温故知新:探究Android UI 绘制刷新流程
一、说明:
-
基于之前的了解知道ui的绘制最终会走到Android的
ViewRootImpl中scheduleTraversals进行发送接收vsync信号绘制,在ViewRootImpl中还会进行主线程检测,也就是我们所谓子线程更新ui会抛出异常。 -
像我们常用的刷新ui,
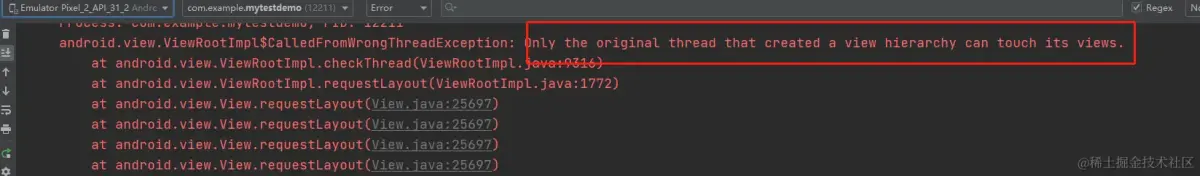
invalidate,和requestLayout方法,(按我之前的理解在ViewRootImpl初始化添加后,在子线程中刷新ui一定会崩溃:如下图)

二、问题:invalidate一定会导致异常崩溃?
2.1、例子:子线程更新TextView文本(注意这里是TextView,为什么是它而不是ImageView,因为我的背景就是使用的TextView,使用它的时候发现了invalidate, 和 requestLayout方法的区别 )
某天我在onResume中利用子线程更新了TextView的一段代码,发现并没有抛出异常崩溃,代码如下:
override fun onResume() {super.onResume()mBind.btTest.setOnClickListener{lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {mBind.btTest.text = "子线程点击改变:${Thread.currentThread().name}"}}}
我在想为什么呢?,看代码: 一步步debug:TextView控件中:
1.、
public final void setText(CharSequence text) {setText(text, mBufferType);
}
2.、
public void setText(CharSequence text, BufferType type) {setText(text, type, true, 0);if (mCharWrapper != null) {mCharWrapper.mChars = null;}
}
3.、
private void setText(CharSequence text, BufferType type,boolean notifyBefore, int oldlen) {...省略if (mLayout != null) {checkForRelayout();}...省略}
以上主要看第三步中的 checkForRelayout()检测是否需要重绘,方法如下
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void checkForRelayout() {// If we have a fixed width, we can just swap in a new text layout// if the text height stays the same or if the view height is fixed.if ((mLayoutParams.width != LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT|| (mMaxWidthMode == mMinWidthMode && mMaxWidth == mMinWidth))&& (mHint == null || mHintLayout != null)&& (mRight - mLeft - getCompoundPaddingLeft() - getCompoundPaddingRight() > 0)) {// Static width, so try making a new text layout.int oldht = mLayout.getHeight();int want = mLayout.getWidth();int hintWant = mHintLayout == null ? 0 : mHintLayout.getWidth();/** No need to bring the text into view, since the size is not* changing (unless we do the requestLayout(), in which case it* will happen at measure).*/makeNewLayout(want, hintWant, UNKNOWN_BORING, UNKNOWN_BORING,mRight - mLeft - getCompoundPaddingLeft() - getCompoundPaddingRight(),false);//1.检测文本的显示类型,就是我们的过长省略号这种if (mEllipsize != TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE) {// In a fixed-height view, so use our new text layout.if (mLayoutParams.height != LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT&& mLayoutParams.height != LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {autoSizeText();invalidate();return;}// Dynamic height, but height has stayed the same,// so use our new text layout.if (mLayout.getHeight() == oldht&& (mHintLayout == null || mHintLayout.getHeight() == oldht)) {autoSizeText();invalidate();return;}}// We lose: the height has changed and we have a dynamic height.// Request a new view layout using our new text layout.requestLayout();invalidate();} else {// Dynamic width, so we have no choice but to request a new// view layout with a new text layout.nullLayouts();requestLayout();invalidate();}
}
从上面的checkForRelayout()方法中的if (mEllipsize != TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE)条件知道成立,因为我们没有设置过mEllipsize = 跑马灯效果,所以走了invalidate()方法然后直接return截断,不会走后面的requestLayout()方法,至于requestLayout() 与 invalidate()的区别我就不讲了
2.2、分析requestLayout方法
基于之前的知识我知道调用requestLayout()方法会崩溃,至于为什么调用requestLayout()方法会崩溃?
我们先看requestLayout()方法,暂停一会invalidate()的跟进:
requestLayout()方法代码如下:
public void requestLayout() {if (mMeasureCache != null) mMeasureCache.clear();if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == null) {// Only trigger request-during-layout logic if this is the view requesting it,// not the views in its parent hierarchyViewRootImpl viewRoot = getViewRootImpl();if (viewRoot != null && viewRoot.isInLayout()) {if (!viewRoot.requestLayoutDuringLayout(this)) {return;}}mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = this;}mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) {mParent.requestLayout();}if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == this) {mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = null;}
}
requestLayout()方法中会循环递归调用 mParent.requestLayout()方法,直到找到ViewRootImpl中的requestLayout()方法,而它的方法做了线程检测如下图:这就是requestLayout()方法会崩溃的原因。

验证猜想: 为TextView设置跑马灯属性,使上面的if (mEllipsize != TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE)不成立,走下面的requestLayout()方法,代码如下:
override fun onResume() {super.onResume()mBind.btTest.ellipsize = TextUtils.TruncateAt.valueOf("MARQUEE")mBind.btTest.setOnClickListener{lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.IO) {mBind.btTest.text = "子线程点击改变:${Thread.currentThread().name}"}}}
果然点击后崩溃:

2.3、继续分析invalidate()方法,为什么不会导致textview的更新崩溃
看代码在View.java文件中
public void invalidate() {invalidate(true);
}
public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) {invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,boolean fullInvalidate) {if (mGhostView != null) {mGhostView.invalidate(true);return;}if (skipInvalidate()) {return;}// Reset content capture cachesmPrivateFlags4 &= ~PFLAG4_CONTENT_CAPTURE_IMPORTANCE_MASK;mContentCaptureSessionCached = false;if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {if (fullInvalidate) {mLastIsOpaque = isOpaque();mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN;}mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DIRTY;if (invalidateCache) {mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;}// Propagate the damage rectangle to the parent view.final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;final ViewParent p = mParent;if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;damage.set(l, t, r, b);p.invalidateChild(this, damage);}// Damage the entire projection receiver, if necessary.if (mBackground != null && mBackground.isProjected()) {final View receiver = getProjectionReceiver();if (receiver != null) {receiver.damageInParent();}}}
}
核心代码是上面第三段invalidateInternal方法中的invalidateChild方法
它回调到ViewGroup中的invalidateChild方法
看:invalidateChild如下图:我们知道
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) 条件成立attachInfo不为空 ,且硬件加速被开启(从API 14 (3.0)起。硬件加速默认开启)。 attachInfo 是一个view在attach至其父window被赋值的一系列信息。

所以条件成立后走的onDescendantInvalidated方法 如下:
@CallSuper
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target) {/** HW-only, Rect-ignoring damage codepath** We don't deal with rectangles here, since RenderThread native code computes damage for* everything drawn by HWUI (and SW layer / drawing cache doesn't keep track of damage area)*/// if set, combine the animation flag into the parentmPrivateFlags |= (target.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAW_ANIMATION);if ((target.mPrivateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) != 0) {// We lazily use PFLAG_DIRTY, since computing opaque isn't worth the potential// optimization in provides in a DisplayList world.mPrivateFlags = (mPrivateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DIRTY;// simplified invalidateChildInParent behavior: clear cache validity to be safe...mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;}// ... and mark inval if in software layer that needs to repaint (hw handled in native)if (mLayerType == LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE) {// Layered parents should be invalidated. Escalate to a full invalidate (and note that// we do this after consuming any relevant flags from the originating descendant)mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED | PFLAG_DIRTY;target = this;}if (mParent != null) {mParent.onDescendantInvalidated(this, target);}
}
上面一段代码核心是 mParent.onDescendantInvalidated(this, target); 类似于requestLayout()方法 onDescendantInvalidated中会循环递归调用 mParent.onDescendantInvalidated(this, target);方法,直到找到ViewRootImpl中的onDescendantInvalidated(this, target)方法,而它的方法没做线程检测如下图:这就是开了硬件加速后invalidate方法不会崩溃的原因。如下图:直接走scheduleTraversals绘制刷新有兴趣可看:


而关闭硬件加速后会怎样呢? 继续看invalidateChild方法
@Deprecated
@Override
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) {// HW accelerated fast pathonDescendantInvalidated(child, child);return;}ViewParent parent = this;if (attachInfo != null) {...do {....parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);....} while (parent != null);}
}
上面一段核心是 parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);方法 同理while循环不停调用 invalidateChildInParent方法直到找到ViewRootImpl中的invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty)方法,如下图内部进行了线程检测

**验证猜想关闭硬件加速:android:hardwareAccelerated="false"**果然崩溃了。

三、总结
这就是我遇到的问题:单纯的根据TextView在子线程可以更新得出的结论,总的来说要想不崩溃还得绕过ViewRootImpl中的checkThread的检测。至于研究它有什么用,只有知道理解源码的流程,才能写出更好的东西。
Android 学习笔录
Android 性能优化篇:https://qr18.cn/FVlo89
Android Framework底层原理篇:https://qr18.cn/AQpN4J
Android 车载篇:https://qr18.cn/F05ZCM
Android 逆向安全学习笔记:https://qr18.cn/CQ5TcL
Android 音视频篇:https://qr18.cn/Ei3VPD
Jetpack全家桶篇(内含Compose):https://qr18.cn/A0gajp
OkHttp 源码解析笔记:https://qr18.cn/Cw0pBD
Kotlin 篇:https://qr18.cn/CdjtAF
Gradle 篇:https://qr18.cn/DzrmMB
Flutter 篇:https://qr18.cn/DIvKma
Android 八大知识体:https://qr18.cn/CyxarU
Android 核心笔记:https://qr21.cn/CaZQLo
Android 往年面试题锦:https://qr18.cn/CKV8OZ
2023年最新Android 面试题集:https://qr18.cn/CgxrRy
Android 车载开发岗位面试习题:https://qr18.cn/FTlyCJ
音视频面试题锦:https://qr18.cn/AcV6Ap
