SystemVerilog interface使用说明
1. Interface概念
System Verilog中引入了接口定义,接口与module 等价的定义,是要在其他的接口、module中直接定义,不能写在块语句中,跟class是不同的。接口是将一组线捆绑起来,可以将接口传递给module。
2. 接口的优点
一)通过接口在module之间或内部进行信号,模块的输入列表就是一个接口,这样简单,避免手动连线的错误。
二)如果需要增加模块的IO,只需要在接口中增加,不需要改变模块的输入列表,防止输入错误、少改了哪个模块的列表。
三)在UVM 中需要在不同的class之间传递信号,用接口的话,传递一组信号只需要uvm_config_db一个接口就可以了,如果不用接口,那么就需要好多条uvm_config_db语句。
四)接口中可以定义一些initial(生成时钟),always块,任务,函数,类的句柄。
3. 定义接口
可以在接口中定义一些信号、函数、任务、class对象,也可以有always,initial语句块。比如可以在initial块中生成时钟clk。
3.1 定义
interface if(input bit clk);logic data;logic valid;logic addr;
endinterface3.2 modport
可以用modport将接口中的信号分组。比如总线接口中,master、slave、arbiter需要的信号是不同的,输入输出也不同。
interface if(input bit clk);logic [7:0] data;logic valid;logic [7:0] addr;logic request;logic grant;logic command;logic ready;modport MASTER(output request,addr,command);modport SLAVE(input request,addr,command,output ready);modport ARBITER(input request,output grant);
endinterface
module Master (if.MASTER if_u);
...
endmodule
module test;if if_u;Master m_u(if_u.MASTER);
endmodule 4. 激励时序
测试平台需要和设计之间的时序密切配合。比如在同一个时间片内,一个信号需要被同时写入和读取,那么采样到新值还是旧值?非阻塞赋值可以解决这个问题,值的计算在active区域,值的更新在NBA区域——采样到的是旧值。
4.1 时钟块控制同步信号的时序
在接口中定义时钟块,时钟块中的任何信号都相对于时钟同步驱动和采样。时钟块大都在测试平台中使用。
interface if(input bit clk);logic [7:0] data;logic valid;logic [7:0] addr;clocking cb@(posedge clk);input valid;input data;input addr;endclockingmodport TEST(clocking cb);modport DUT(input valid ,input data);
endinterface一个接口中可以有多个时钟块,但每个时钟块只有一个时钟表达式。如@(posedge clk)定义了单时钟;@(clk)定义了DDR时钟(双数据率,两个沿)。
4.2 logic还是wire
在测试平台中,如果用过程赋值语句驱动接口中的信号,那么信号要在接口中定义为logic,如果是连续赋值驱动,定义成wire。
定义成logic的一个好处是,如果多个信号驱动logic,那么编译器会报错,这样你就知道写错了,如果是wire,这个错误就隐藏了。
4.3 对测试平台和DUT中事件的调度
如果没有用时钟块,测试平台对DUT的驱动和采样存在竞争,这是因为测试平台的事件和DUT的事件混合在同一个时间片中。
SV中将测试平台中的事件和DUT中的事件分离。时间片划分:
SV的主要调度区域: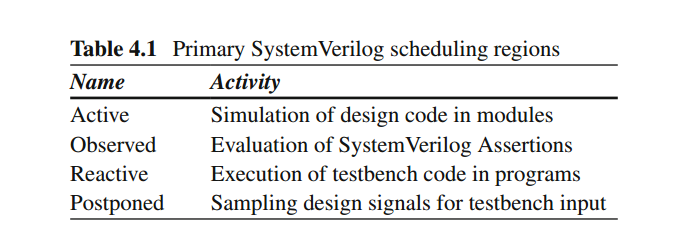
4.4 设计和测试平台之间的时序
时钟块(测试平台)在#1step延时之后采样DUT,也就是采样上一个时间片postponed区域的数据。也就是前面讲的采样旧值。
时钟块(测试平台)在#0延时之后驱动DUT信号。0延迟说明还在同一个time slot,DUT能够捕捉到变化。
更细致的时间片划分:
| time slot | |
|---|---|
| active | design |
| inactive | 显示0延迟阻塞赋值; |
| observed | SVA |
| reactive | SV |
| postponed | SV 采样 |
5. 接口采样和驱动信号的时序
为了同步接口中的信号,可以在时钟沿采样或者驱动接口信号。可以在接口中定义时钟块来同步接口信号:
interface if(input bit clk);logic data;logic valid;logic addr;clocking cb@(posedge clk);input valid;input data;input addr;endclockingmodport TEST(clocking cb);modport DUT(input valid ,input data);
endinterface在测试平台中的信号才需要同步。
5.1 接口信号采样时序
如果时钟块中的信号采样DUT中的信号,采样的是上一个时间片(time slot)postponed区域的数据。即如果DUT信号在时钟沿发生0-1跳变,那么采样到0。DUT接口想要驱动TEST接口中时钟块里的信号,需要先给DUT接口信号赋值:
module dut(if.DUT if0);....#10 if0.valid = 1;#10 if0.valid = 2;....
endmodule
5.2 接口信号驱动时序
如果时钟块驱动DUT信号,值会立即传入到设计中。即如果时钟块中的信号在时钟沿发生0-1跳变,则时钟沿之后DUT中为1。时钟块想要驱动DUT,需要在testbench给时钟块中的信号赋值,在tb中驱动时钟块中的信号需要同步驱动,用“<=”符号。时钟块中的信号驱动采样
program tb(if.TEST if1);...#10 if1.cb.valid <= 1;#10 if1.cb.valid <= 0;...
endprogram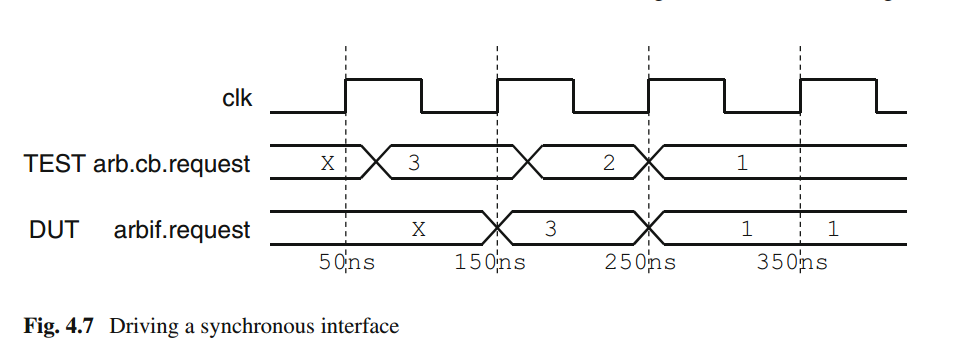
6. 使用虚接口
之前介绍的接口都是跟module一样来描述硬件的;在SV中有面向对象的概念,在class里面使用虚接口——virtual interface。
虚接口是一个物理接口的句柄(handler),同这个句柄来访问硬件接口。虚接口是唯一链接动态对象和静态模块、接口的一种机制。
6.1 在测试平台中使用接口
interface inf; //定义接口
...
endinterface
program test(inf if0); // 接口传入测试平台driver drv;initial begindrv = new(if0); // 接口传给driver对象end
endprogram
class driver;virtual vif; // 在class中为虚接口function new(inf i);vif=i;endfunction
endclass
module top;inf inf0(); // 例化接口test t1(inf0);dut d1(inf0);
endmodule也可以在tb中跨模块引用XMR(cross module reference)接口
program test(); //没有接口参数virtual inf if0=top.inf0;//top是顶层模块...
endprogram
module top;inf inf0(); // 例化接口test t1(); // tb无接口列表dut d1(inf0);
endmodule6.2 使用端口传递接口数组
interface inf(input clk);
...
endinterface
parameter NUM=10;
module top;inf xi[NUM](clk); // 顶层例化多个接口,接口名后跟个数test t1(xi);// 接口作为参数dut...
endmodule
program test(inf xi[NUM]); // 接口参数列表virtual inf vxi[NUM];initial beginvxi=xi;end
endprogram也可以用跨模块引用。
7. 接口中的代码
接口中可以定义信号、函数、任务、class对象,也可以有always,initial语句块。
下面给一个在《UVMPrimer》中的例子:
interface tinyalu_bfm;import tinyalu_pkg::*;
byte unsigned A;byte unsigned B;bit clk;bit reset_n;wire [2:0] op;bit start;wire done;wire [15:0] result;operation_t op_set;
assign op = op_set;
task reset_alu();reset_n = 1'b0;@(negedge clk);@(negedge clk);reset_n = 1'b1;start = 1'b0;endtask : reset_alutask send_op(input byte iA, input byte iB, input operation_t iop, shortint result);if (iop == rst_op) begin@(posedge clk);reset_n = 1'b0;start = 1'b0;@(posedge clk);#1;reset_n = 1'b1;end else begin@(negedge clk);op_set = iop;A = iA;B = iB;start = 1'b1;if (iop == no_op) begin@(posedge clk);#1;start = 1'b0; end else begindo@(negedge clk);while (done == 0);start = 1'b0;endend // else: !if(iop == rst_op)endtask : send_opcommand_monitor command_monitor_h;
function operation_t op2enum();case(op)3'b000 : return no_op;3'b001 : return add_op;3'b010 : return and_op;3'b011 : return xor_op;3'b100 : return mul_op;default : $fatal("Illegal operation on op bus");endcase // case (op)endfunction : op2enum
always @(posedge clk) begin : op_monitorstatic bit in_command = 0;command_s command;if (start) begin : start_highif (!in_command) begin : new_commandcommand.A = A;command.B = B;command.op = op2enum();command_monitor_h.write_to_monitor(command);in_command = (command.op != no_op);end : new_commandend : start_highelse // start lowin_command = 0;end : op_monitor
always @(negedge reset_n) begin : rst_monitorcommand_s command;command.op = rst_op;command_monitor_h.write_to_monitor(command);end : rst_monitorresult_monitor result_monitor_h;
initial begin : result_monitor_threadforever begin@(posedge clk) ;if (done) result_monitor_h.write_to_monitor(result);endend : result_monitor_threadinitial beginclk = 0;forever begin#10;clk = ~clk;endend
endinterface : tinyalu_bfm函数使用的时候通过接口对象调用就行了
virtual tinyalu_bfm inf;
initial begininf.send_op(..);
end8. 接口使用注意事项
-
接口不能在package中被`include 。
下面这种写法是会报错的。
package pkg;`include "apb_if.sv"…… endpackage而要放在package外面
`include "apb_if.sv" package pkg;…… endpackage如果要在UVM中要通过hierarchy访问DUT中的信号,最好将这些信号放在interface中,然后将virtual interface传给UVM
// 在接口中定义信号 interface bfm;bit[7:0 addr; endinterface// 实例化接口 bfm u_bfm();// 将虚接口传给UVM initial beginuvm_config_db#(vitual bfm)::set("", uvm_test_top, "bfm", bfm); end// 在UVM可直接操作虚接口如果不这样的话,当uvm component(driver, monitor, agent等)文件是通过package来管理的话,就不能在UVM中hierarchy引用DUT中的信号。
