设计模式C++实现20: 桥接模式(Bridge)
部分内容参考大话设计模式第22章;本实验通过C++语言实现。
一 基本原理
意图:将抽象部分和实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立变化。
上下文:某些类型由于自身的逻辑,具有两个或多个维度的变化。如何应对“多维度的变化”?如何使得该类型既能够沿着多个方向进行变化,又不引入额外的复杂度?
桥接模式静态类图 
Abstraction:定义抽象类的接口;维护一个指向Implementor类型对象的指针。RefinedAbstraction:扩充Abstraction定义的接口。
Implementor:定义Implementor类型的接口,这个接口可以和Abstraction接口完全不同。一般而言,Implementor接口提供基本操作,而Abstraction接口定义较高层次的操作。ConcreteImplementor:实现Implementor接口。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;class Implementor
{
public:virtual void Operation() = 0;
};
class ConcreteImplementorA:public Implementor
{// Implementor interface
public:void Operation(){cout << "ConcreteImplementorA" << endl;}
};
class ConcreteImplementorB:public Implementor
{// Implementor interface
public:void Operation(){cout << "ConcreteImplementorB" << endl;}
};class Abstraction{
public:Implementor *implementor = nullptr;virtual void Operation() = 0;void setImplementor(Implementor *value){this->implementor = value;}
};class RefinedAbstraction:public Abstraction{// shouji interface
public:void Operation(){this->implementor->Operation();}
};int main()
{Abstraction *ab = new RefinedAbstraction();ab->setImplementor(new ConcreteImplementorA());ab->Operation();ab->setImplementor(new ConcreteImplementorB());ab->Operation();return 0;
}
运行结果:
ConcreteImplementorA
ConcreteImplementorB二 手机和软件的实例
结构图

实际的编程使用的UML图是介样的。
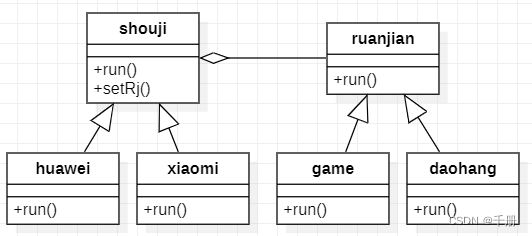
代码实现是介样的:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <mutex>
using namespace std;class ruanjian
{
public:virtual void run() = 0;
};
class game:public ruanjian
{// ruanjian interface
public:void run(){cout << "play game" << endl;}
};
class daohang:public ruanjian
{// ruanjian interface
public:void run(){cout << "go to somewhere" << endl;}
};class shouji{
public:ruanjian *rj = nullptr;virtual void run() = 0;void setRj(ruanjian *value);
};void shouji::setRj(ruanjian *value)
{rj = value;
}class xiaomi:public shouji{// shouji interface
public:void run();
};void xiaomi::run()
{this->rj->run();
}
class huawei:public shouji{// shouji interface
public:void run();
};void huawei::run()
{this->rj->run();
}
int main()
{shouji *hw = new huawei();hw->setRj(new game());hw->run();shouji *xm = new xiaomi();xm->setRj(new daohang());xm->run();return 0;
}
运行结果
play game
go to somewhere
