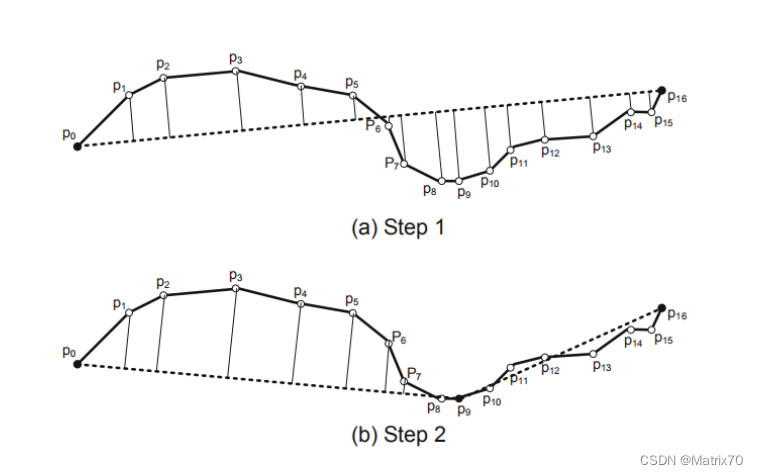
图片来源:郑宇博士《computing with spatial trajectories》
Haversine公式计算距离和Douglas-Peucker压缩算法代码实现-scala版
import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame, SparkSession}
import org.apache.spark.sql.functions._
import scala.math._// 定义表示点的类
case class Point(lon: Double, lat: Double, time: String, id: String)// Haversine距离计算函数
def haversineDistance(point1: Point, point2: Point): Double = {val R = 6371000.0 // 地球半径(米)val dLat = toRadians(point2.lat - point1.lat)val dLon = toRadians(point2.lon - point1.lon)val a = pow(sin(dLat / 2), 2) + cos(toRadians(point1.lat)) * cos(toRadians(point2.lat)) * pow(sin(dLon / 2), 2)val c = 2 * atan2(sqrt(a), sqrt(1 - a))R * c
}// Douglas-Peucker轨迹压缩函数
def douglasPeucker(points: List[Point], epsilon: Double): List[Point] = {if (points.length < 3) {return points}val dmax = points.view.zipWithIndex.map { case (point, index) =>if (index != 0 && index != points.length - 1) {perpendicularDistance(point, points.head, points.last)} else {0.0}}.maxif (dmax > epsilon) {val index = points.view.zipWithIndex.maxBy { case (point, index) =>if (index != 0 && index != points.length - 1) {perpendicularDistance(point, points.head, points.last)} else {0.0}}._2val recResults1 = douglasPeucker(points.take(index+1), epsilon)val recResults2 = douglasPeucker(points.drop(index), epsilon)recResults1.init ::: recResults2} else {List(points.head, points.last)}
}// 创建Spark会话
val spark = SparkSession.builder().appName("TrajectoryCompression").getOrCreate()// 创建包含lon、lat、time和id列的示例DataFrame
//https://blog.csdn.net/qq_52128187?type=blog,by_laoli
val data = Seq((40.7128, -74.0060, "2023-11-18 08:00:00", "1"),(40.7215, -74.0112, "2023-11-18 08:05:00", "1"),(40.7312, -74.0146, "2023-11-18 08:10:00", "1"),(40.7356, -74.0162, "2023-11-18 08:15:00", "1"),(40.7391, -74.0182, "2023-11-18 08:20:00", "1"),(40.7483, -74.0224, "2023-11-18 08:25:00", "1"),(40.7527, -74.0260, "2023-11-18 08:30:00", "1")
).toDF("lon", "lat", "time", "id")// 为DataFrame添加id列
val dfWithId = data.withColumn("id", monotonically_increasing_id())// 将DataFrame转换为Point列表
val points = dfWithId.as[(Double, Double, String, Long)].collect().map(p => Point(p._1, p._2, p._3, p._4.toString)).toList// 执行轨迹压缩
val compressedPoints = douglasPeucker(points, epsilon = 10) // 设置您期望的epsilon值// 将压缩后的数据重新转换为DataFrame
import spark.implicits._
val df2 = compressedPoints.toDF("lon", "lat", "time", "id")
参考文章
- Douglas, D.H., and Peucker, T.K. "Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature." The Canadian Cartographer 10.2 (1973): 112-122.
- Visvalingam, M., and Whyatt, J.D. "Line generalization by repeated elimination of the smallest-area triangle." Cartographic Journal 30.1 (1993): 46-51.
- 轨迹数据压缩的Douglas-Peucker算法(附代码及原始数据) - 知乎
