手撕 视觉slam14讲 ch7 / pose_estimation_3d2d.cpp (1)
首先理清我们需要实现什么功能,怎么实现,提供一份整体逻辑:包括主函数和功能函数
主函数逻辑:
1. 读图,两张rgb(cv::imread)
2. 找到两张rgb图中的特征点匹配对
2.1定义所需要的参数:keypoints1, keypoints2,matches
2.2 提取每张图像的检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置并匹配筛选(调用功能函数1)
3. 建立3d点(像素坐标到相机坐标)
3.1读出深度图(cv::imread)
3.2取得每个匹配点对的深度
3.2.1 得到第y行,第x个像素的深度值
(ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (row)[column])
3.2.2 去除没有深度的点
3.2.3 转到相机坐标系(调用功能函数2)
4. 调用epnp求解(input:3d点,2d点对,内参,是否去畸变,求解方式)
4.1求解(cv::solvePnP)
4.2 求解结果为向量,需要转成矩阵(cv::Rodrigues)
int main( int agrc, char** agrv) {
// 1. 读图(两张rgb)Mat image1 = imread(agrv[1] , CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );Mat image2 = imread(agrv[2] , CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR );assert(image1.data && image2.data && "Can not load images!");// 2. 找到两张rgb图中的特征点匹配对// 2.1定义keypoints1, keypoints2,matchesstd::vector<KeyPoint>keypoints1,keypoints2;std::vector<DMatch>matches;// 2.2 提取每张图像的检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置并匹配筛选Featurematcher(image1,image2, keypoints1,keypoints2,matches);// 3. 建立3d点(像素坐标到相机坐标)Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 520.9, 0, 325.1, 0, 521.0, 249.7, 0, 0, 1);//内参vector<Point3f> pts_3d;vector<Point2f> pts_2d;//3.1读出深度图Mat d1 =imread(agrv[3],CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED);//3.2取得每个匹配点对的深度(ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short> (row)[column];就是指向d1的第row行的第column个数据。数据类型为无符号的短整型 )for (DMatch m: matches){//3.2.1 得到第y行,第x个位置的像素的深度值ushort d = d1.ptr<unsigned short>(int (keypoints1[m.queryIdx].pt.y)) [int(keypoints1[m.queryIdx].pt.x)];// 3.2.2 去除没有深度的点if(d==0){continue;}float dd=d/5000.0 ;//3.2.3 转到相机坐标系Point2d p1 = pixtocam(keypoints1[m.queryIdx].pt , K);pts_3d.push_back(Point3f(p1.x*dd,p1.y*dd,dd));pts_2d.push_back(keypoints2[m.trainIdx].pt);}cout << "3d-2d pairs: " << pts_3d.size() << endl;// 4. 调用epnp求解(input:3d点,2d点对,内参,false,求解方式)// solvePnP( InputArray objectPoints, InputArray imagePoints, InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, OutputArray rvec, OutputArray tvec, bool useExtrinsicGuess = false, int flags = SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE );Mat r,t;// 4.1求解solvePnP(pts_3d,pts_2d,K,Mat(), r,t,false,SOLVEPNP_EPNP);// 4.2 求解结果为向量,需要转成矩阵Mat R;cv::Rodrigues(r,R);cout<<"R="<<R<<endl;cout<<"T="<<t<<endl;// 5.可视化匹配Mat img_goodmatch;drawMatches(image1, keypoints1, image2, keypoints2, matches, img_goodmatch);imshow("good matches", img_goodmatch);waitKey(0);return 0;
}功能函数1: Featurematcher
实现过程在前几篇中已经详细说明:视觉slam14讲 逐行解析代码 ch7 / orb_cv.cpp
2.2.1初始化存储特征点数据的变量
2.2.2 提取每张图像的检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
2.2.3 计算图像角点的BRIEF描述子
2.2.4 根据刚刚计算好的BRIEF描述子,对两张图的角点进行匹配
2.2.5 匹配点对筛选计算最小距离和最大距离
2.2.6 当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
void Featurematcher( const Mat &image1, const Mat &image2, std::vector<KeyPoint>&keypoints1, std::vector<KeyPoint> &keypoints2, std::vector<DMatch> &matches){// 2.2.1初始化存储特征点数据的变量Mat descr1, descr2;Ptr<FeatureDetector> detector = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorExtractor> descriptor = ORB::create();Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");// 2.2.2 提取每张图像的检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置detector->detect(image1, keypoints1);detector->detect(image2, keypoints2);// 2.2.3 计算图像角点的BRIEF描述子descriptor->compute(image1, keypoints1, descr1);descriptor->compute(image2, keypoints2, descr2);// 2.2.4 根据刚刚计算好的BRIEF描述子,对两张图的角点进行匹配std::vector<DMatch> match;matcher->match(descr1, descr2, match);Mat img_match;drawMatches(image1, keypoints1, image2, keypoints2, match, img_match);imshow("all matches", img_match);waitKey(0);// 2.2.5 匹配点对筛选计算最小距离和最大距离double min_dis = 10000, max_dis = 0;// 2.2.5.1找出所有匹配之间的最小距离和最大距离, 即是最相似的和最不相似的两组点之间的距离for (int i = 0; i < descr1.rows; i++){double dist = match[i].distance;if (dist < min_dis)min_dis = dist;if (dist > max_dis)max_dis = dist;}cout<<"max_dis="<<max_dis<<endl;cout<<"min_dis="<<min_dis<<endl;//2.2.6 当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.for (int i = 0; i < descr1.rows; i++){if (match[i].distance<= max(2*min_dis,30.0)){matches.push_back(match[i]);} }cout<<"matches.size="<<matches.size()<<endl;
}
功能函数2:
将输入的像素坐标(x ,y)转化到归一化相机坐标系下得到(X,Y)
我们知道:相机的投影模型为:, 即
所以 ,
Point2d pixtocam(const Point2d &p , const Mat &K){return Point2d(// X=(u-cx)/fx(p.x - K.at<double>(0,2)) / K.at<double>(0,0) ,// Y=(v-cy)/fy(p.y-K.at<double>(1,2)) / K.at<double>(1,1));
}
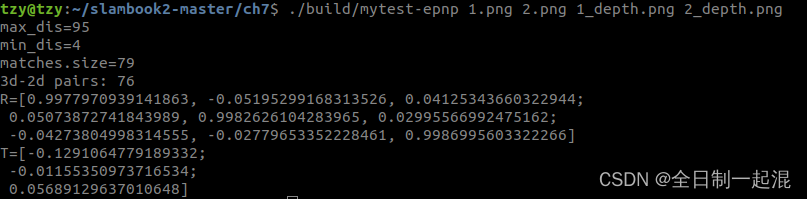
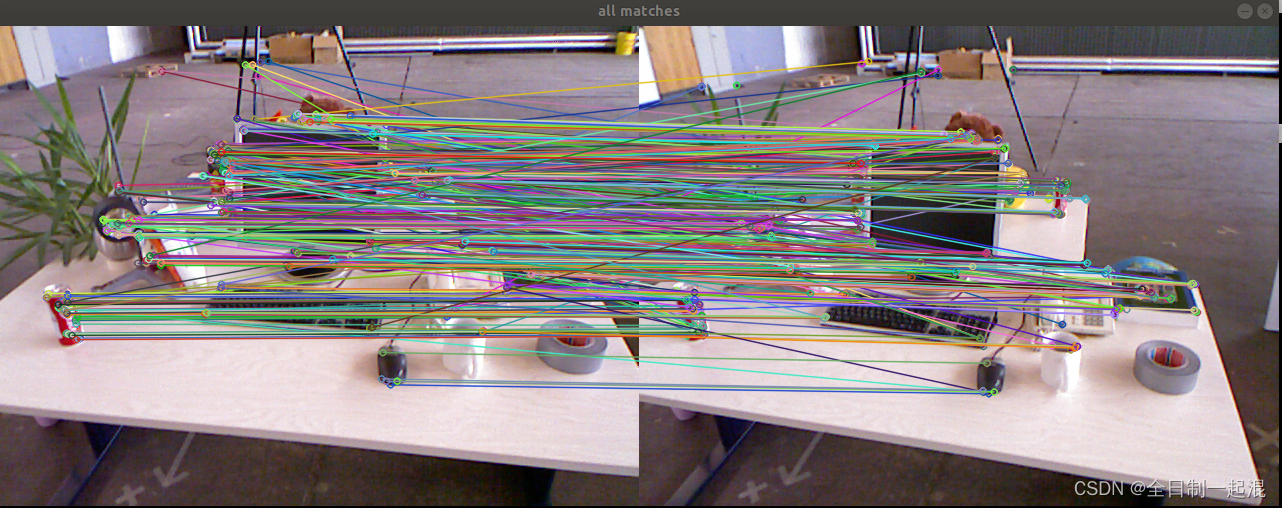
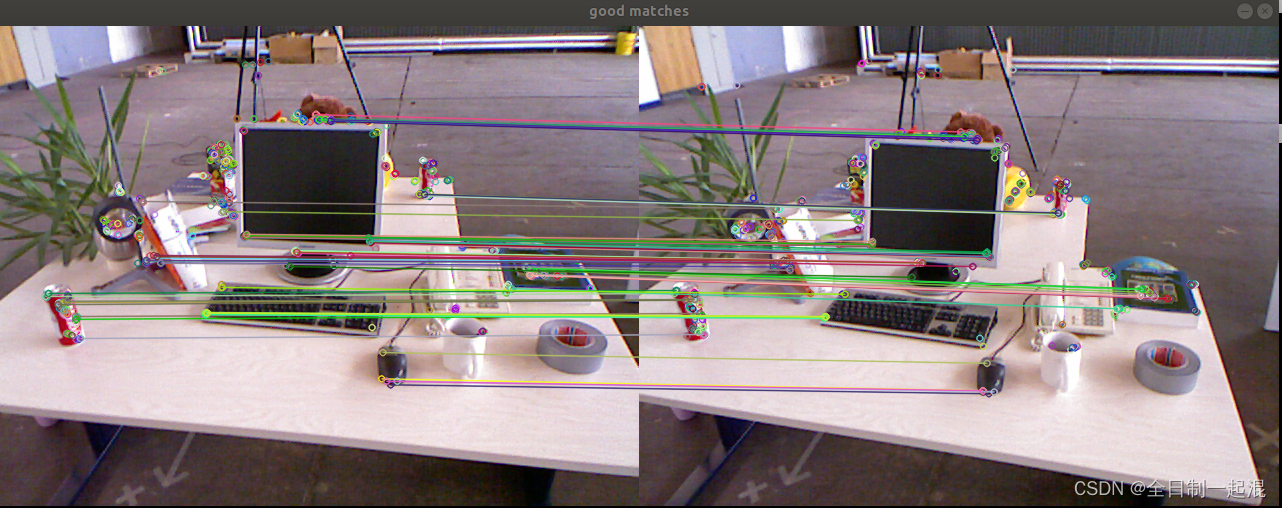
最后匹配效果及位姿结果:
allmatch:

goodmatch:

位姿输出:R,T: