Java 常用类(包装类)
目录
- 八大Wrapper类
- 包装类的分类
- 装箱和拆箱
- 包装类和基本数据类型之间的转换
- 常见面试题
- 包装类方法
- 包装类型和String类型的相互转换
- 包装类常用方法(以Integer类和Character类为例)
- Integer类和Character类的常用方法
- Integer创建机制(面试题)
- 面试题1
- 面试题2
八大Wrapper类
包装类的分类
1.针对8种基本数据类型相应的引用类型—包装类
2.有了类的特点,就可以调用类的方法。
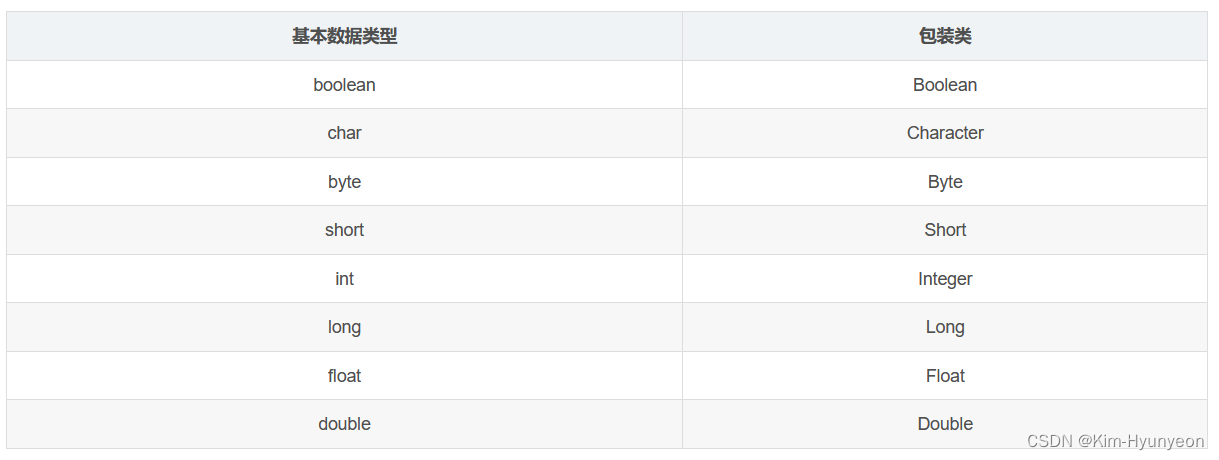
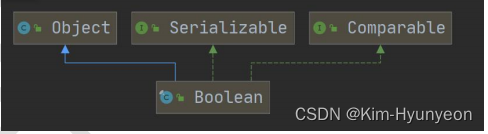
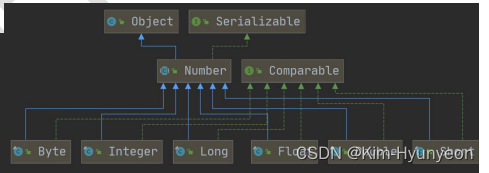
相关类图如下:

示例代码:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperType {public static void main(String[] args) {//boolean -> Boolean//char -> Character//byte -> Byte//int -> Integer//long -> long//float -> Float//double -> Double//short -> Short}
}装箱和拆箱
包装类和基本数据类型之间的转换
1.jdk5 前需手动装箱和拆箱。装箱:基本类型 -> 包装类型;反之为拆箱
2.jdk5 以后(含jdk5)采用自动装箱和拆箱的方式【即jdk会在底层自动的帮我们调用相应方法进行转换】
3.自动装箱底层调用的是valueOf方法,如Integer.valueOf()
示例代码:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class Integer01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//演示int <--> Integer 的装箱和拆箱//jdk5前是手动装箱和拆箱//手动装箱 int->Integerint n1 = 100;Integer integer = new Integer(n1);Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);//手动拆箱//Integer -> intint i = integer.intValue();//jdk5后,就可以自动装箱和自动拆箱int n2 = 200;//自动装箱 int->IntegerInteger integer2 = n2; //底层使用的是 Integer.valueOf(n2)//自动拆箱 Integer->intint n3 = integer2; //底层仍然使用的是 intValue()方法}
}其它包装类的用法类似
常见面试题

示例代码:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperExercise01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Double d = 100d; //ok, 自动装箱 Double.valueOf(100d);Float f = 1.5f; //ok, 自动装箱 Float.valueOf(1.5f);Object obj1 = true? new Integer(1) : new Double(2.0);//三元运算符【是一个整体】 一真大师System.out.println(obj1);// 什么? 1.0Object obj2;if(true)obj2 = new Integer(1);elseobj2 = new Double(2.0);System.out.println(obj2);//1//输出什么 ? 1, 分别计算}
}解析:
① 第一题中由于应该将三元运算符看做一个整体,故会以三元运算符中精度最高的那个类型作为基准来提升其他值的精度;
② 而第二题中的 if 和 else 是两条独立的语句,故精度不会互相影响
包装类方法
包装类型和String类型的相互转换
示例代码(代码中以Integer为例,其余包装类用法类似):
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperVSString {public static void main(String[] args) {//包装类(Integer)->StringInteger i = 100;//自动装箱//方式1String str1 = i + "";//方式2String str2 = i.toString();//方式3String str3 = String.valueOf(i);//String -> 包装类(Integer)String str4 = "12345";Integer i2 = Integer.parseInt(str4);//使用到自动装箱Integer i3 = new Integer(str4);//构造器System.out.println("ok~~");}
}这里介绍的是包装类与String类之间的相互转换。实际我们可以将这里介绍的方法中的所有包装类的位置替换成基本数据类型,因为底层会自动进行拆装箱
包装类常用方法(以Integer类和Character类为例)
Integer类和Character类的常用方法
示例代码:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE); //返回最小值System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);//返回最大值System.out.println(Character.isDigit('a'));//判断是不是数字System.out.println(Character.isLetter('a'));//判断是不是字母System.out.println(Character.isUpperCase('a'));//判断是不是大写System.out.println(Character.isLowerCase('a'));//判断是不是小写System.out.println(Character.isWhitespace('a'));//判断是不是空格System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase('a'));//转成大写System.out.println(Character.toLowerCase('A'));//转成小写}
}Integer创建机制(面试题)
面试题1

代码及解析:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperExercise02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer i = new Integer(1);Integer j = new Integer(1);System.out.println(i == j); //False//所以,这里主要是看范围 -128 ~ 127 就是直接返回/*老韩解读//1. 如果i 在 IntegerCache.low(-128)~IntegerCache.high(127),就直接从数组返回//2. 如果不在 -128~127,就直接 new Integer(i)源码如下:public static Integer valueOf(int i) {if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];return new Integer(i);}*/// 这里1是在-128~127之间。故是从缓存数组中返回,而缓存数组又已经在类加载时就创建好了,是不可变的,所以返回的是同一个对象Integer m = 1; //底层 Integer.valueOf(1); -> 阅读源码Integer n = 1;//底层 Integer.valueOf(1);System.out.println(m == n); //T//所以,这里主要是看范围 -128 ~ 127 就是直接返回//,否则,就new Integer(xx);Integer x = 128;//底层Integer.valueOf(1);Integer y = 128;//底层Integer.valueOf(1);System.out.println(x == y);//False}
}Integer.valueOf()中IntegerCache为Integer类的静态内部类,而其中的Integer cache[]数组为static final静态常量,而缓存数组是在类加载时就已经事先创建好了
面试题2

代码及解析:
package com.hspedu.wrapper;/*** @author 韩顺平* @version 1.0*/
public class WrapperExercise03 {public static void main(String[] args) {//示例一Integer i1 = new Integer(127);Integer i2 = new Integer(127);System.out.println(i1 == i2);//F
//示例二Integer i3 = new Integer(128);Integer i4 = new Integer(128);System.out.println(i3 == i4);//F//示例三Integer i5 = 127;//底层Integer.valueOf(127)Integer i6 = 127;//-128~127System.out.println(i5 == i6); //T
//示例四Integer i7 = 128;Integer i8 = 128;System.out.println(i7 == i8);//F
//示例五Integer i9 = 127; //Integer.valueOf(127)Integer i10 = new Integer(127);System.out.println(i9 == i10);//F//示例六Integer i11=127;int i12=127;
//只有有基本数据类型,判断的是
//值是否相同System.out.println(i11==i12); //T
//示例七Integer i13=128;int i14=128;System.out.println(i13==i14);//T}
}注意:当使用"=="运算符时,若存在基本数据类型,则判断的是值是否相同
