c语言练习84:动态内存管理
动态内存管理
例题:
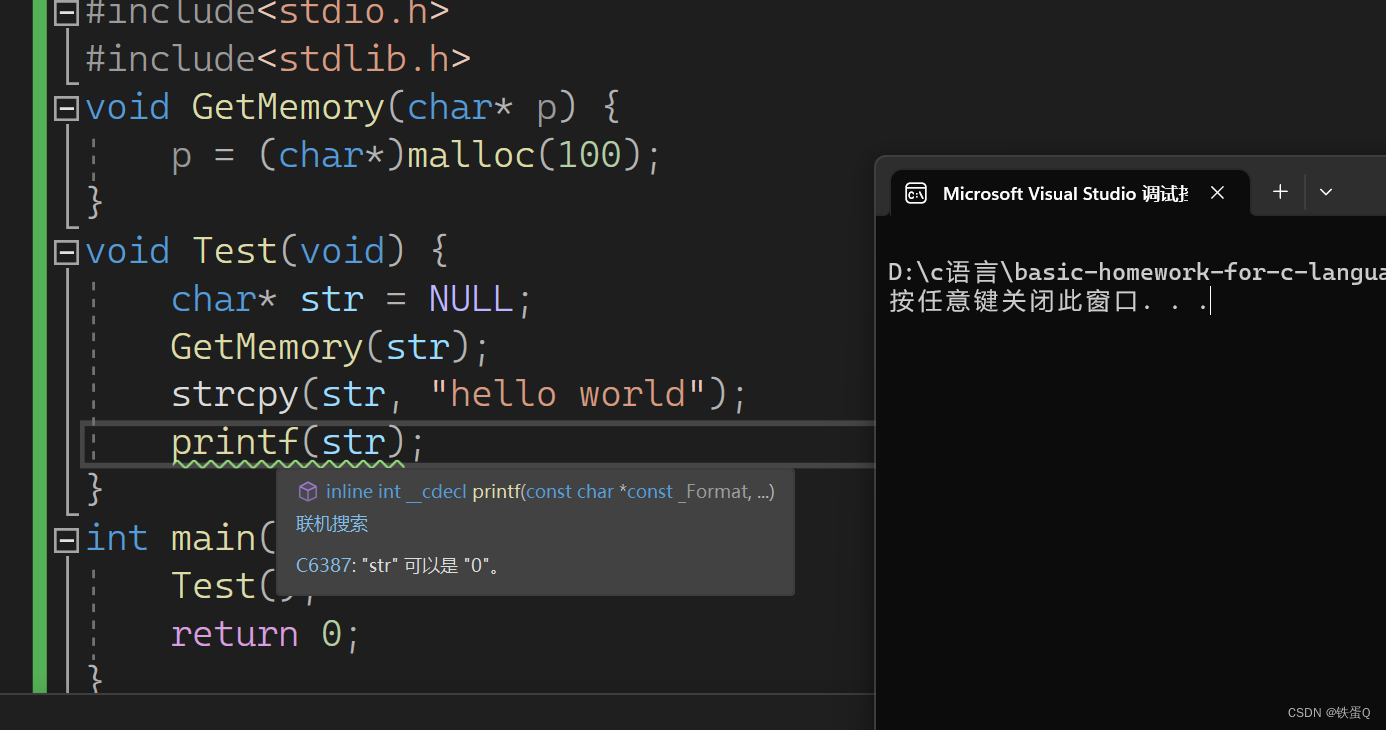
错误代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void GetMemory(char* p) {p = (char*)malloc(100);
}
void Test(void) {char* str = NULL;GetMemory(str);strcpy(str, "hello world");printf(str);
}
int main() {Test();return 0;
}
正确代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void GetMemory(char** p) {*p = (char*)malloc(100);
}
void Test(void) {char* str = NULL;GetMemory(&str);strcpy(str, "hello world");printf(str);
}
int main() {Test();return 0;
}因为使用了malloc所以需要free。
错误案例:
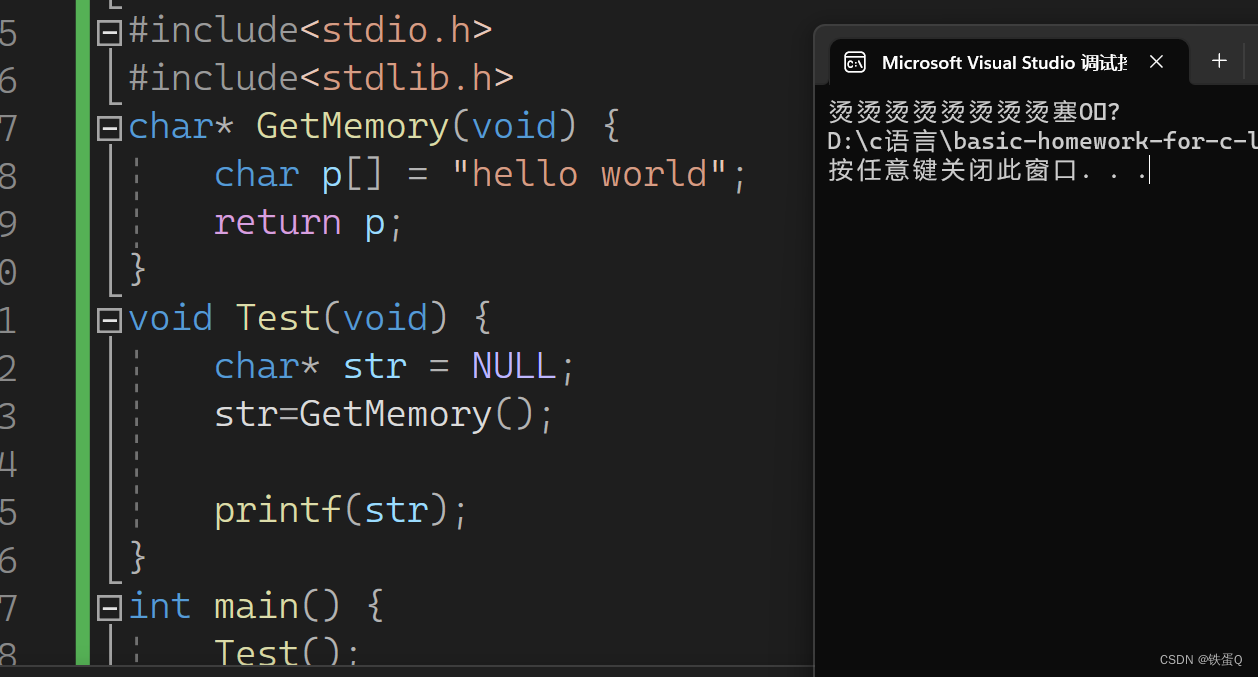
错误代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
char* GetMemory(void) {char p[] = "hello world";return p;
}
void Test(void) {char* str = NULL;str=GetMemory();printf(str);
}
int main() {Test();return 0;
}原因分析(返回栈空间地址的问题):

str会变为野指针
出了函数之后局部变量就会销毁(p)对应的空间会还给操作系统,其对应空间的内容1可能被修改(被其他内容覆盖掉),printf打印的时候会形成非法访问。
错误案例:
void Test(void)
{
char *str = (char *) malloc(100);
strcpy(str, "hello");
free(str);
if(str != NULL)
{
strcpy(str, "world");
printf(str);
}
}原因分析:
free(str)后str成为了野指针,printf(str)时会形成非法访问。
ptr未初始化(即为野指针)对也指针解应用会形成非法访问内存。
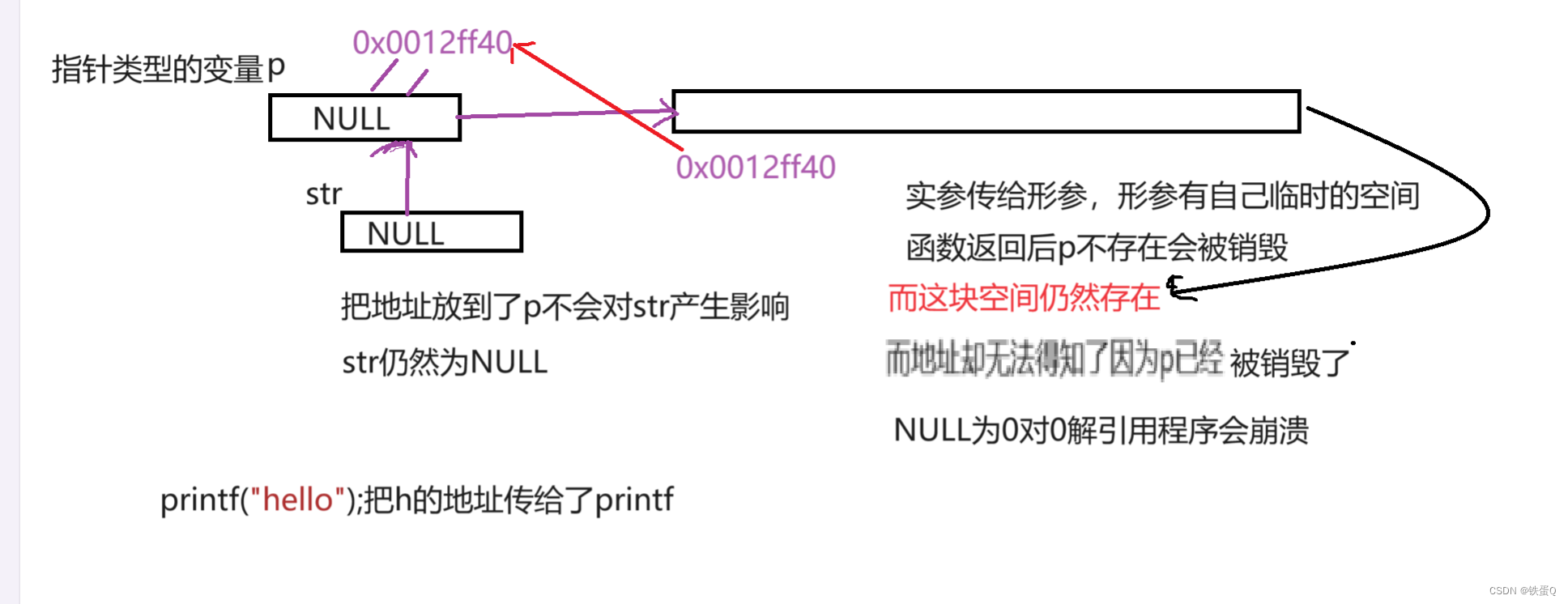
的打印原理:
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {printf("hello\n");char* p = "hello";printf(p);return 0;
}