c++系列之string的模拟实现

💗 💗 博客:小怡同学
💗 💗 个人简介:编程小萌新
💗 💗 如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏 🌞
string()
//注意事项:
1.初始化列表随声明的顺序进行初始化
2.const char* str = nullptr 是错误写法,编译器会报错
3.const char* str = ‘\0’类型不匹配
4.capacity+1 的原因是 _capacity是有效字符的数量加一是为了给‘\0’留空间
//构造函数
string(const char* str = "")
{_size = strlen(str);_capacity = _size;_str = new char(_capacity + 1);memcpy(_str, str, _size + 1);
}
string()
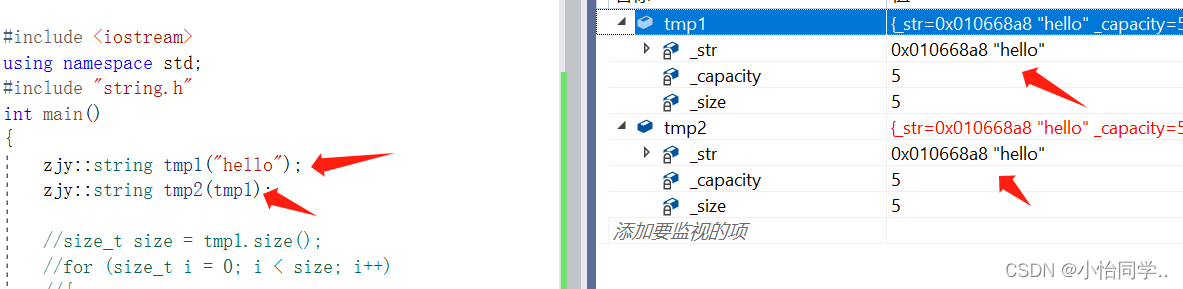
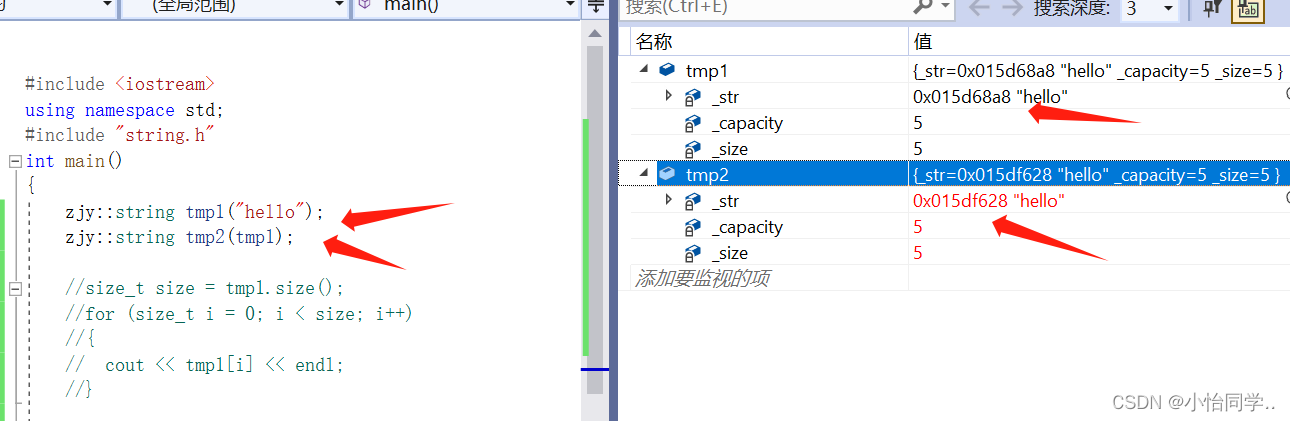
//这里重点注意深浅拷贝
浅拷贝:也称位拷贝,编译器只是将对象中的值拷贝过来.(如果自己没写拷贝函数,编译器会自动生成浅拷贝的拷贝函数)
浅拷贝的两大缺陷:
1.如果对象中管理资源,最后就会导致多个对象共
享同一份资源.
2.当一个对象销毁时就会将该资源释放掉,而此时另一些对象不知道该资源已经被释放,以为
还有效,所以当继续对资源进项操作时,就会发生发生了访问违规。
深拷贝:如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。一般情况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。
//拷贝构造函数
string(const string& s){_size = s._size;_capacity = s._capacity;_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];memcpy(_str,s._str,_size+1);}
3.~string()
//析构函数
~string(){_size = _capacity = 0;delete[] _str;_str = nullptr;}
4. push_back()
//尾插字符
void push_back(char c)
{if (_size == _capacity){int newcapacity = _capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2;reserve(newcapacity);_str[_size++] = c;_str[_size] = '\0';}
}
5.append()
//尾插字符串
void append(const char* str)
{size_t len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity){reserve(_size+len);}/*strcpy(_str+_size, str);*/memcpy(_str+_size,str,len+1);_size = _size + len;
}
6.insert()
//在pos添加字符或字符串
string& insert(size_t pos, size_t n,char c)
{assert(pos <= _size);if (_size+n > _capacity){reserve(_size+n);}size_t end = _size;while (end >= pos && end != npos){_str[end + n] = _str[end];end--;}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){_str[pos+i] = c;}_size += n;return *this;}string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{assert(pos <= _size);int len = strlen(str);if (_size + len > _capacity){reserve(_size + len);}size_t end = _size;while (end >= pos && end != npos){_str[end + len] = _str[end];end--;}for (int i = 0; i < len; i++){_str[pos + i] = str[i];}_size += len;return *this;
}
7.erase()
//消除从pos位置开始n个字符
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{assert(pos < _size);if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size){_str[pos] = '\0';_size = pos;}while (pos <= _size-len){_str[pos] = _str[pos + len];pos++;}_size -= len;return *this;
}
8.find()
返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const
{for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; i++){if (_str[i] == c){return i;}}} 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{char* str = _str + pos;while (*str){const char* scopy = s;const char* strcopy = str;while (*scopy && *scopy == *strcopy){scopy++;strcopy++; }if (*scopy == '\0'){return str - _str;}else{str++;}}
return npos;
}
9.clear()
//清理字符
void clear()
{_size = 0;_str[0] ='\0';
}
10.size()
//返回有效字符大小
//这里const 是为了能让const对象和非const对象都能够调用
size_t size() const
{return _size;
}
11.c_str()
//返回字符串
//这里const 是为了能让const对象和非const对象都能够调用
const char* c_str() const
{return _str;
}
12.capacity()
//返回有效容量大小
//这里const 是为了能让const对象和非const对象都能够调用
size_t capacity() const
{return _capacity;
}
13. operator<
bool operator<(const string& s)const
{int ret = memcmp(_str, s._str, _size < s._size ? _size : s._size);return ret == 0 ? _size < s._size : ret < 0;
}
14.operator==
bool operator==(const string& s))const
{return s._size == _size && memcmp(_str, s._str, _size ) == 0;
}
15.operator<=
bool operator<=(const string& s)const
{return *this < s && *this == s;
}
16.operator>
bool operator>(const string& s)const
{return !(*this <= s);
}
17.operator>=
bool operator>=(const string& s)const
{return !(*this < s);
}
18.operator!=
bool operator!=(const string& s)
{return !(*this == s);
}
19.operator[]
//可读可改
char& operator[](size_t index)
{assert(index < _size);return _str[index];
}
//只读不改
const char& operator[](size_t index)const;
{assert(index < _size);return _str[index];
}
20.operator=
string& operator=(string s)//这里调用拷贝构造,不改变原对象
{if (this != &s){std::swap(_size, s._size);std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);std::swap(_str, s._str);}return *this;
}string& operator=(const string& s)
{if (&s != this){string tmp(s);std::swap(_size, tmp._size);std::swap(_capacity, tmp._capacity);std::swap(_str, tmp._str);}
return *this;
}
21.operator +=
//添加字符
string& operator+=(char ch)
{push_back(ch);return *this;
}
//添加字符串
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{append(str);return *this;
}
22.operator<<
//输出输入流只能用引用接受和返回
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const string& s)
{for (auto ch : s){out << ch;}return out;
}
23.operator>>
ostream& operator>>(ostream& in, string& s)
{s.clear();char ch = in.get();while (ch == ' ' || ch == '&'){ch = in.get();}char buff[128];int i = 0;while (ch != ' ' && ch != '\n'){if (i == 127){buff[i++] = '\0';i = 0;s += buff;}s += ch;ch =in.get();}if (i != 0){buff[i] = '\0';s += buff;}return in;
}
24.resize()
//设置有效字符大小,如果比原先小则保持不变,如果比原先大则在尾部添加。
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{if (n < _size){_size = n;_str[_size] = '\0';}else{reserve(n);for (size_t i = _size; i < n; i++){_str[i] = c;}_size = n;_str[_size] = '\0';}
}
25.reserve()
//设置容量大小,只增不减
void reserve(size_t n)
{if (n > _capacity){char* tmp = new char[n + 1];memcpy(tmp, _str, _size + 1);_capacity = n;delete[] _str;_str = tmp; }
}
26.substr()
string substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
{assert(pos < _size);int n = 0;if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size){n = _size - pos;}string tmp;tmp.reserve(n);for (size_t i = pos; i < pos+n; i++){tmp+=_str[i];//为什么不加\0 }return tmp;
}