【Java8特性】——Stream API
一、概述
<1> 是什么
是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合、数组等)所生成的元素序列。
- Stream 不会存储数据
- Stream 不会改变数据源,相反,会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
- Stream 操作是延迟执行的,这意味着会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
<2> Stream 和collection的区别
Connection是一种静态的内存数据结构,Stream是有关计算的,前者主要面向内存,存储在内存中,后者是面向CPU,通过CPU实现计算。
集合讲的是数据,Stream讲的是计算。
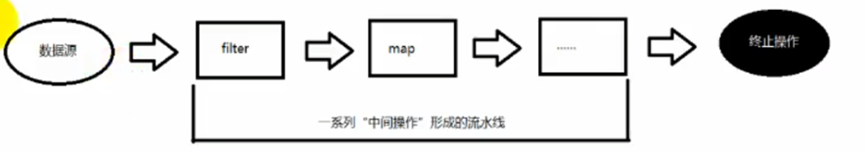
<3> 执行步骤
- 创建Stream
一个数据源,会获取一个流 - 中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理。 - 终止操作(终端操作)
一旦执行终止操作,就执行中间操作链,并产生结果,之后,不会再被使用。
二、创建方式
<1> 通过集合
default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
/*** 方式一: 通过集合创建流* default Stream<E> stream() ,返回一个顺序流* default Stream<E> parallelStream() ,返回一个并行流*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();// default Stream<E> stream() ,返回一个顺序流Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream();// default Stream<E> parallelStream() ,返回一个并行流Stream<Employee> parallelStream = employees.parallelStream();}
<2> 通过数组创建流
Java8 中的Arrays的静态方法stream()可以获取数据流。
static IntStream stream(int[] array)
/*** 方式二: 通过数组创建流* Java8 中的Arrays的静态方法stream()可以获取数据流。* <p>* static IntStream stream(int[] array)*/@Testpublic void test2() {int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};// static IntStream stream(int[] array)IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr);Employee employee1 = new Employee(1002, "玛火腿", 34, 123);Employee employee2 = new Employee(1003, "tom", 23, 2222);Employee[] employees = new Employee[]{employee1, employee2};Stream<Employee> stream1 = Arrays.stream(employees);}<3> 通过Stream的of()
可以调用Stream类的静态方法of(),通过显示值创建一个流。他可以接受任意数量的参数
public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values)
/*** 方式三: 通过Stream的of()* 可以调用Stream类的静态方法of(),通过显示值创建一个流。他可以接受任意数量的参数* public static<T> Stream<T> of(T... values)*/@Testpublic void test3() {Stream<Integer> integerStream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);}
<4> 创建无限流
以使用静态方法Stream.iterate()和Stream.generate(),创建无限流
/*** 方式四: 创建无限流* 可以使用静态方法Stream.iterate()和Stream.generate(),创建无限流*/@Testpublic void test4() {//迭代// public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f)Stream.iterate(0, t -> t + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);//出生//public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<T> s)Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);}三、中间操作
<1> 筛选&切片
多个中间操作可以连接起来形成一个流水线,除非流水线上触发种植操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何的处理,而在种植操作时一次性全部处理,称为“惰性求值”。
1. filter
从流中排除某些元素
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
/*** 从流中排除某些元素* Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);* filter 中 参数 通过Lambda表达式 实现 Predicate 函数式接口*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 23).forEach(System.out::println);}
2. limit
截断流 ,使元素不超过给定数量
/*** 截断流 ,使元素不超过给定数量* Stream<T> limit(long maxSize);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);}
3. skip
掉过元素,返回一个扔掉前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,,则返回一个空流
/*** 掉过元素,返回一个扔掉前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,,则返回一个空流* Stream<T> skip(long n);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().skip(5).forEach(System.out::println);}
4. distinct
筛选,通过流所生成的元素的hashcode()和equals()去除重复元素。
/*** 筛选, 通过流所生成的元素的hashcode()和equals()去除重复元素。* Stream<T> distinct();*/@Testpublic void test4() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}
<2> 映射
1. map
接受一个函数作为参数,将元素转换为其他形式或者提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素
/*** 映射* 接受一个函数作为参数,将元素转换为其他形式或者提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素* <R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);*/@Testpublic void test5() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);}
2. flatMap
接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
/*** 接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。* <R> Stream<R> flatMap(Function<? super T, ? extends Stream<? extends R>> mapper);*/@Testpublic void test6() {List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","bbbb");Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream);streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");list.stream().map(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream).forEach(e->{e.forEach(System.out::println);});System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------------");Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(Stream_api_test2::formStringtoStream);characterStream.forEach(System.out::println);}/*** 将字符串中的多个字符构成的集合转换为对应Stream的实例* @param str 字符串* @return Stream实例*/public static Stream<Character> formStringtoStream(String str) {List<Character> arrayList = new ArrayList();for (Character s :str.toCharArray()) {arrayList.add(s);}Stream<Character> stream = arrayList.stream();return stream;}
<3> 排序
1. sorted-自然排序
自然排序 , 产生一个新的流,其中按自然顺序排序
/*** 自然排序 , 产生一个新的流,其中按自然顺序排序* Stream<T> sorted();*/@Testpublic void test7() {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(23, 44, 34, 6, 1, 334, 546, 23, 1211, 453435, 2, 1, 3, 3);list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);}
2. sorted-定制排序
定制排序 ,产生一个新的流,其中按比较器顺序排序
/*** 定制排序 ,产生一个新的流,其中按比较器顺序排序* Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator);*/@Testpublic void test8() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().sorted((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge())).forEach(System.out::println);}
四、 终止操作
<1> 匹配 & 查找
1. allMatch
检查是否匹配所有元素,所有元素匹配就是ture ,否则为false
/*** 检查是否匹配所有元素,所有元素匹配就是ture ,否则为false* boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//都大于18 则为ture,否则为falseboolean b = employees.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18);System.out.println(b);}
2. anyMatch
检查是否至少一个匹配的元素,有一个匹配就是ture ,否则为false
/*** 检查是否至少一个匹配的元素,有一个匹配就是ture ,否则为false* boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//有一个大于33 则为ture,否则为falseboolean b = employees.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 33);System.out.println(b);}
3. noneMatch
是否没有匹配的元素 ,有一个匹配就是false ,全都不匹配则为ture
/*** 是否没有匹配的元素 ,有一个匹配就是false ,全都不匹配则为ture* boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();//有大于33的元素 则为false,否则为tureboolean b = employees.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 33);System.out.println(b);}
4. findFirst
返回第一个元素
/*** 返回第一个元素* Optional<T> findFirst();*/@Testpublic void test4() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findFirst();System.out.println(employee);}
5. findAny
返回任意一个元素
/*** 返回任意一个元素* Optional<T> findAny();*/@Testpublic void test5() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findAny();System.out.println(employee);}
6. count
返回流中元素的总个数
/*** 返回流中元素的总个数* long count();*/@Testpublic void test6() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();long count = employees.stream().filter(e->e.getAge()>30). count ();System.out.println(count);}
7. max
返回流最大值
/*** 返回流最大值*/@Testpublic void test7() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> maxEmployee = employees.stream().max((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge()));System.out.println(maxEmployee);}
8. min
返回流中最小值
/*** 返回流中最小值*/@Testpublic void test8() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Employee> maxEmployee = employees.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(), e2.getAge()));System.out.println(maxEmployee);}
9. forEach
/*** 内部迭代*/@Testpublic void test9() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println);}
<2> 规约
1. reduce-T
将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回 T
/*** 将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回 T* T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);* T identity 为一个初始值*/@Testpublic void test1() {List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);Integer reduce = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);System.out.println(reduce);}
2. reduce - Optional
将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回一个Optional
/*** 将流中的元素返回结合起来,得到一个值,返回一个Optional<T>* Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);*/@Testpublic void test2() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();Optional<Double> reduce = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).reduce(Double::sum);System.out.println(reduce);System.out.println("-------------------------------------");employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).reduce((d1, d2) -> {System.out.println("d1 : "+d1);System.out.println("d2 : "+d2);System.out.println("d1 + d2 : "+(d1 + d2));System.out.println("-----------");return d1 + d2;});}
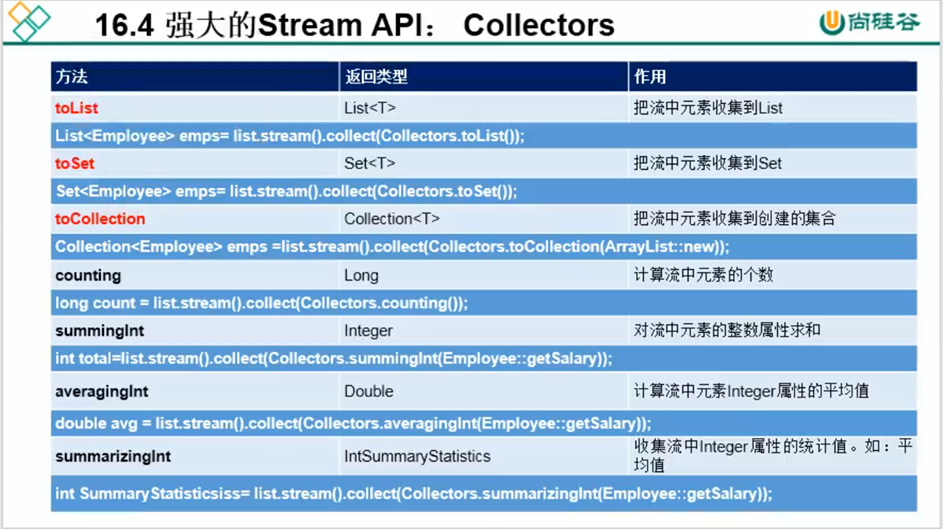
<3> 收集
将流转换为其他形式,接受一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法。Collector接口中发给发的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作 , 如收集到 List,Set,Map。Collector实用类提供了很多静态方法,可以方便地创建收集器实例。如下:
/*** 将流转换为其他形式,接受一个Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法* Collector接口中发给发的实现决定了如何对流执行收集操作 , 如收集到 List,Set,Map* Collector实用类提供了很多静态方法,可以方便地创建收集器实例。* <R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector);*/@Testpublic void test3() {List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployee();List<String> collect = employees.stream().filter(e->e.getAge()>30).map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect);System.out.println("-------------------------------------");Set<String> collect1 = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() > 30).map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(collect1);}
