SpringMVC源码分析(二)启动过程之RequestMappingHandlerMapping分析
a、http请求中的url是如何与对应Handler的即Controller对应method映射的?
在上篇中提到在SpringMVC中,初始化9大内置组件的时候其中有一个组件就是HandlerMapping,在初始化HandlerMapping的时候会加载代码中所有标注了@Controller和@RequestMapping的类到spring容器中,作为一个个bean对象。
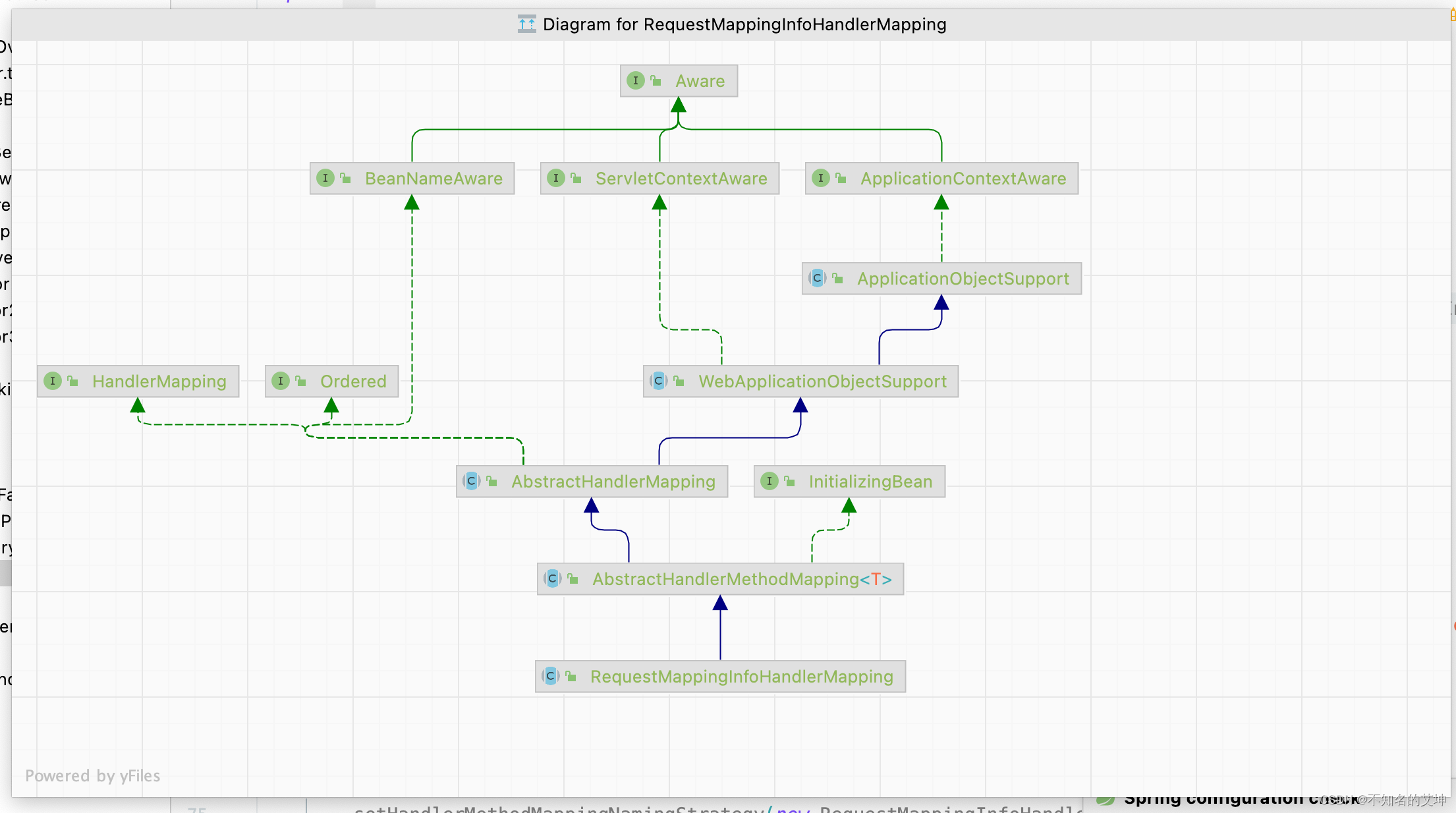
关键类RequestMappingHandlerMapping
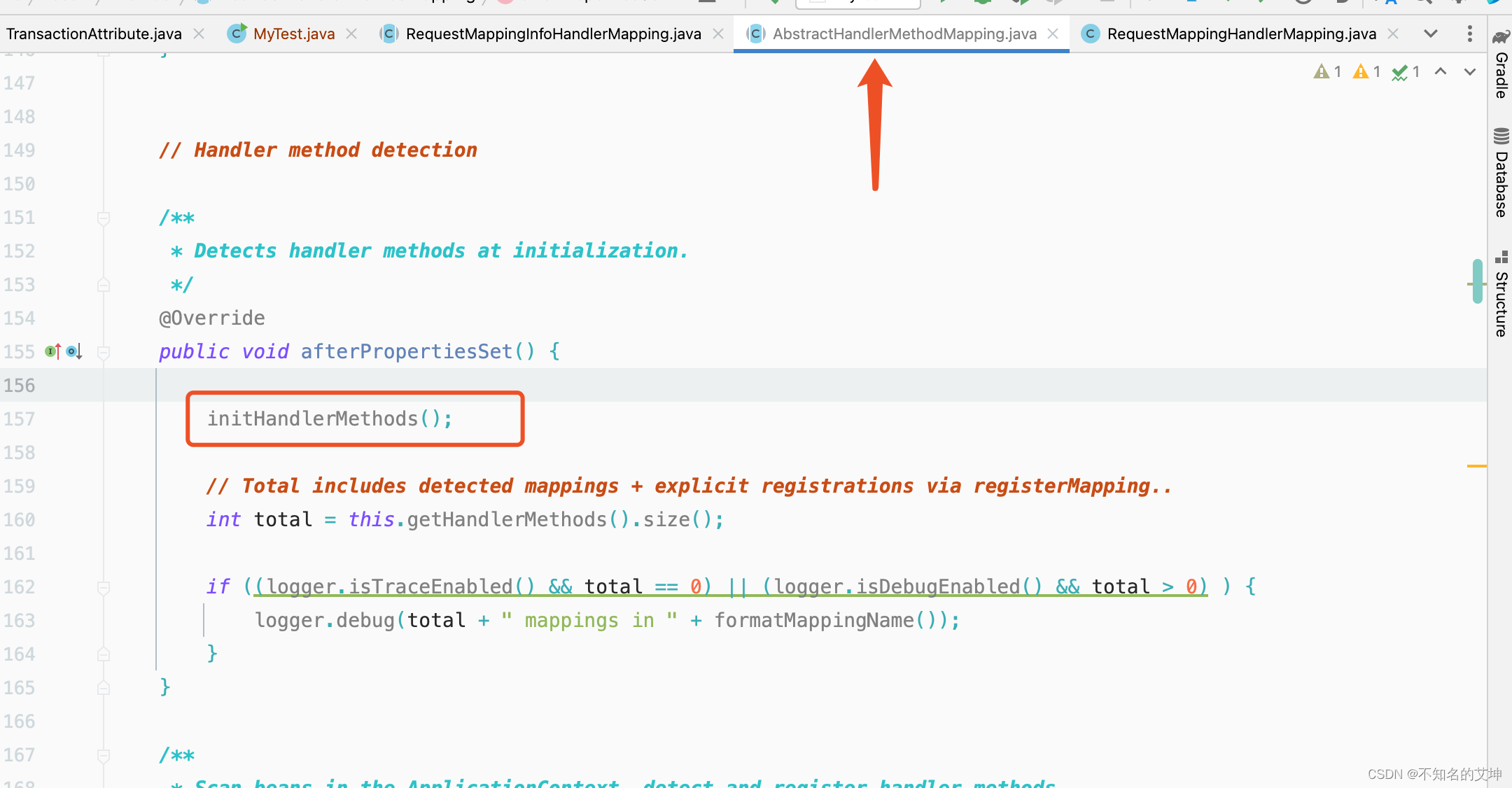
类图上看出RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping继承了AbstractHandlerMethodMapping。实现了InitializingBean接口并且实现了afterPropertiesSet方法。所以在spring初始化这个RequestMappingHandlerMapping对象的时候会进入到afterPropertiesSet()中,这个里面会调用父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的afterPropertiesSet(),然后调用initHandlerMethods()。在其中会初始化所有的HandlerMethods。
1、initHandlerMethods()
在当前方法中,主要做了几件事:
- 扫描所有的Handler类,获取所有带有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解的类。
- 遍历每个Handler类,获取类中的所有方法。
- 对于每个方法,判断是否存在@RequestMapping注解。
- 如果存在@RequestMapping注解,则解析该注解,获取其中的属性值,如请求路径、请求方法、请求参数等。
- 根据解析到的属性值,生成一个RequestMappingInfo对象,该对象代表了一个请求路径和请求方法的映射关系。
- 将生成的RequestMappingInfo对象与对应的HandlerMethod对象进行关联,形成一个映射关系
- 将该映射关系保存到RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping中的pathLookup和registry两个Map中。
- pathLookup是一个Map,以请求路径作为键,将对应的RequestMappingInfo对象作为值存储起来,用于后续处理请求时的查找。
- registry是一个Map,以RequestMappingInfo对象作为键,将对应的HandlerMethod对象作为值存储起来,用于后续执行相应的方法。
- 遍历完所有的Handler类和方法后,初始化完成,此时已经将请求路径、请求方法和对应的HandlerMethod对象都保存起来了。
当有实际的请求进来时,RequestMappingHandlerMapping会根据请求的路径和方法,从pathLookup中查找对应的RequestMappingInfo对象。
然后,通过RequestMappingInfo对象从registry中获取对应的HandlerMethod对象,从而执行相应的方法。HandlerMethod对象是在处理请求时动态生成的,它包含了方法的相关信息,如所属的类、方法名、参数列表等。
protected void initHandlerMethods() {if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + this.getApplicationContext());}//这里是获取应用中所有Object的bean的名字String[] beanNames = this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts?BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class):this.obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);String[] var2 = beanNames;int var3 = beanNames.length;//遍历这个含有应用中所有beanName的字符串数组,并得到这个beanName对应的bean的类型for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {String beanName = var2[var4];if(!beanName.startsWith("scopedTarget.")) {Class beanType = null;try {//根据这个beanName对应的beanType的类型beanType = this.obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);} catch (Throwable var8) {if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name \'" + beanName + "\'", var8);}}//判断这个根据这个bean的类型判断是不是一个handlerif(beanType != null && this.isHandler(beanType)) {this.detectHandlerMethods(beanName);}}}this.handlerMethodsInitialized(this.getHandlerMethods());}
1.1 isHandler()
这个Bean是否含有@Controller注解或@RequestMapping注解,如果是就表示是一个handler
* {@inheritDoc}* Expects a handler to have a type-level @{@link Controller} annotation.*/@Overrideprotected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));}
1.2 detectHandlerMethods()
获取这个handler中所有requestMappinng的方法,然后循环去注册该方法与对应requestMapping信息到一个名为registry的一个HashMap中去
protected void detectHandlerMethods(Object handler) {Class handlerType = handler instanceof String?this.obtainApplicationContext().getType((String)handler):handler.getClass();if(handlerType != null) {Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);//获取这个handler中有requestMapping的方法//这个methods的Map结构为key是一个Method对象,value是一个RequestMappingInfo对象Map methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType, (method) -> {try {return this.getMappingForMethod(method, userType);} catch (Throwable var4) {throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" + userType.getName() + "]: " + method, var4);}});if(this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {this.logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);}//循环去注册Method与RequestMappingInfo的关系methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);this.registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);});}}
1.2.1 第一步selectMethods()
1、若这个targetType不是一个代理类,就获得它本身的类以及它的接口放入handlerTypes这么一个Set中去。
2、遍历这个handlerTypes,找到用户自己定义的方法并过滤出有requestMapping的方法,并将之塞入一个methodMap中
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {LinkedHashMap methodMap = new LinkedHashMap();LinkedHashSet handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet();Class specificHandlerType = null;//若这个targetType不是一个代理类,就获得它本身的类以及它的接口if(!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);}handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));Iterator var5 = handlerTypes.iterator();//遍历while(var5.hasNext()) {Class currentHandlerType = (Class)var5.next();Class targetClass = specificHandlerType != null?specificHandlerType:currentHandlerType;//找到用户自己定义的方法并过滤出有requestMapping的方法,并将之塞入一个methodMap中ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, (method) -> {Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);Object result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);if(result != null) {Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);if(bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);}}}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);}return methodMap;}
1 ReflectUtilsl.doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback, ReflectionUtils.MethodFilter)
入参1: Class<?> targetType
入参2: MethodCallback 一个方法回调
入参3: MethodFilter方法过滤器
在当前方法中主要做了3件事:
1、首先获取这个Class中所有定义的方法并且将之存入一个methods的Method数组中
2、遍历这个methods数组中的method如果这个mf方法拦截器为空或者这个method与方法拦截器mf的匹配规则对应,就回调mc.doWith方法。这个mc.doWith()就会调用回到去执行doWithMethods()的第二个lamda表达式。在这个表达式中又会继续回掉执行另一个方法。
3、后面我们还发现对这个类的父类和接口都有一个递归调用
其中这个mf方法拦截器就是这个RelectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS;顾名思义就是用户自己定义的方法,而非继承与Object类的方法什么的。
/*** 执行给定回调操作在给定类和父类(或者给定的接口或父接口)的所有匹配方法*/public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, @Nullable MethodFilter mf) {// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.// 从缓存中获取clazz的所有声明的方法,包括它的所有接口中所有默认方法;没有时就从{@code clazz}中获取,再添加到缓存中,Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz, false);// 遍历所有方法for (Method method : methods) {// 如果mf不为null 且 method不满足mf的匹配要求if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {// 跳过该methodcontinue;}try {// 对method执行回调操作mc.doWith(method);}catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Not allowed to access method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex);}}// 如果clazz的父类不为null且(mf不是与未在{@code java.lang.Object}上声明的所有非桥接非合成方法匹配的预购建方法过滤器或者clazz的父类不为Objectif (clazz.getSuperclass() != null && (mf != USER_DECLARED_METHODS || clazz.getSuperclass() != Object.class)) {// 递归方法// 执行给定回调操作在clazz的父类的所有匹配方法, 子类和父类发生的相同命名方法将出现两次,// 子类和父类发生的相同命名方法将出现两次,除非被mf排查doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf);}// 如果clazz是接口else if (clazz.isInterface()) {// 遍历clazz的所有接口for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {// 递归方法// 执行给定回调操作在superIfc的所有匹配方法, 子类和父类发生的相同命名方法将出现两次,// 子类和父类发生的相同命名方法将出现两次,除非被mf排查doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);}}}
2 mc.doWith(method)–> 回调3
当执行到这个方法时会回掉执行doWithMethods()中的第二个入参即lamda表达式
method -> {Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);if (result != null) {Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);}}}
3 metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod)–> 回调1.2.1
执行到inspect()方法的时候又会继续调用MethodIntrospector.selectMethods()方法中的第二个入参数去执行第二个lamda表达式。
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {try {return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);}});
4 getMappingForMethod()
最终执行到getMappingForMethod(),找到这个方法上的RequestMapping,如果这个方法上的requestMapping信息不为空的话就去照这个handler类上面的requestMapping信息然后将之合并.
最后返回一个RequestMappingInfo ;
@Override@Nullableprotected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);if (info != null) {RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);if (typeInfo != null) {info = typeInfo.combine(info);}String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);if (prefix != null) {info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);}}return info;}
createRequestMappingInfo()
RequestMappingInfo 是请求映射信息的封装对象,用来确定请求的URL、请求方法、请求参数等信息
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path())).methods(requestMapping.method()).params(requestMapping.params()).headers(requestMapping.headers()).consumes(requestMapping.consumes()).produces(requestMapping.produces()).mappingName(requestMapping.name());if (customCondition != null) {builder.customCondition(customCondition);}return builder.options(this.config).build();}
1.2.2 第二步 registerHandlerMethod()
遍历methods注册handlerMethod
。。。。。省略selectMethods()中的代码
//循环去注册Method与RequestMappingInfo的关系methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);this.registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);});}
1 registerHandlerMethod()
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);}
2 register()
通过handler与method创建HandlerMethod对象;确保requestMapping唯一映射一个method, 最后注册requestMappingInfo与对应handlerMethod的关系。
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();try {//创建HandlerMethod对象,这个对象包含了handler与method的信息HandlerMethod handlerMethod = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.createHandlerMethod(handler, method);//确保同一个requestMapping唯一映射一个method// 例如:url路径 /aaa/bbb 只能对应methodA 不能对应对应methodBthis.assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);if(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {//SpringBoot项目或者SpringMVC项目启动的时候控制台上输出的就是这个AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);}//注册requestMapping与HandlerMethodInfo的关系this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);List directUrls = this.getDirectUrls(mapping);Iterator name = directUrls.iterator();while(name.hasNext()) {String corsConfig = (String)name.next();this.urlLookup.add(corsConfig, mapping);}String name1 = null;if(AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getNamingStrategy() != null) {name1 = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);this.addMappingName(name1, handlerMethod);}CorsConfiguration corsConfig1 = AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.this.initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);if(corsConfig1 != null) {this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig1);}this.registry.put(mapping, new AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.MappingRegistration(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name1));} finally {this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();}}
