Linux驱动实现IO模型
在Linux系统分为内核态和用户态,CPU会在这两个状态之间进行切换。当进行IO操作时,应用程序会使用系统调用进入内核态,内核操作系统会准备好数据,把IO设备的数据加载到内核缓冲区。
然后内核操作系统会把内核缓冲区的数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间。但是进行IO操作时,CPU和内存的速度远远高于外设的速度,所以需要我们使用IO模型编程解决。
IO模型的种类:
- 阻塞IO
- 非阻塞IO
- IO多路复用
- 信号驱动IO
- 异步IO
阻塞IO
当进程以阻塞的方式打开设备文件时(默认方式),如果资源不可用,那么进程阻塞,也就是进程休眠。既然有休眠,就有对应的唤醒操作,否则进程将会一直休眠下去。驱动程序应该在资源可用时负责唤醒操作。相比于非阻塞IO,其最大的优点就是,资源不可用时,不占用CPU的时间,而非阻塞IO必须要定期尝试,看看资源是否可以获得,这对于键盘鼠标这类设备来说,其效率非常低。但是阻塞IO也有一个明显的缺点,那就是进程在休眠期间再也不能做其他事情。
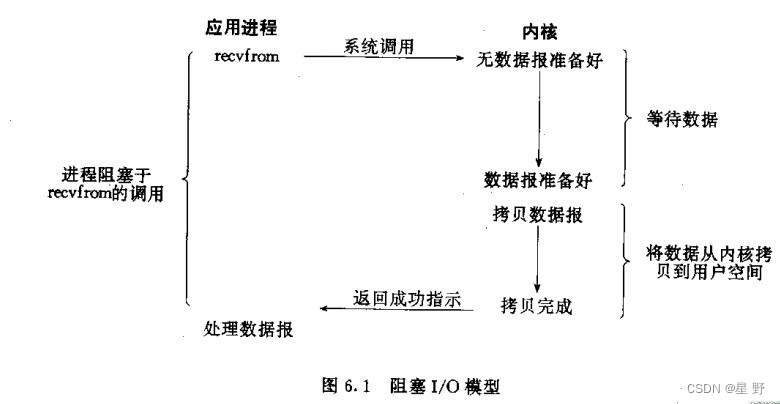
通过上面的描述,发现要实现阻塞操作最重要的数据结构就是等待队列。不了解等待队列的请参考(等待队列)。
下面通过一个简单的驱动程序来实现阻塞IO模型。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>struct devices {char buffer[32];int flag;
};struct devices qw_dev;DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wqh);int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{filp->private_data = &qw_dev;printk("dev open!\n");return 0;
}ssize_t test_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;wait_event_interruptible(wqh, dev->flag);if(copy_to_user(buf, dev->buffer, size)!=0) {printk("copy to user error\n");return -EFAULT;}return size;
}ssize_t test_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if(copy_from_user(dev->buffer, buf, size)) {printk("copy from user error\n");return -EFAULT;}dev->flag = 1;wake_up_interruptible(&wqh);printk("WRITE: %s\n", dev->buffer);return size;}int test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{printk("dev close!\n");return 0;
}//声明操作函数集合
struct file_operations wq_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = test_open,.read = test_read,.write = test_write,.release = test_release,
};//分配初始化miscdevice
struct miscdevice misc_dev = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//系统分配次设备号.name = "qw",//设备文件名.fops = &wq_fops,//操作函数集合
};//加载函数
int test_init(void)
{int ret;//注册miscdeviceret = misc_register(&misc_dev);if (ret < 0) {misc_deregister(&misc_dev);return -1;}qw_dev.flag = 0;return 0;}//卸载函数
void test_exit(void)
{//注销miscdevice misc_deregister(&misc_dev);
}//声明为模块的入口和出口
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//GPL模块许可证
MODULE_AUTHOR("xin");//作者
MODULE_VERSION("2.0");//版本
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("WQ driver!");//描述信息
向驱动写数据的应用程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd;char buf2[32] = "hello world";fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR);if (fd < 0) {perror("open error");return fd;}write(fd, buf2, strlen(buf2));close(fd);return 0;
}向驱动读数据的应用程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd;char buf1[32] = {0};fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR);if (fd < 0) {perror("open error");return fd;}read(fd, buf1, 32);printf("READ:%s\n",buf1);close(fd);return 0;
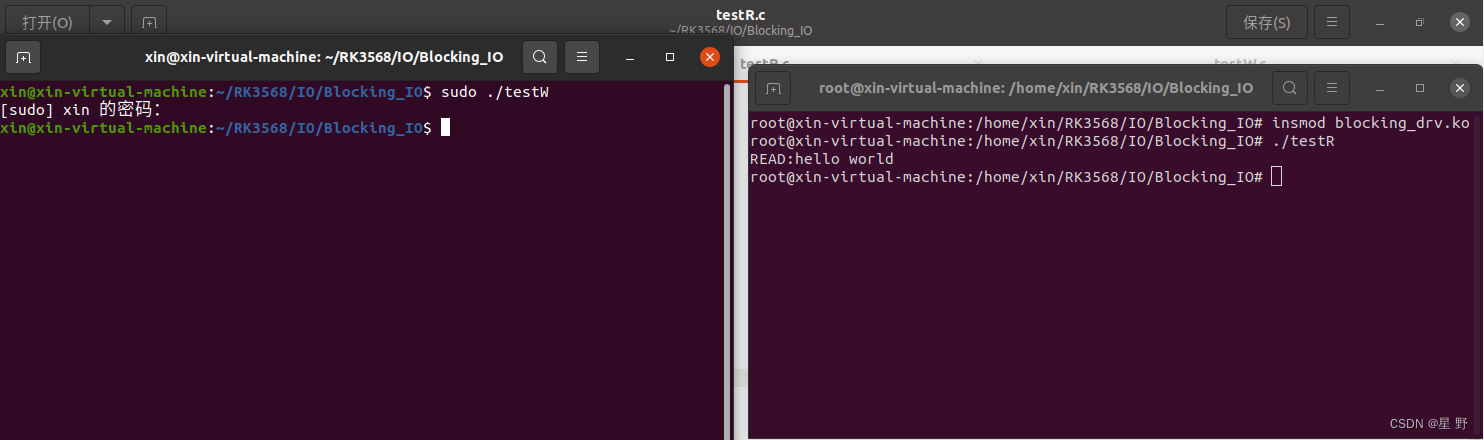
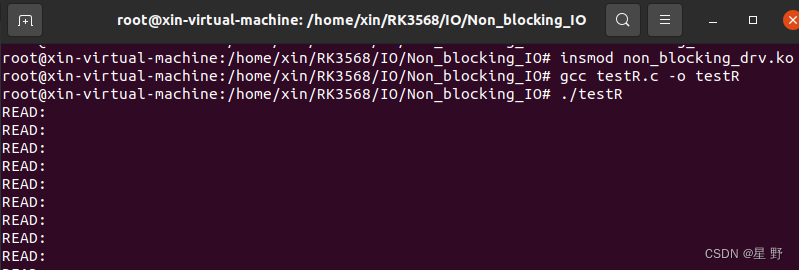
}将驱动模块加载到内核中后,先运行读程序,发现程序会阻塞。然后另开一个终端运行写程序,读程序才会打印写程序的数据。

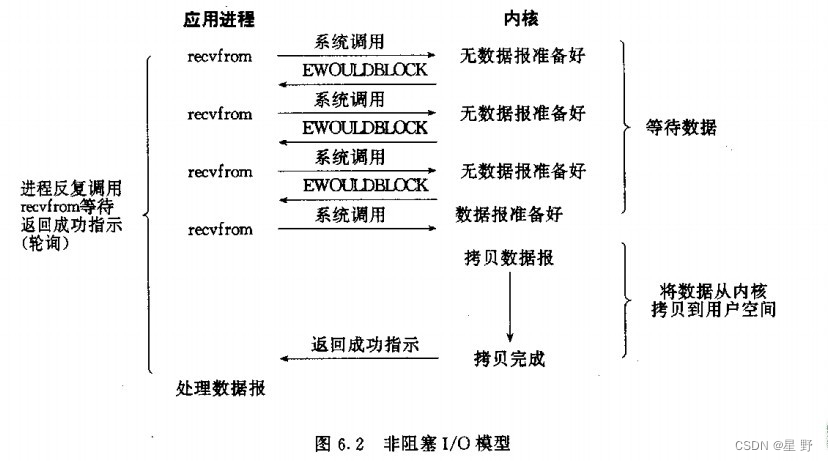
非阻塞IO
设备不一定随时都能给用户提供服务,这就有了资源可用和不可用两种状态。如果应用程序以非阻塞的方法打开设备文件,当资源不可用时,驱动就应该立即返回,并用一个错误码EAGAIN来通知应用程序此时资源不可用,应用程序应该稍后再尝试。
下面通过一个简单的驱动程序来实现阻塞IO模型。在阻塞IO模型上进行修改,当应用程序打开设备文件时,以非阻塞方式打开 。
fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);驱动程序读函数中判断设备是否以非阻塞方式打开,并且资源是否准备好。struct file 结构体中的f_flags成员存储打开设备文件的标志。
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {if (dev->flag != 1) {return -EAGAIN;}
}驱动程序
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>struct devices {char buffer[32];int flag;
};struct devices qw_dev;DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wqh);int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{filp->private_data = &qw_dev;printk("dev open!\n");return 0;
}ssize_t test_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {if (dev->flag != 1) {return -EAGAIN;}}wait_event_interruptible(wqh, dev->flag);if(copy_to_user(buf, dev->buffer, size)!=0) {printk("copy to user error\n");return -EFAULT;}return size;
}ssize_t test_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if(copy_from_user(dev->buffer, buf, size)) {printk("copy from user error\n");return -EFAULT;}dev->flag = 1;wake_up_interruptible(&wqh);printk("WRITE: %s\n", dev->buffer);return size;}int test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{printk("dev close!\n");return 0;
}//声明操作函数集合
struct file_operations wq_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = test_open,.read = test_read,.write = test_write,.release = test_release,
};//分配初始化miscdevice
struct miscdevice misc_dev = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//系统分配次设备号.name = "qw",//设备文件名.fops = &wq_fops,//操作函数集合
};//加载函数
int test_init(void)
{int ret;//注册miscdeviceret = misc_register(&misc_dev);if (ret < 0) {misc_deregister(&misc_dev);return -1;}qw_dev.flag = 0;return 0;}//卸载函数
void test_exit(void)
{//注销miscdevice misc_deregister(&misc_dev);
}//声明为模块的入口和出口
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//GPL模块许可证
MODULE_AUTHOR("xin");//作者
MODULE_VERSION("2.0");//版本
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("WQ driver!");//描述信息
读应用程序如下所示,写程序前面的一样就不展示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd;char buf1[32] = {0};fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);if (fd < 0) {perror("open error");return fd;}while(1) {read(fd, buf1, 32);printf("READ:%s\n",buf1);sleep(1);}close(fd);return 0;
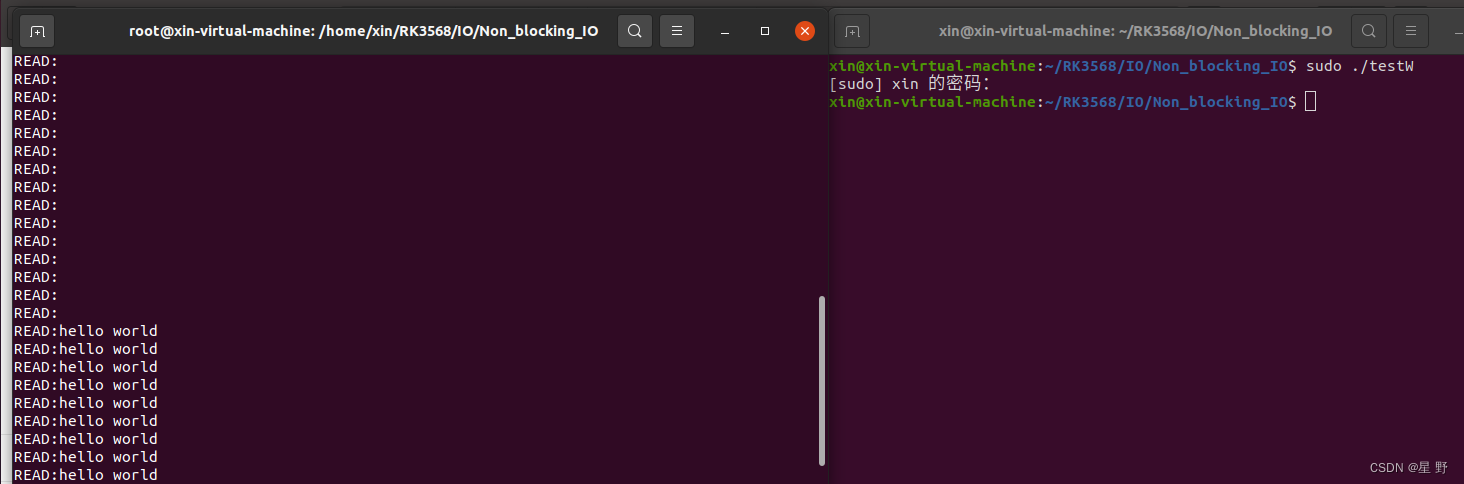
}将驱动模块加载到内核中后,先运行读程序,发现程序不会阻塞,但是没有数据。然后另开一个终端运行写程序,读程序才会打印出写程序的数据。
IO多路复用
阻塞IO优点是在设备资源不可用时,进程主动放弃CPU,但是进程阻塞后不能做其他操作。非阻塞IO优点是资源不可用时不会阻塞,但是会不停地轮询,系统效率降低。当一个进程要同时对多个设备进程操作时以上两种方法显得非常不方便。这就需要使用到IO复用模型。
它允许一个进程可以同时监视多个文件描述符,并且可以在其中任何一个文件描述符上等待数据可读或可写,从而实现并发IO操作。在应用程序中Linux提供了三种API函数:poll,select和epoll。在驱动程序中只需要实现poll函数。
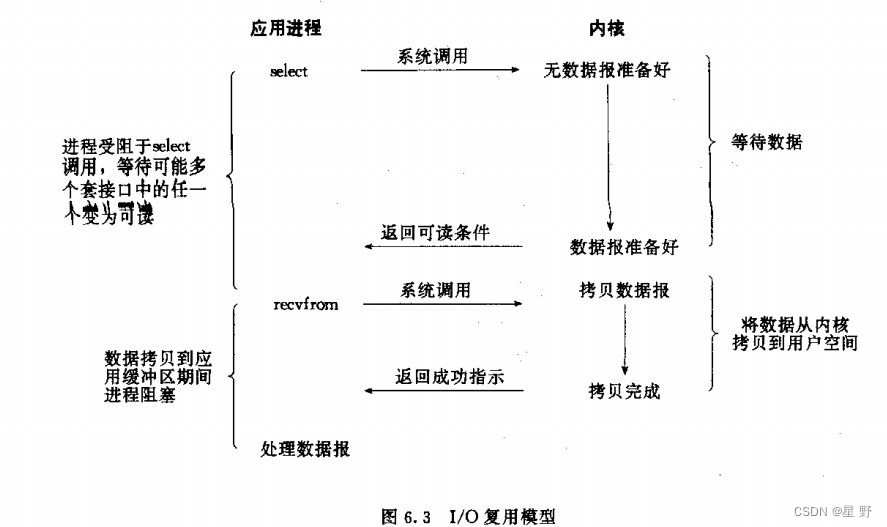
poll和select基本上是一样 ,都可以监听多个文件描述符,通过轮询多个文件描述符来获得已经准备好的文件描述符。epoll是将主动轮询变成了被动通知,当事件发生时,被动的接受通知。
接下来以poll为例进行说明,应用程序中poll系统调用的原型及相关的数据类型如下。
int poll (struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
struct pollfd {
int fd;
short events;
short revents;
};
POLLIN There is data to read.
POLLOUT Writing now will not block.
POLLRDNORM Equivalent to POLLIN.
POLLWRNORM Equivalent to POLLOUT.
poll的第一个参数是要监听的文件描述符集合,类型为指向struct pollfd的指针,struct pollfd有3个成员,fd是要监听文件描述符,events是监听的事件,revents是返回的事件。常见的事件有POLLIN、POLLOUT,分别表示设备可以无阻塞地读、写。POLLRDNORM和POLLWRNORM是在_XOPEN_SOURCE宏被定义时所引入的事件,POLLRDNORM通常和POLLIN等价,POLLWRNORM通常和POLLOUT等价。
poll函数的第二个参数是要监听的文件描述符的个数,第三个参数的毫秒的超时值,负数表示一直监听,直到被监听的文件描述符集合中的任意一个设备发生了事件才会返回。函数返回值为-1表示失败,成功返回revents不为0的文件描述符个数。
读应用程序如下所示,写程序前面的一样就不展示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <poll.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd;int ret;char buf1[32] = {0};struct pollfd fds[1];fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);if (fd < 0) {perror("open error");return fd;}fds[0].fd = fd;fds[0].events = POLLIN;while(1) {ret = poll(fds, 1, 5000);if (!ret) {printf("timeout\n");} else if (fds[0].revents == POLLIN) {read(fd, buf1, 32);printf("READ:%s\n",buf1);sleep(1);}}close(fd);return 0;
}驱动中poll函数需要完成两点:1. 对可能引起设备文件状态变化的等待队列调用poll_wait函数,将对应的等待队列头添加到poll_table。2. 返回表示是否能对设备进行无阻塞读写访问的掩码。
static __poll_t test_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;__poll_t mask = 0;poll_wait(filp, &wqh, p);if (dev->flag = 1) {mask |= POLLIN;}return mask;
}注意:poll_wait函数不会阻塞。
驱动程序
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>struct devices {char buffer[32];int flag;
};struct devices qw_dev;DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wqh);int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{filp->private_data = &qw_dev;printk("dev open!\n");return 0;
}ssize_t test_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {if (dev->flag != 1) {return -EAGAIN;}}wait_event_interruptible(wqh, dev->flag);if(copy_to_user(buf, dev->buffer, size)!=0) {printk("copy to user error\n");return -EFAULT;}return size;
}ssize_t test_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if(copy_from_user(dev->buffer, buf, size)) {printk("copy from user error\n");return -EFAULT;}dev->flag = 1;wake_up_interruptible(&wqh);printk("WRITE: %s\n", dev->buffer);return size;}static __poll_t test_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;__poll_t mask = 0;poll_wait(filp, &wqh, p);if (dev->flag == 1) {mask |= POLLIN;}return mask;
}int test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{printk("dev close!\n");return 0;
}//声明操作函数集合
struct file_operations wq_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = test_open,.read = test_read,.write = test_write,.poll = test_poll,.release = test_release,
};//分配初始化miscdevice
struct miscdevice misc_dev = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//系统分配次设备号.name = "qw",//设备文件名.fops = &wq_fops,//操作函数集合
};//加载函数
int test_init(void)
{int ret;//注册miscdeviceret = misc_register(&misc_dev);if (ret < 0) {misc_deregister(&misc_dev);return -1;}qw_dev.flag = 0;return 0;}//卸载函数
void test_exit(void)
{//注销miscdevice misc_deregister(&misc_dev);
}//声明为模块的入口和出口
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//GPL模块许可证
MODULE_AUTHOR("xin");//作者
MODULE_VERSION("2.0");//版本
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("WQ driver!");//描述信息
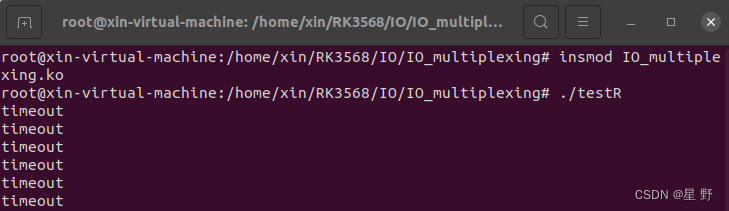
将驱动模块加载到内核中后,先运行读程序,发现程序不会阻塞,但是没有数据且每5s打印超时。然后另开一个终端运行写程序,读程序才会打印出写程序的数据。
信号驱动IO
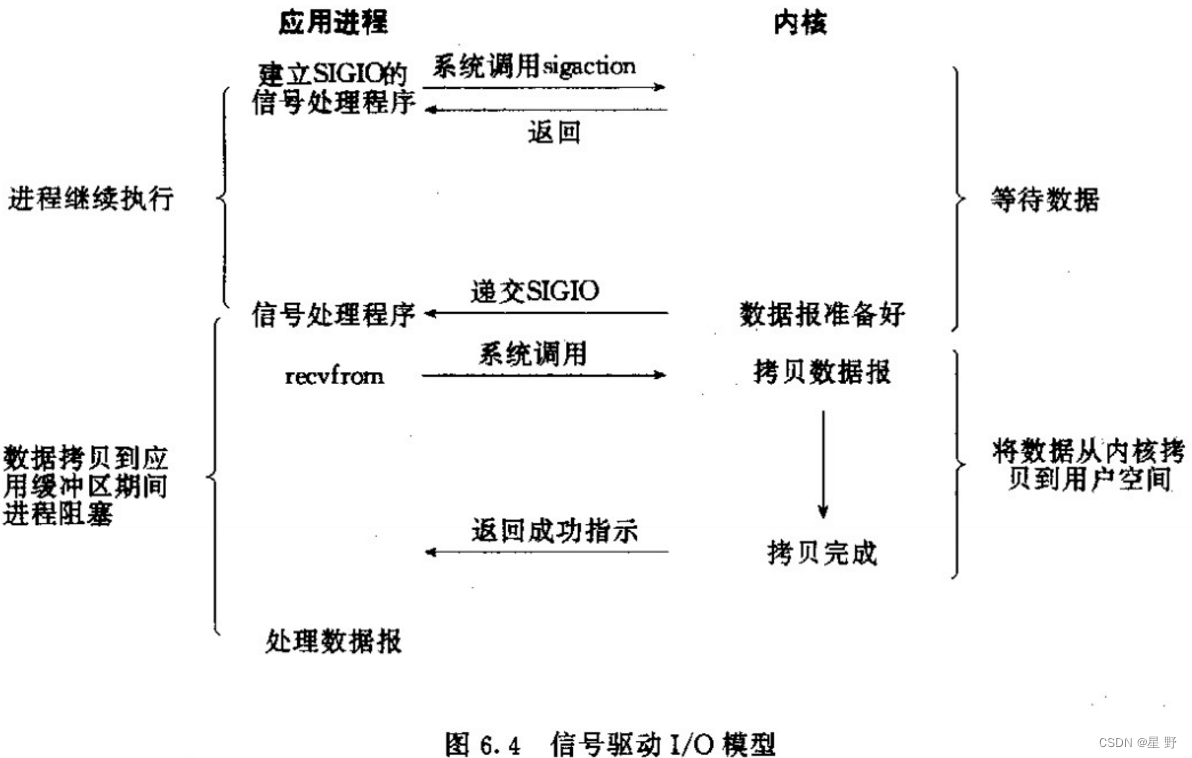
在信号驱动IO中,进程使用系统调用 sigaction() 来注册一个信号处理函数,该函数会在IO事件就绪时被内核调用。当进程调用 sigaction() 注册一个信号处理函数时,它需要指定一个描述符和一个事件,内核在检测到该描述符上发生指定事件时,会向进程发送指定信号。进程可以通过捕获该信号并执行信号处理函数。
与其他IO多路复用技术相比,信号驱动IO也避免了轮询机制的开销,从而减少了 CPU 的占用。但是,信号驱动IO也存在一些缺点。首先,它对信号的处理需要一定的时间,因此它不适合高速IO操作。其次,由于信号是不可靠的,因此在使用信号驱动IO时需要考虑到信号可能会丢失的情况。
在应用程序使用信号驱动IO,需要完成以下几步:1. 注册信号处理函数,应用程序使用 sigaction()来注册一个信号处理函数。2. 设置能接受这个信号的进程。 3. 开启信号驱动IO,通常是使用fcntl函数的F_SETFL命令打开FASYNC标志。
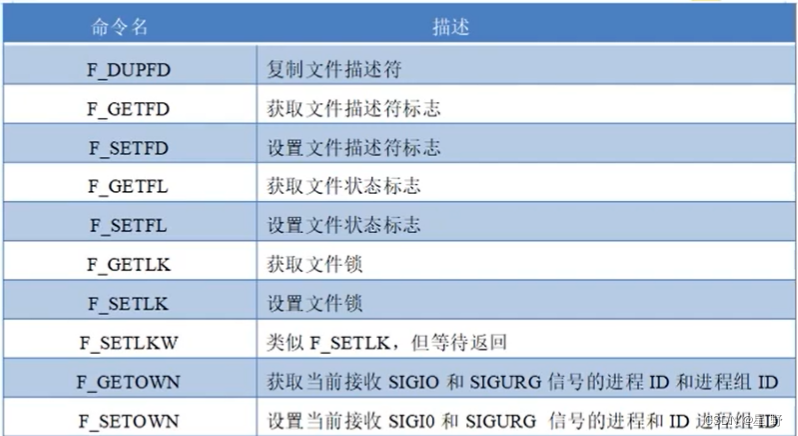
fcntl系统调用可以用来对已打开的文件描述符进行各种控制操作以改变已打开文件的的各种属性。
函数原型:
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd);
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, long arg);
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd ,struct flock* lock);
fcntl函数功能依据cmd的值的不同而不同。参数对应功能如下:
读应用程序如下所示,写程序前面的一样就不展示出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>int fd;
char buf1[32] = {0};static void test_func(int signal)
{read(fd, buf1, 32);printf("READ:%s\n",buf1);
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int flags;fd = open("/dev/qw", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);if (fd < 0) {perror("open error");return fd;}signal(SIGIO, test_func); //注册信号处理函数test_funcfcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()); //设置当前进程接收SIGIO信号flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD); //获得文件描述符标志fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags | FASYNC); //设置文件状态标志,在原来文件描述符标志上开启FASYNC标志while(1);close(fd);return 0;
}当应用程序开启信号驱动IO时,会触发驱动程序中的fasync函数,而fasync函数会调用fasync_helper函数去初始化fasync_struct结构体。 当数据到达时调用kill_fasync函数用来通知应用程序,然后应用程序执行信号处理函数,它的参数是被传递的信号(常常是 SIGIO)和 band 。band:可读时设置成POLLIN,可写时设置成POLLOUT。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>struct devices {char buffer[32];int flag;struct fasync_struct *fasync;
};struct devices qw_dev;DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(wqh);int test_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{filp->private_data = &qw_dev;printk("dev open!\n");return 0;
}ssize_t test_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {if (dev->flag != 1) {return -EAGAIN;}}wait_event_interruptible(wqh, dev->flag);if(copy_to_user(buf, dev->buffer, size)!=0) {printk("copy to user error\n");return -EFAULT;}return size;
}ssize_t test_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;if(copy_from_user(dev->buffer, buf, size)) {printk("copy from user error\n");return -EFAULT;}dev->flag = 1;wake_up_interruptible(&wqh);kill_fasync(&dev->fasync, SIGIO, POLLIN);printk("WRITE: %s\n", dev->buffer);return size;}static __poll_t test_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;__poll_t mask = 0;poll_wait(filp, &wqh, p);if (dev->flag == 1) {mask |= POLLIN;}return mask;
}static int test_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on)
{struct devices *dev = (struct devices *)filp->private_data;return fasync_helper(fd, filp, on, &dev->fasync); //对fasync_struct结构体进行初始化
}int test_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{printk("dev close!\n");return 0;
}//声明操作函数集合
struct file_operations wq_fops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = test_open,.read = test_read,.write = test_write,.poll = test_poll,.fasync = test_fasync,.release = test_release,
};//分配初始化miscdevice
struct miscdevice misc_dev = {.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,//系统分配次设备号.name = "qw",//设备文件名.fops = &wq_fops,//操作函数集合
};//加载函数
int test_init(void)
{int ret;//注册miscdeviceret = misc_register(&misc_dev);if (ret < 0) {misc_deregister(&misc_dev);return -1;}qw_dev.flag = 0;return 0;}//卸载函数
void test_exit(void)
{//注销miscdevice misc_deregister(&misc_dev);
}//声明为模块的入口和出口
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//GPL模块许可证
MODULE_AUTHOR("xin");//作者
MODULE_VERSION("2.0");//版本
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("WQ driver!");//描述信息
将驱动模块加载到内核中后,先运行读程序,发现程序会阻塞,这是因为用while(1)来模拟程序继续处理其他事情。然后另开一个终端运行写程序,读程序才会打印出写程序的数据。
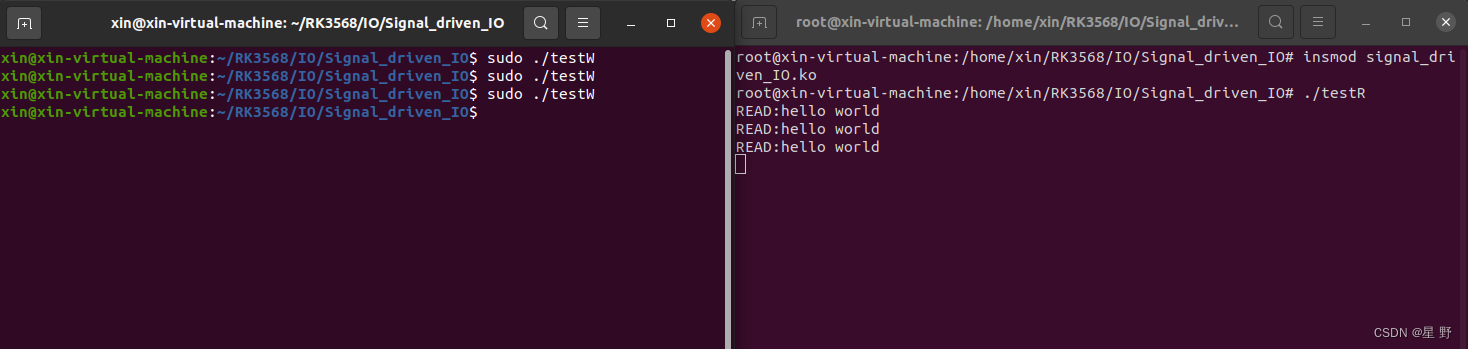
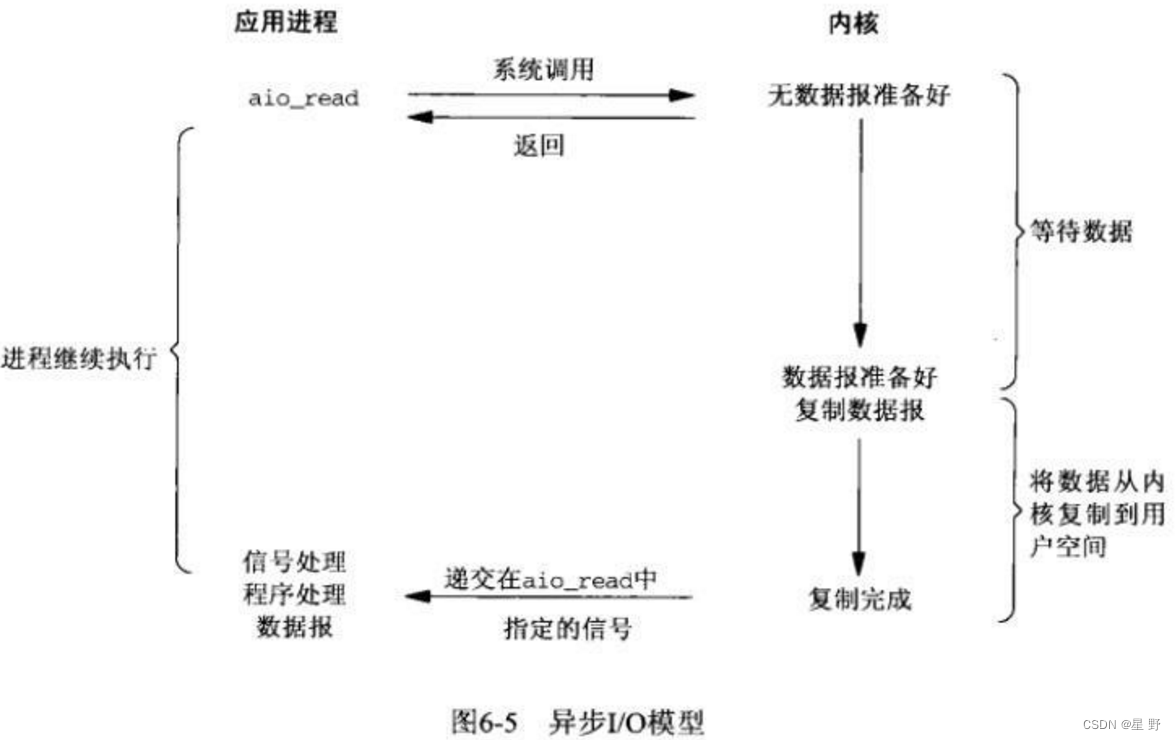
异步IO
相对于同步IO,异步IO不是顺序执行。用户进程进行aio_read系统调用之后,无论内核数据是否准备好,都会直接返回给用户进程,然后用户态进程可以去做别的事情。等到设备数据准备好了,内核直接复制数据给进程,然后从内核向进程发送通知。IO两个阶段,进程都是非阻塞的。异步IO可以在空户空间的glibc库实现,不依赖内核就不举实例了。
总结
阻塞IO实现简单,但是性能不佳,非阻塞IO虽然不需要阻塞线程,但是他需要轮询操作低效。
IO多路复用有三种实现,select和poll都是使用了轮询的方式,监听文件描述符不能太多。epoll的实现使用了红黑树,增删改文件描述符效率高,并且使用了事件触发机制,不需要进行轮询。
信号驱动IO依赖于信号机制,它对信号的处理需要一定的时间,因此它不适合高速IO操作。
异步IO模型的实现比同步IO模型更加复杂,需要使用操作系统提供的通知机制来处理IO完成的事件,同时也需要考虑到异步IO可能会引入的竞争条件和死锁问题。
参考文章:深入理解Linux的五种IO模型,linux五种IO模型。