数据结构——树
深度优先/广度优先遍历
深度优先:
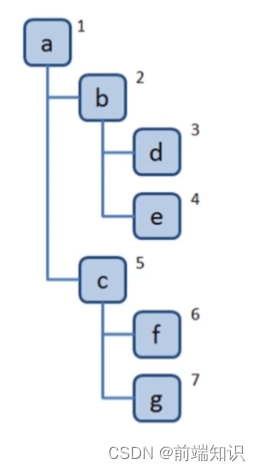
访问根节点
对根节点的 children 挨个进行深度优先遍历
const tree = {val: "a",children: [{val: "b",children: [{val: "d",children: [],},{val: "e",children: [],},],},{val: "c",children: [{val: "f",children: [],},{val: "g",children: [],},],},],
};const dfs = (root) => {console.log(root.val);root.children.forEach((child) => {dfs(child);});
};dfs(tree);广度优先:
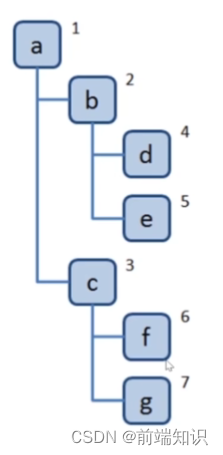
新建立一个队列,根节点入队
对头出队并访问
把对头的children挨个入队
重复2,3,直到队列为空
const tree = {val: "a",children: [{val: "b",children: [{val: "d",children: [],},{val: "e",children: [],},],},{val: "c",children: [{val: "f",children: [],},{val: "g",children: [],},],},],
};const bfs = (root) => {const q = [root];while (q.length > 0) {const n = q.shift();console.log(n.val);n.children.forEach((child) => {q.push(child);});}
};bfs(tree);二叉树的先中后序遍历
二叉树:每个节点最多只能有两个节点
先序遍历(根、左、右):
访问根节点
对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
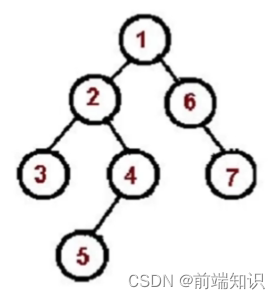
1、2、3、4、5、6、7
const tree = {val: "1",left: {val: "2",left: {val: "3",left: null,right: null,},right: {val: "4",left: {val: "5",},right: null,},},right: {val: "6",left: null,right: {val: "7",right: null,left: null,},},
};const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;console.log(root.val);preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);
};
preorder(tree);中序遍历(左、中、右):
对根节点左子树遍历
访问根节点
对根节点右子树遍历
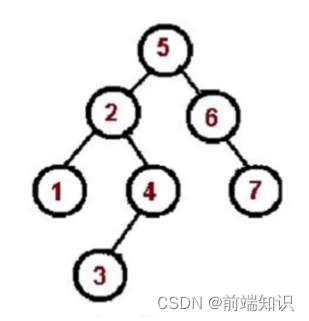
1、2、3、4、5、6、7
const tree = {val: "5",left: {val: "2",left: {val: "1",left: null,right: null,},right: {val: "4",left: {val: "3",},right: null,},},right: {val: "6",left: null,right: {val: "7",right: null,left: null,},},
};const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;inorder(root.left);console.log(root.val);inorder(root.right);
};
inorder(tree);后序遍历(左、右、根):
对根节点左子树遍历
对根节点右子树遍历
访问根节点
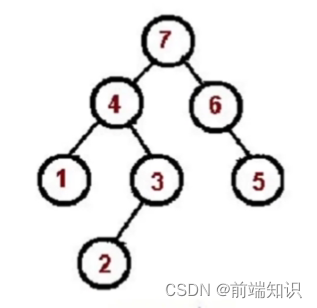
1、2、3、4、5、6、7
const tree = {val: "7",left: {val: "4",left: {val: "1",left: null,right: null,},right: {val: "3",left: {val: "2",},right: null,},},right: {val: "6",left: null,right: {val: "5",right: null,left: null,},},
};const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;postorder(root.left);postorder(root.right);console.log(root.val);
};
postorder(tree);非递归写法
递归调用函数,会不断的入栈出栈,所以考虑用栈实现。
先序遍历:
// 递归
const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;console.log(root.val);preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);
};// 非递归
const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;const stack = [root]while(stack.length){const n = stack.pop()console.log(n.val)// 栈后进先出,先右后左if(n.right) stack.push(n.right)if(n.left) stack.push(n.left)}
}中序遍历:
// 递归
const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;inorder(root.left);console.log(root.val);inorder(root.right);
};
// 非递归
const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;const stack = [];let p = root;while (stack.length || p) {// 所有的左子树进栈while (p) {stack.push(p);p = p.left;}//最尽头的左子树出栈const n = stack.pop();console.log(n.val);p = n.right;}
};后续遍历:
const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;postorder(root.left);postorder(root.right);console.log(root.val);
};
// 先序遍历是 根、左、右,后续遍历时:左、右、根,倒过来是根、右、左,只需要把先序遍历的后面两个颠倒顺序const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) return;const outputStack = [];const stack = [root];while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();outputStack.push(n);if (n.left) stack.push(n.left);if (n.right) stack.push(n.right);}while (outputStack.length) {const n = outputStack.pop();console.log(n.val);}
};