【Java】定时任务 - Timer/TimerTask 源码原理解析
一、背景及使用
日常实现各种服务端系统时,我们一定会有一些定时任务的需求。比如会议提前半小时自动提醒,异步任务定时/周期执行等。那么如何去实现这样的一个定时任务系统呢? Java JDK提供的Timer类就是一个很好的工具,通过简单的API调用,我们就可以实现定时任务。
现在就来看一下java.util.Timer是如何实现这样的定时功能的。
首先,我们来看一下一个使用demo
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() { public void run() { System.out.println("executing now!"); }
};// 延迟 1s 打印一次
timer.schedule(task, 1000)
// 延迟 1s 固定时延每隔 1s 周期打印一次
timer.schedule(task, 1000, 1000);
// 延迟 1s 固定速率每隔 1s 周期打印一次
timer.scheduleAtFixRate(task, 1000, 1000)基本的使用方法:
-
创建一个Timer对象
-
创建一个TimerTask对象,在这里实现run方法
-
将TimerTask对象作为参数,传入到Timer对象的scheule方法中,进行调度执行。
加入任务的API如下:
-
一次性任务的API
// 指定时延后运行// 默认fixed-delay模式,周期时间按上一次执行结束时间计算public void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) {if (delay < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, 0);}// 指定时间点运行public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date time) {sched(task, time.getTime(), 0);}-
周期任务的APi:
// 指定时延后运行,之后以指定周期运行public void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) {if (delay < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");if (period <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, -period);}// 指定时间点运行,之后以指定周期运行public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) {if (period <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");sched(task, firstTime.getTime(), -period);}// 指定时延后运行,之后以指定周期运行// 默认fixedRate模式,周期时间按任务执行开始时间计算public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) {if (delay < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");if (period <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, period);}public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime,long period) {if (period <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");sched(task, firstTime.getTime(), period);}可以看到API方法内部都是调用sched方法,其中time参数下一次任务执行时间点,是通过计算得到。period参数为0的话则表示为一次性任务。
二、实现原理
那么我们来看一下Timer内部是如何实现调度的。
2.1、内部结构
先看一下Timer的组成部分:
public class Timer {// 任务队列private final TaskQueue queue = new TaskQueue();// 工作线程,循环取任务private final TimerThread thread = new TimerThread(queue);private final Object threadReaper = new Object() {protected void finalize() throws Throwable {synchronized(queue) {thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled = false;queue.notify(); // In case queue is empty.}}};// Timer的序列号,命名工作线程(静态变量,在启动多个Timer的情况可以用于区分对应的工作线程)private final static AtomicInteger nextSerialNumber = new AtomicInteger(0); }Timer有3个重要的模块,分别是 TimerTask, TaskQueue, TimerThread
-
TimerTask,即待执行的任务
-
TaskQueue,任务队列,TimerTask加入后会按执行时间自动排序
-
TimerThread,工作线程,真正循环执行TimerTask的线程
那么,在加入任务之后,整个Timer是怎么样运行的呢?可以看下面的示意图:
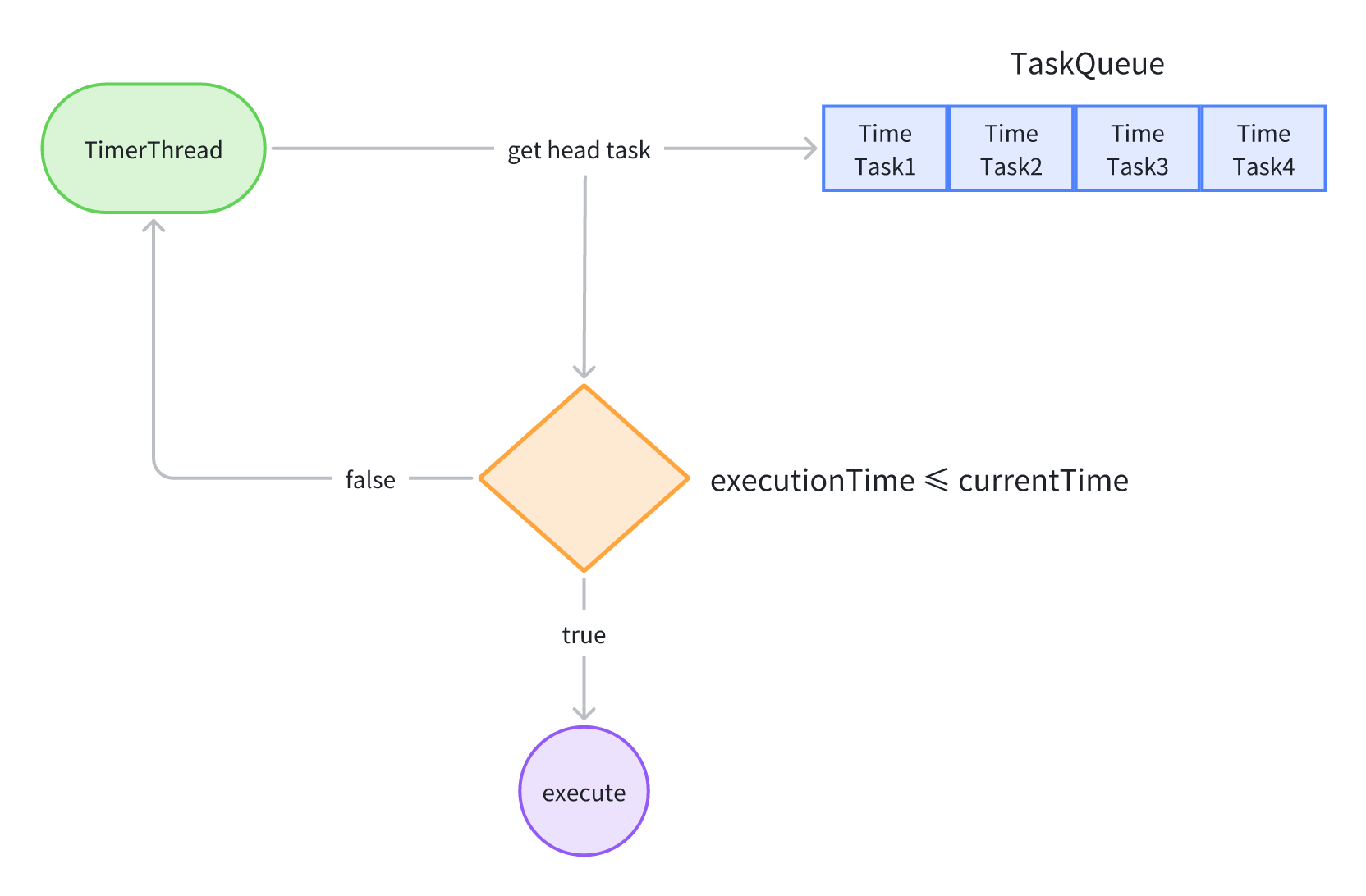
2.2、工作线程
- 创建任务,调用scheule方法
public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) { if (period <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period."); sched(task, firstTime.getTime(), -period);
}-
内部调用sched方法
// sched方法的入参是task任务,执行的时间,以及执行周期
private void sched(TimerTask task, long time, long period) {if (time < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal execution time.");// 防止溢出if (Math.abs(period) > (Long.MAX_VALUE >> 1))period >>= 1;// 对queue加锁,避免并发入队synchronized(queue) {if (!thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled)throw new IllegalStateException("Timer already cancelled.");// 对task加锁,避免并发修改synchronized(task.lock) {if (task.state != TimerTask.VIRGIN)throw new IllegalStateException("Task already scheduled or cancelled");task.nextExecutionTime = time;task.period = period;task.state = TimerTask.SCHEDULED;}// 任务入队queue.add(task);/* 如果任务是队列当前第一个任务,则唤醒工作线程这里是因为工作线程处理完上一个任务之后,会 sleep 到下一个 task 的执行时间点。如果有 nextExecutionTime 更早的 task 插队到前面,则需要马上唤醒工作线程进行检查避免 task 延迟执行*/if (queue.getMin() == task)queue.notify();}
}流程中加了一些锁,用来避免同时加入TimerTask的并发问题。可以看到sched方法的逻辑比较简单,task赋值之后入队,队列会自动按照nextExecutionTime排序(升序,排序的实现原理后面会提到)。
- 工作线程的mainLoop
public void run() {try {mainLoop();} finally {synchronized(queue) {newTasksMayBeScheduled = false;queue.clear();}}
}/*** 工作线程主逻辑,循环执行*/
private void mainLoop() {while (true) {try {TimerTask task;boolean taskFired; // 标记任务是否应该执行synchronized(queue) {// 如果队列为空,且newTasksMayBeScheduled为true,此时等待任务加入while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)queue.wait();// 如果队列为空,且newTasksMayBeScheduled为false,说明此时线程应该退出if (queue.isEmpty())break;// 队列不为空,尝试从队列中取task(目标执行时间最早的task)long currentTime, executionTime;task = queue.getMin();synchronized(task.lock) {// 校验task状态if (task.state == TimerTask.CANCELLED) {queue.removeMin();continue;}currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();executionTime = task.nextExecutionTime;// 当前时间 >= 目标执行时间,说明任务可执行,设置taskFired = trueif (taskFired = (executionTime<=currentTime)) {if (task.period == 0) { // period == 0 说明是非周期任务,先从队列移除queue.removeMin();task.state = TimerTask.EXECUTED;} else { // 周期任务,会根据period重设执行时间,再加入到队列中queue.rescheduleMin(task.period<0 ? currentTime - task.period: executionTime + task.period);}}}if (!taskFired) // 任务为不需执行状态,则等待queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);}if (taskFired) // 任务需要执行,则调用task的run方法执行,这里执行的其实就是调用方创建task时候run方法的逻辑task.run();} catch(InterruptedException e) {}}
}从 mainLoop的源码中可以看出,基本的流程如下所示
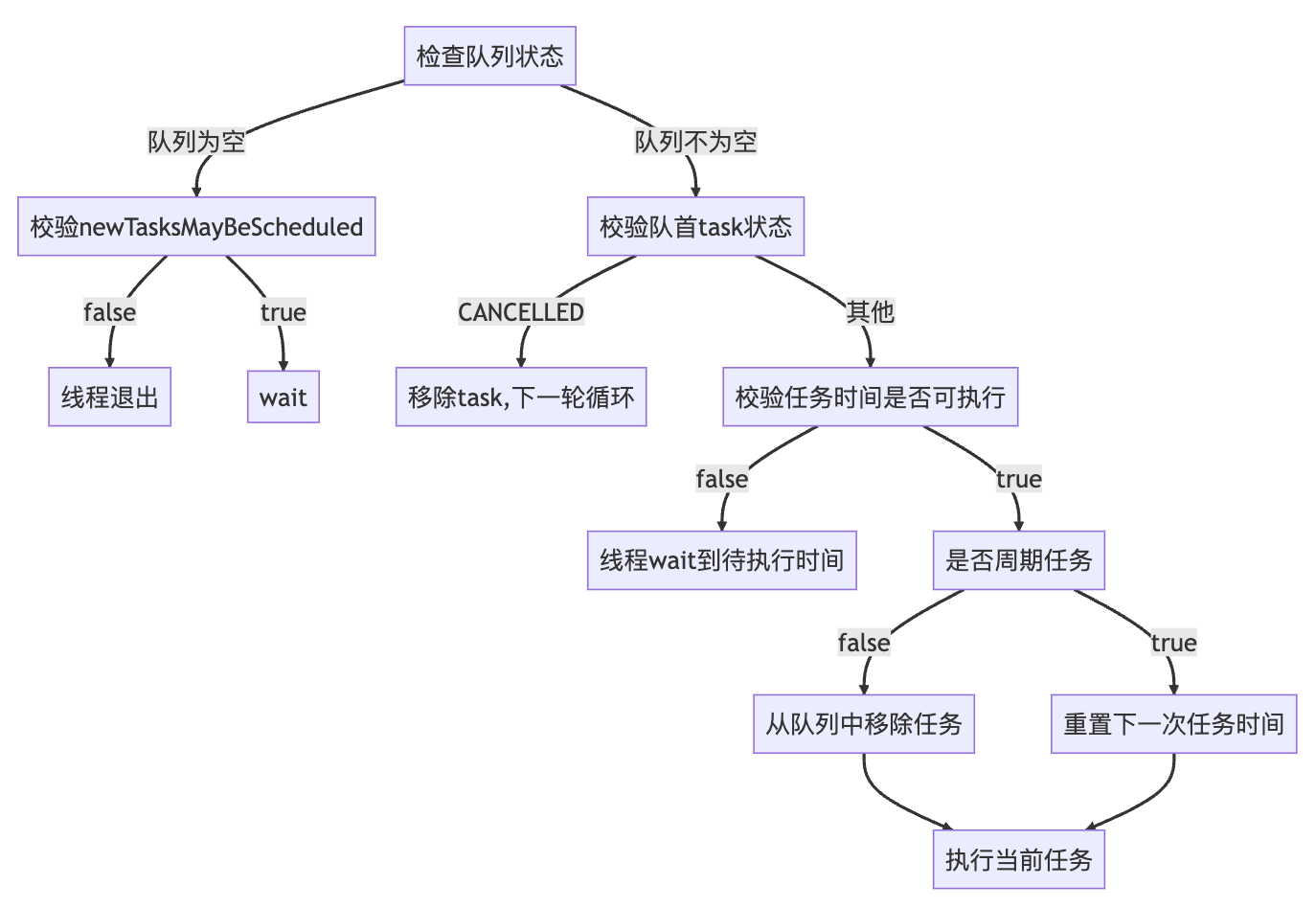
当发现是周期任务时,会计算下一次任务执行的时间,这个时候有两种计算方式,即前面API中的
-
schedule:period为负值,下次执行时间
-
scheduleAtFixedRate:period为正值
queue.rescheduleMin( task.period<0 ? currentTime - task.period : executionTime + task.period);2.3、优先队列
当从队列中移除任务,或者是修改任务执行时间之后,队列会自动排序。始终保持执行时间最早的任务在队首。 那么这是如何实现的呢?
看一下TaskQueue的源码就清楚了
class TaskQueue {private TimerTask[] queue = new TimerTask[128];private int size = 0;int size() {return size;}void add(TimerTask task) {if (size + 1 == queue.length)queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, 2*queue.length);queue[++size] = task;fixUp(size);}TimerTask getMin() {return queue[1];}TimerTask get(int i) {return queue[i];}void removeMin() {queue[1] = queue[size];queue[size--] = null; // Drop extra reference to prevent memory leakfixDown(1);}void quickRemove(int i) {assert i <= size;queue[i] = queue[size];queue[size--] = null; // Drop extra ref to prevent memory leak}void rescheduleMin(long newTime) {queue[1].nextExecutionTime = newTime;fixDown(1);}boolean isEmpty() {return size==0;}void clear() {for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)queue[i] = null;size = 0;}private void fixUp(int k) {while (k > 1) {int j = k >> 1;if (queue[j].nextExecutionTime <= queue[k].nextExecutionTime)break;TimerTask tmp = queue[j]; queue[j] = queue[k]; queue[k] = tmp;k = j;}}private void fixDown(int k) {int j;while ((j = k << 1) <= size && j > 0) {if (j < size &&queue[j].nextExecutionTime > queue[j+1].nextExecutionTime)j++; // j indexes smallest kidif (queue[k].nextExecutionTime <= queue[j].nextExecutionTime)break;TimerTask tmp = queue[j]; queue[j] = queue[k]; queue[k] = tmp;k = j;}}void heapify() {for (int i = size/2; i >= 1; i--)fixDown(i);}
}可以看到其实TaskQueue内部就是基于数组实现了一个最小堆 (balanced binary heap), 堆中元素根据 执行时间nextExecutionTime排序,执行时间最早的任务始终会排在堆顶。这样工作线程每次检查的任务就是当前最早需要执行的任务。堆的初始大小为128,有简单的倍增扩容机制。
2.4、其他方法
TimerTask 任务有四种状态:
-
VIRGIN: 任务刚刚创建,还没有schedule
-
SCHEDULED:任务已经schedule,进入到队列中
-
EXECUTED: 任务已执行/执行中
-
CANCELLED:任务已取消
Timer 还提供了cancel和purge方法
-
cancel,清除队列中所有任务,工作线程退出。
-
purge,清除队列中所有状态置为取消的任务。
2.5、常见应用实现
Java的Timer广泛被用于实现异步任务系统,在一些开源项目中也很常见, 例如消息队列RocketMQ的 延时消息/消费重试 中的异步逻辑。
public void start() {if (started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {super.load();// 新建了一个timerthis.timer = new Timer("ScheduleMessageTimerThread", true);for (Map.Entry<Integer, Long> entry : this.delayLevelTable.entrySet()) {// ...}// 调用了Timer的scheduleAtFixedRate方法this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {if (started.get()) {ScheduleMessageService.this.persist();}} catch (Throwable e) {log.error("scheduleAtFixedRate flush exception", e);}}}, 10000, this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDelayOffsetInterval());}
}上面这段代码是RocketMQ的延时消息投递任务 ScheduleMessageService 的核心逻辑,就是使用了Timer实现的异步定时任务。
三、总结
不管是实现简单的异步逻辑,还是构建复杂的任务系统,Java的Timer确实是一个方便实用,而且又稳定的工具类。从Timer的实现原理,我们也可以窥见定时系统的一个基础实现:线程循环 + 优先队列。这对于我们自己去设计相关的系统,也会有一定的启发。
设计亮点个人总结:
-
流程中加了一些锁,用来避免TimeTask同时加入TimerTaskQueue、对TimeTsk修改所带来的并发问题
-
通过newTasksMayBeScheduled 来控制工作线程对TimerTaskQueue的执行
-
采用小根堆算法来对TimerTaskQueue进行优先级排序
-
工作线程通过循环来执行TimerTaskQueue的任务,还判断并处理了Task的状态机及流转
