c++11 标准模板(STL)(std::basic_stringbuf)(六)
定义于头文件 <sstream>
| template< class CharT, |
std::basic_stringbuf 是关联字符序列为内存常驻的任意字符序列的 std::basic_streambuf 。能从 std::basic_string 的实例初始化它,或将它做成该类的实例。
std::basic_stringbuf 的典型实现保有一个 std::basic_string 类型对象,或等价的可伸缩序列容器作为数据成员,并将它同时用作受控制字符序列(为 std::basic_streambuf 的六个指针所指向的数组)和关联字符序列(所有输入操作的字符源和输出操作的目标)。
另外,典型的实现保有一个 std::ios_base::openmode 类型的数据成员,以指示流的状态(只读、只写、读写、尾端写等)。
| 若 overflow() 使用过分配策略,则可存储另外的高水位指针,以跟踪最后初始化的字符。 | (C++11 起) |
亦提供二个对常用字符类型的特化:
| 类型 | 定义 |
stringbuf | basic_stringbuf<char> |
wstringbuf | basic_stringbuf<wchar_t> |
受保护成员函数
试图以数组替换受控字符序列
std::basic_stringbuf<CharT,Traits,Allocator>::setbuf| protected: |
若 s 为空指针且 n 为零,则此函数无效果。
否则,效果是实现定义的:一些实现不做任何事,而一些实现清空当前用作缓冲区的 std::string 成员,并开始以用户提供的大小为 n ,首元素为 s 所指向的字符数组,为输入/输出字符序列的缓冲区。
此函数为受保护虚,仅可通过 pubsetbuf() 或导出自 std::basic_stringbuf 的用户定义类的成员函数调用它。
参数
| s | - | 指向用户提供缓冲区首个 CharT 的指针或空指针 |
| n | - | 用户提供缓冲区中的 CharT 元素数或零 |
返回值
this 。
注意
弃用的流缓冲 std::strstreambuf 或 boost.IOStreams 设备 boost::basic_array 可用于以可移植方式实现用户提供的字符数组上的 I/O 缓冲。
调用示例
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
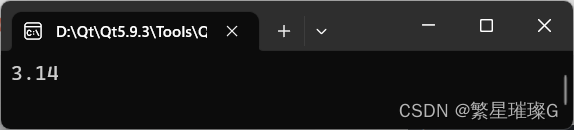
#include <iostream>int main()
{std::stringbuf sbuf;char c[1024] = {};sbuf.pubsetbuf(c, 1024);std::iostream stream(&sbuf);stream << 3.14 << std::endl;std::cout << c << std::endl;return 0;
}输出
用相对寻址,重定位输入序列、输出序列或两者中的下一位置指针
std::basic_stringbuf<CharT,Traits,Allocator>::seekoff| protected: virtual pos_type seekoff(off_type off, |
若可能,则重寻位 std::basic_streambuf::gptr 和/或 std::basic_streambuf::pptr 到对应距流的获取和/或放置区起始、结尾或当前位置准确 off 个字符的位置。
- 若
which包含ios_base::in而此缓冲为读取打开(即 ((which & ios_base::in) == ios_base::in ),则重寻位获取区内的读指针 std::basic_streambuf::gptr 如后述 - 若
which包含ios_base::out而此缓冲为写入打开(即 (which & ios_base::out) == ios_base::out ),则重寻位放置区内的写指针 std::basic_streambuf::pptr 如后述 - 若
which包含ios_base::in和ios_base::out两者而缓冲为读和写打开( (which & (ios_base::in|ios_base::out)) ==(ios_base::in|ios_base::out) )而dir为 ios_base::beg 或 ios_base::end 之一,则重寻位读和写指针如后述。 - 否则,此函数失败。
若重寻位( gptr 或 pptr 或两者),则按下列方式进行:
1) 若要重寻位的指针为空指针且新偏移 newoff 会为非零,则函数失败。
2) 确定 off_type 类型的新指针偏移 newoff
a) 若 dir == ios_base::beg ,则 newoff 为零
b) 若 dir == ios_base::cur ,则 newoff 为指针的当前位置( gptr()-eback() 或 pptr()-pbase() )
c) 若 dir == ios_base::end ,则 newoff 为缓冲区的整个已初始化部分的长度(若使用过分配,则为高水位指针减起始指针)
3) 若 newoff + off < 0 (重寻位会移动指针到缓冲区的起始指针之前)或若 newoff + off 会指向缓冲区结尾后(或若使用过分配,则为缓冲区中最后未初始化字符之后),则函数失败
4) 否则,如同以 gptr() = eback() + newoff + off 或 pptr() = pbase() + newoff + off 赋值指针。
参数
| off | - | 要设置下一位置指针到的相对位置 | ||||||||
| dir | - | 定义应用偏移到的基位置。它能为下列常量之一:
| ||||||||
| which | - | 定义影响的是输入序列、输出序列还是两者。它能为下列常量之一或其组合:
|
返回值
成功时为 pos_type(newoff) ,失败时或若 pos_type 不能表示结果流位置则为 pos_type(off_type(-1)) 。
调用示例
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>// typedef basic_stringbuf<char> stringbuf;
struct mybuf : std::stringbuf
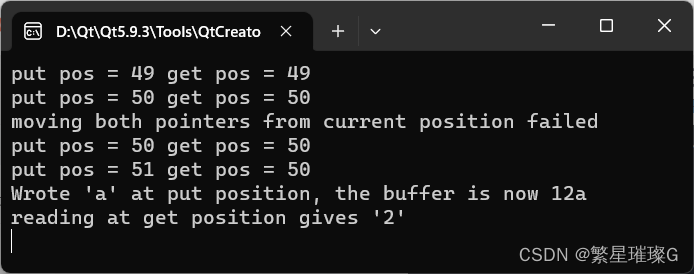
{mybuf(const std::string& new_str,std::ios_base::openmode which =std::ios_base::in | std::ios_base::out): std::stringbuf(new_str, which) {}pos_type tellp(){char ch = *pptr();return ch;}pos_type tellg(){char ch = *gptr();return ch;}};int main()
{mybuf sbuf("123"); // 入/出std::cout << "put pos = " << sbuf.tellp()<< " get pos = " << sbuf.tellg() << std::endl;// 两个指针绝对寻位sbuf.pubseekoff(1, std::ios_base::beg); // 都前移 1std::cout << "put pos = " << sbuf.tellp()<< " get pos = " << sbuf.tellg() << std::endl;// 试图从当前位置前移两个指针 1if (-1 == sbuf.pubseekoff(1, std::ios_base::cur)){std::cout << "moving both pointers from current position failed\n";}std::cout << "put pos = " << sbuf.tellp()<< " get pos = " << sbuf.tellg() << std::endl;// 前移写指针 1 ,但不前移读指// can also be called as ss.seekp(1, std::ios_base::cur);sbuf.pubseekoff(1, std::ios_base::cur, std::ios_base::out);std::cout << "put pos = " << sbuf.tellp()<< " get pos = " << sbuf.tellg() << std::endl;sbuf.sputc('a'); // 写入输出位置std::cout << "Wrote 'a' at put position, the buffer is now "<< sbuf.str() << std::endl;char ch = sbuf.sgetc();std::cout << "reading at get position gives '"<< ch << "'" << std::endl;return 0;
}输出