Linux —— 进程信号
一,信号概念
信号是进程之间事件异步通知的一种方式,属于软中断;
系统定义的信号
- 每个信号都有一个编号和一个宏定义名称(可在signal.h查看);
- 编号34以上的为实时信号;
[wz@192 Desktop]$ kill -l1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
21) SIGTTIN 22) SIGTTOU 23) SIGURG 24) SIGXCPU 25) SIGXFSZ
26) SIGVTALRM 27) SIGPROF 28) SIGWINCH 29) SIGIO 30) SIGPWR
31) SIGSYS 34) SIGRTMIN 35) SIGRTMIN+1 36) SIGRTMIN+2 37) SIGRTMIN+3
38) SIGRTMIN+4 39) SIGRTMIN+5 40) SIGRTMIN+6 41) SIGRTMIN+7 42) SIGRTMIN+8
43) SIGRTMIN+9 44) SIGRTMIN+10 45) SIGRTMIN+11 46) SIGRTMIN+12 47) SIGRTMIN+13
48) SIGRTMIN+14 49) SIGRTMIN+15 50) SIGRTMAX-14 51) SIGRTMAX-13 52) SIGRTMAX-12
53) SIGRTMAX-11 54) SIGRTMAX-10 55) SIGRTMAX-9 56) SIGRTMAX-8 57) SIGRTMAX-7
58) SIGRTMAX-6 59) SIGRTMAX-5 60) SIGRTMAX-4 61) SIGRTMAX-3 62) SIGRTMAX-2
63) SIGRTMAX-1 64) SIGRTMAX //vim /usr/include/bits/signum.h
/* Signals. */
#define SIGHUP 1 /* Hangup (POSIX). */
#define SIGINT 2 /* Interrupt (ANSI). */
#define SIGQUIT 3 /* Quit (POSIX). */
#define SIGILL 4 /* Illegal instruction (ANSI). */
#define SIGTRAP 5 /* Trace trap (POSIX). */
#define SIGABRT 6 /* Abort (ANSI). */
#define SIGIOT 6 /* IOT trap (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGBUS 7 /* BUS error (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGFPE 8 /* Floating-point exception (ANSI). */
#define SIGKILL 9 /* Kill, unblockable (POSIX). */
#define SIGUSR1 10 /* User-defined signal 1 (POSIX). */
#define SIGSEGV 11 /* Segmentation violation (ANSI). */
#define SIGUSR2 12 /* User-defined signal 2 (POSIX). */
#define SIGPIPE 13 /* Broken pipe (POSIX). */
#define SIGALRM 14 /* Alarm clock (POSIX). */
#define SIGTERM 15 /* Termination (ANSI). */
#define SIGSTKFLT 16 /* Stack fault. */
#define SIGCLD SIGCHLD /* Same as SIGCHLD (System V). */
#define SIGCHLD 17 /* Child status has changed (POSIX). */
#define SIGCONT 18 /* Continue (POSIX). */
#define SIGSTOP 19 /* Stop, unblockable (POSIX). */
#define SIGTSTP 20 /* Keyboard stop (POSIX). */
#define SIGTTIN 21 /* Background read from tty (POSIX). */
#define SIGTTOU 22 /* Background write to tty (POSIX). */
#define SIGURG 23 /* Urgent condition on socket (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGXCPU 24 /* CPU limit exceeded (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGXFSZ 25 /* File size limit exceeded (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGVTALRM 26 /* Virtual alarm clock (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGPROF 27 /* Profiling alarm clock (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGWINCH 28 /* Window size change (4.3 BSD, Sun). */
#define SIGPOLL SIGIO /* Pollable event occurred (System V). */
#define SIGIO 29 /* I/O now possible (4.2 BSD). */
#define SIGPWR 30 /* Power failure restart (System V). */
#define SIGSYS 31 /* Bad system call. */
#define SIGUNUSED 31
ctrl + c
此键盘输入将产生一个硬件中断,被OS获取并解释成信号,发送给目标前台进程;此前台进程收到信号,引起进程退出;
- ctrl + c 产生的信号只能发送给前台进程;如一个命令后加上&,可放入后台运行;
- shell可同时运行一个前台进程和任意多个后台进程,只有前台进程才可接收ctrl+c产生的信号;
- 前台进程在运行过程中可随时按下ctrl+c,即该进程的用户空间代码执行到任何位置都有可能收到SIGINT信号而终止,所以信号相当于进程的控制流来说是异步的;
信号的产生
信号的阻塞
信号的捕捉
二,信号的产生
- 通过终端按键产生信号
- 调用系统函数向进程发送信号
- 由软件条件产生信号
- 硬件异常产生信号
1,通过终端按键产生信号
- SIGINT默认处理动作为终止进程;
- SIGQUIT默认处理动作为终止进程并Core Dump;
Core Dump,即当一进程异常终止时,可选择把进程的用户空间内存数据全部保存到磁盘上,文件名通常是core(叫做core dump);异常终止通常是因为bug,如非法内存访问导致的段错误,事后可调试器检查core文件以查清错误原因(叫做事后调试Post-mortem Debug);一个进程允许产生多大的core文件取决于进程的Resource Limit(此消息保存于PCB中);默认是不允许产生core文件的,因为core文件可能包含用户密码等敏感消息;在开发阶段可使用ulimit命令改变此限制,允许产生core文件;用ulimit命令改变shell进程的Resource Limit,允许core文件最大1024K(ulimit -c 1024);
[wz@192 ~]$ ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 0
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 7154
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 1024
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 4096
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
[wz@192 ~]$ ulimit -c 1024
[wz@192 ~]$ ulimit -a
core file size (blocks, -c) 1024
data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited
scheduling priority (-e) 0
file size (blocks, -f) unlimited
pending signals (-i) 7154
max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64
max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited
open files (-n) 1024
pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8
POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200
real-time priority (-r) 0
stack size (kbytes, -s) 8192
cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited
max user processes (-u) 4096
virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited
file locks (-x) unlimited
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(){ int count = 0; while(1){ printf("%d,pid:%d\n",count++,getpid()); sleep(1); } return 0;
} //ctrl+\终止进程并生成core文件
[wz@192 Desktop]$ ./test
0,pid:44041
1,pid:44041
2,pid:44041
3,pid:44041
4,pid:44041
5,pid:44041
^\Quit (core dumped)
[wz@192 Desktop]$ ll
total 268
-rw-------. 1 wz wz 253952 8月 31 08:31 core.44041
-rw-rw-r--. 1 wz wz 60 8月 29 08:15 makefile
-rwxrwxr-x. 1 wz wz 8464 8月 31 08:29 test
-rw-rw-r--. 1 wz wz 157 8月 31 08:31 test.c
[wz@192 Desktop]$ gdb test
GNU gdb (GDB) Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.6.1-120.el7
Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying"
and "show warranty" for details.
This GDB was configured as "x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu".
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>...
Reading symbols from /home/wz/Desktop/test...(no debugging symbols found)...done.
(gdb) core-file core.44041
[New LWP 44041]
Core was generated by `./test'.
Program terminated with signal 3, Quit.
#0 0x00007ff68f2e19e0 in __nanosleep_nocancel () from /lib64/libc.so.6
Missing separate debuginfos, use: debuginfo-install glibc-2.17-326.el7_9.x86_64
(gdb)
2,调用系统函数向进程发送信号
//也可kill -11 51993
[wz@192 ~]$ kill -SIGSEGV 51993
[wz@192 Desktop]$ ./test
0,pid:51993
1,pid:51993
2,pid:51993
Segmentation fault (core dumped)

- kill命令是调用kill函数实现的,该函数可给指定进程发送特定信号;
- raise函数可给当前进程发送指定信号(自己给自己发送信号);
- abort函数使当前进程接收到信号而异常终止;



3,由软件条件产生信号
- alarm函数,可设定一个闹钟,告诉内核在多少秒后给当前进程发送SIGALRM信号;
- SIGALRM信号,默认处理动作为终止当前进程;

#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(){ int count = 0; alarm(1); while(1){ printf("%d,pid:%d\n",count++,getpid()); } return 0;
} [wz@192 Desktop]$ ./test
...
174838,pid:53084
174839,pid:53084
174840,pid:53084
174841,pid:53084
174842,pid:53084Alarm clock
4,硬件异常产生信号
即被硬件以某种方式检测到并通知内核,然后内核向当前进程发送适当的信号;如当前进程执行了除0的指令,CPU的运算单元会产生异常,内核将这个异常解释为SIGFPE信号发送给进程;在如当前进程访问了非法内存地址,内核将异常解释为SIGSEGV信号发送给进程;
在C/C++中除零、内存越界等异常,在系统层面是被当成信号处理的;
信号捕捉
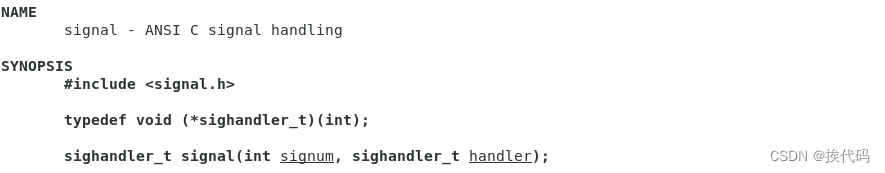
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h> void handler(int sig){ printf("catch a sig: %d\n", sig);
}
int main(){ signal(2, handler); int count = 0; while(1){ printf("%d,pid:%d\n",count++,getpid()); sleep(1); } return 0;
} [wz@192 Desktop]$ ./test
0,pid:53899
1,pid:53899
^Ccatch a sig: 2
2,pid:53899
3,pid:53899
4,pid:53899
^Ccatch a sig: 2
野指针异常
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h> void handler(int sig){ printf("catch a sig: %d\n", sig);
}
int main(){ //signal(SIGSEGV, handler); int *p = NULL; *p = 100; int count = 0; while(1){ printf("%d,pid:%d\n",count++,getpid()); sleep(1); } return 0;
} [wz@192 Desktop]$ ./test
Segmentation fault (core dumped)
所有信号的产生,最终都是由OS进行执行的;
信号不是立即处理的,是在合适的时候才进行处理的;
