linux之cpu模拟负载程序
工作中我们经常会遇到这样的问题,需要模拟cpu的负载程序,例如模拟cpu占有率抬升10%、20%、50%、70%等,那这样的程序应该如何实现呢?它的原理是什么样的呢?
思想
创建一个应用程序,该应用程序的作用可以根据用户的设置占用指定的cpu占有率。例如用户指定占用10%,则该应用程序占用cpu占有率为10%;若设置cpu占有率为50%,则应用程序程序的cpu占有率为50%。
占用固定cpu占有率的程序
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;typedef long long int int64;
const int NUM_THREADS = 8; //CPU core nums
int INTERVAL = 100;
int cpuinfo = 70; //CPU utilization rate// time unit is "ms"
int64 GetTickCount()
{timespec now;int64 sec, nsec;clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &now);sec = now.tv_sec;nsec = now.tv_nsec;return sec * 1000 + nsec / 1000000;
}void* CPUCost(void *args)
{int busyTime = INTERVAL * cpuinfo / 100;int idleTime = INTERVAL - busyTime;int64 startTime = 0;std::cout << "XXXX CPUCost" << std::endl;std::cout << "XXXX cpuinfo = " << cpuinfo << std::endl;/** within INTERVAL ms, INTERVAL = busyTime + idleTime,* spend busyTime ms to let cpu busy,* spend idleTime ms top let cpu idle*/while (true) {startTime = GetTickCount();while((GetTickCount() - startTime) <= busyTime);usleep(idleTime * 1000);}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t t[NUM_THREADS];int ret;std::cout << "please input cpu utilization rate" << std::endl;std::cin >> cpuinfo;for(int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++) {ret = pthread_create(&t[i], NULL, CPUCost, NULL);if(ret)std::cout << "XXXX create err" << std::endl;std::cout<<"pthread_create i= "<<i<<std::endl;}pthread_exit(NULL);return 0;
}
上文代码中NUM_THREADS变量的含义是cpu有几个核,该变量修改为cpu的核数;INTERVAL值默认为100,无需修改;cpuinfo,全局变量,用于保存应用程序占用的cpu占有率;GetTickCount函数的作用是获取毫秒时间;CPUCost函数是线程函数,核心逻辑:
/** within INTERVAL ms, INTERVAL = busyTime + idleTime,* spend busyTime ms to let cpu busy,* spend idleTime ms top let cpu idle*/while (true) {startTime = GetTickCount(); //获取一个开始时间,单位为ms//busyTime和idleTime的总和为100ms,即在100ms的时间间隔内,程序运行时间为//busyTime,程序空闲时间为idleTime,通过这样的方式来控制cpu占用率,如下的是循环是控制程序运行busyTime时间while((GetTickCount() - startTime) <= busyTime);
//usleep控制程序睡眠idleTime时间,让出cpuusleep(idleTime * 1000);}注意事项:
由于我的环境cpu有8个核,若指定cpu占有率的为70%,则每个核的cpu占有率为70%,总的cpu占有率为70%,所有的cpu核占有率综合为560%左右(70%*8)。
运行结果如下所示:


 可以看到cpu各个核的cpu占有率均在70%以上,综合的cpu占有率也是79%,各个核的cpu占有率总计为520.9基本与预期相符,达到预期目的。
可以看到cpu各个核的cpu占有率均在70%以上,综合的cpu占有率也是79%,各个核的cpu占有率总计为520.9基本与预期相符,达到预期目的。
cpu占有率动态变化程序(按照正弦函数规律控制cpu占有率)
代码如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>using namespace std;#define PI acos(-1)
#define DISCRETEVALUE 100
typedef long long int int64;
const int NUM_THREADS = 8; //CPU core nums
int INTERVAL = 100;
int cpuinfo = 70; //CPU utilization rate// time unit is "ms"
int64 GetTickCount()
{timespec now;int64 sec, nsec;clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &now);sec = now.tv_sec;nsec = now.tv_nsec;return sec * 1000 + nsec / 1000000;
}void* CPUCost(void *args)
{
// int busyTime = INTERVAL * cpuinfo / 100;
// int idleTime = INTERVAL - busyTime;
// int64 startTime = 0;int busyTime = 50;int idleTime = 50;int64 startTime = 0;//每次递增间隔float value = 2*PI/DISCRETEVALUE;int index = 0;cout<<"value = "<<value <<" PI = "<<sin(PI)<<endl;std::cout << "XXXX CPUCost" << std::endl;std::cout << "XXXX cpuinfo = " << cpuinfo << std::endl;/** within INTERVAL ms, INTERVAL = busyTime + idleTime,* spend busyTime ms to let cpu busy,* spend idleTime ms top let cpu idle*/while (true) {startTime = GetTickCount();while((GetTickCount() - startTime) <= busyTime);usleep(idleTime * 1000);//添加正弦曲线,if(index > DISCRETEVALUE)index = 0;busyTime = 50 + sin(index*value)*50;idleTime = 100 - busyTime;cout<<"busyTime = "<<busyTime<<" idleTime = "<<idleTime << "index*value = "<< index*value<<" sin(index*value)*50 = "<<sin(index*value)*50<<endl;index++;}
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{pthread_t t[NUM_THREADS];int ret;std::cout << "please input cpu utilization rate" << std::endl;std::cin >> cpuinfo;for(int i = 0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++) {ret = pthread_create(&t[i], NULL, CPUCost, NULL);if(ret)std::cout << "XXXX create err" << std::endl;std::cout<<"pthread_create i= "<<i<<std::endl;}pthread_exit(NULL);return 0;
}
结果显示
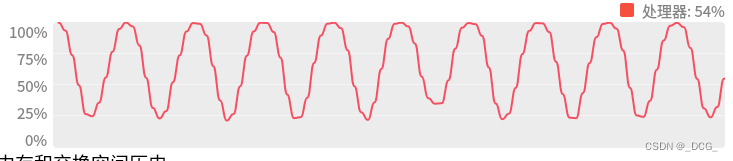
完美实现cpu占有率动态控制。
总结
核心思想是在100ms内动态的分配应用程序运行时间和空闲时间的比例,从而实现达到控制cpu占有率的目的。
