MyBatis-Plugin源码全面分析
三、MyBatis-Plugin
1. 基本开发方式
需求:在MyBatis执行之前打印一行醒目的日志,携带参数
实现Interceptor接口:
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class,method = "query",args = {MappedStatement.class,Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public class MyPlugin implements Interceptor {private String param;@Overridepublic Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {System.out.println("====================================="+param+"===================================");// 继续执行原始的 SQL 逻辑return invocation.proceed();}@Overridepublic Object plugin(Object target) {return Interceptor.super.plugin(target);}@Overridepublic void setProperties(Properties properties) {this.param = properties.getProperty("log");}
}
修改配置:
<plugins><plugin interceptor="com.mybatis.study.plugin.MyPlugin"><property name="log" value="wz-MyBatis"/></plugin></plugins>
2. Plugin机制与源码
Mybatis插件又称拦截器,Mybatis采用责任链模式,通过动态代理组织多个插件(拦截器),通过这些插件可以改变Mybatis的默认行为(诸如SQL重写之类的),MyBatis 允许你在已映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用。默认情况下,MyBatis 允许使用插件来拦截的方法调用包括:
//拦截执行器中的方法
Executor (update, query, flushStatements, commit, rollback, getTransaction, close, isClosed)//拦截对参数的处理
ParameterHandler (getParameterObject, setParameters)//拦截对结果集的处理
ResultSetHandler (handleResultSets, handleOutputParameters)//拦截SQL构建的处理
StatementHandler (prepare, parameterize, batch, update, query)
2.1 Plugin创建时机
Plugin的创建我们可以追溯到xml的解析,XMLConfigBuilder类中:
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {try {propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));loadCustomVfs(settings);loadCustomLogImpl(settings);typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));//解析插件pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));settingsElement(settings);environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);}}
如果获取到plugins节点,就遍历plugins创建plugin拦截器:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {if (parent != null) {for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();//核心代码Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);//加入到责任链configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);}}}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {//加入到责任链中interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);}2.2 Plugin的使用时机
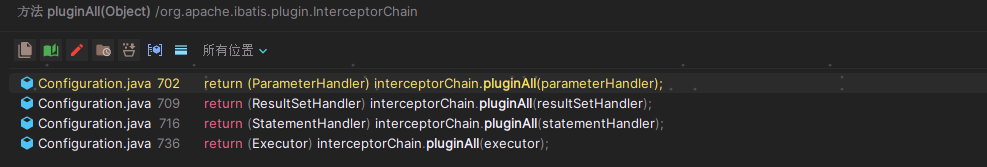
将插件逻辑植入到Executor是发生在InterceptorChain的pluginAll() 方法中。如果在MyBatis的配置文件中配置了插件,那么配置的插件会在加载配置文件的时候被解析成拦截器Interceptor并添加到Configuration的InterceptorChain中。
下面是Executor的创建源码:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;Executor executor;if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);} else {executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);}if (cacheEnabled) {executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);}//将插件逻辑添加到Executor中return (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);}PS:插件的应用位置不同,作用地点也不同:
我们发现,interceptorChain(拦截器链)在Plugin的创建和应用上都起了关键作用,下面来分析一下源码:
public class InterceptorChain {/*** 用于存储拦截器对象的列表*/private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();/*** 用于对目标对象应用所有的拦截器* @param target 目标对象* @return 处理后的目标对象*/public Object pluginAll(Object target) {//遍历拦截器列表,一次对目标对象应用每一个拦截器的plugin方法for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {target = interceptor.plugin(target);}return target;}/*** 向拦截器列表中添加一个拦截器* @param interceptor 拦截器*/public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {interceptors.add(interceptor);}/*** 返回拦截器列表的不可变列表,防止外部修改,保证列表的不可变* @return 不可变列表*/public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);}}
2.3 核心类源码分析
分析了Plugin的创建于使用时机,我们可以清楚的知道,当我们自定义一个拦截器的时候,会将其加入到拦截器链,并执行plugin方法,下面再来看看plugin方法:
default Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}进入到Plugin.wrap静态方法中,该方法的核心作用是:对目标方法进行包装,返回一个代理对象来实现拦截器的功能
/*** 返回代理对象,该代理对象实现了目标对象的接口,并在方法调用时应用拦截器的逻辑(典型的代理设计模式)* @param target 目标对象* @param interceptor 拦截器* @return 代理对象*/public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {//根据拦截器对象生成一个签名映射表,签名映射表将拦截器中定义的拦截方法按照类和方法进行组织,以便快速查找对应的拦截方法// 将插件的@Signature注解内容获取出来并生成映射结构Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);//获取目标对象的类型Class<?> type = target.getClass();//根据目标对象的类型和签名映射表获取所有需要被代理的接口Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);if (interfaces.length > 0) {//为需要被代理的几口创建代理对象。代理方法的调用将被转发到Plugin的实例对象上,Plugin类实现了InvocationHandler接口,负责处理拦截逻辑的执行。return Proxy.newProxyInstance(type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));}//返回目标对象return target;}
下面来看看代理对象的创建逻辑与代理对象中的额外方法都做了什么?从上面创建代理的方法我们可以知道,使用了JDK的动态代理(Proxy.newProxyIntance(ClassLoader,Interface,InvocationHandler)),Plugin类实现了InvocationHandler接口,所以代理的额外方法在invoke中:
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {//根据正在调用的方法的声明类,从签名白哦中获取对应的方法集合Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {//如果方法集合不为空并且包含正在调用的方法,则执行以下代码块。这个判断确保只有在目标对象需要被拦截的方法上才会执行拦截逻辑//创建 Invocation 对象,传入目标对象、正在调用的方法和方法参数,作为拦截器的调用参数。//调用拦截器的 intercept 方法,将 Invocation 对象传入进行拦截逻辑的执行。return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));}//使用反射调用 method.invoke 方法来执行目标对象的方法。return method.invoke(target, args);} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);}}
下面我们来看看Invocation是什么?
public class Invocation {// 插件作用的目标对象(四大对象)private final Object target;// 插件作用的目标方法private final Method method;// 插件作用的目标方法的参数private final Object[] args;public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {this.target = target;this.method = method;this.args = args;}public Object getTarget() {return target;}public Method getMethod() {return method;}public Object[] getArgs() {return args;}// 执行目标方法public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {return method.invoke(target, args);}}
Invocation用于插件获取插件作用的目标对象的信息,包括:作用对象本身,作用的方法和参数,同时Invocation的proceed() 方法可以执行被插件作用的方法。所以插件可以在其实现的intercept() 方法中通过Invocation获取到插件作用目标的完整信息,也可以通过Invocation的proceed() 方法运行作用目标的原本逻辑。
最后在看一下拦截器的接口:
public interface Interceptor {/*** 拦截器在此方法中可以对目标对象的方法进行拦截和修改。* @param invocation 封装了目标对象的信息* @return 处理后的目标对象*/Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;default Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}/*** 接收参数* @param properties 配置信息*/default void setProperties(Properties properties) {// NOP}}
到这里,对于Plugin的创建及使用核心原理应该都已经掌握,那么思考一下,如果是(对同一个组件的)多个插件,如何决定插件的执行顺序呢?
如果定义了多个插件,那么会根据插件在MyBatis配置文件中的声明顺序,一层一层的生成代理对象,比如如下的配置中,先后声明了两个插件。
<plugins><plugin intercepter="插件1"></plugin><plugin intercepter="插件2"></plugin>
</plugins>
那么生成的代理对象可以用下图进行示意。

即为四大对象植入插件逻辑时,是根据声明插件时的顺序从里向外一层一层的生成代理对象,反过来四大对象实际运行时,是从外向里一层一层的调用插件的逻辑。
2.4 Debug 验证
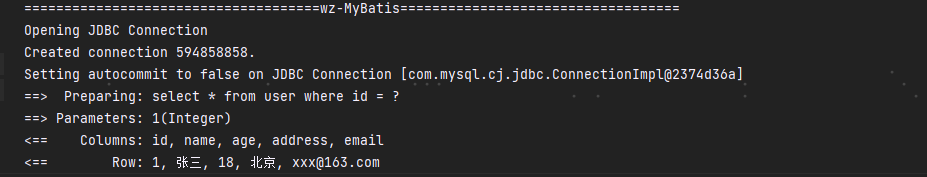
经过上面的源码分析,下面我们来验证一下,首先创建两个插件。最开始我们创建了一个打印日志的插件,下面再创建一个打印参数的插件:
@Intercepts({@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,method = "prepare",args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class ParamPlugin implements Interceptor {@Overridepublic Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(invocation);Object value = metaObject.getValue("target.delegate.parameterHandler.parameterObject");System.out.println("拦截到 prepare 方法,并打印参数:" + value.toString());return invocation.proceed();}
}
并将其在配置文件中注册:
<plugins><plugin interceptor="com.mybatis.study.plugin.MyPlugin"><property name="log" value="wz-MyBatis"/></plugin><plugin interceptor="com.mybatis.study.plugin.ParamPlugin"></plugin></plugins>
下面开始Debug,首先从创建开始:
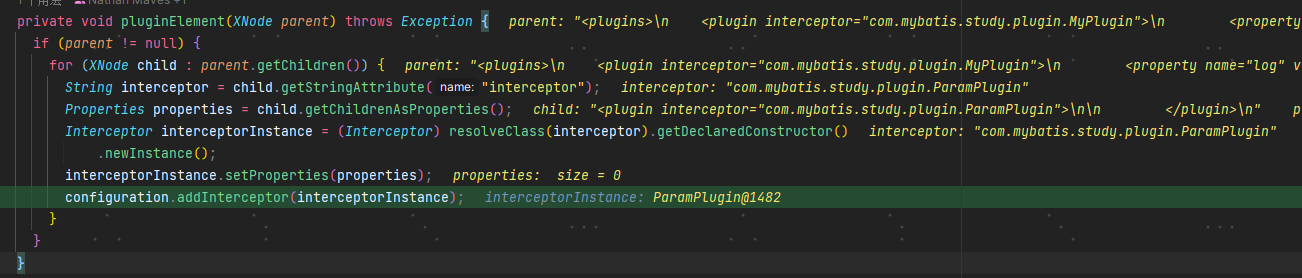
遍历完之后,可以看到拦截链中已经存在:
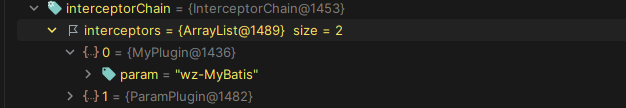
之后,我们再到pluginAll打一个断点,观察到四大组件创建都会进入这里:
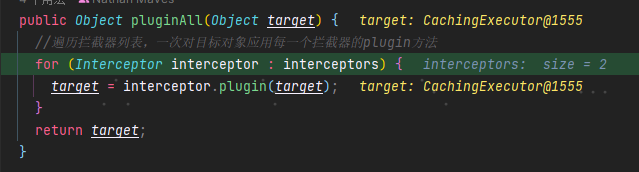
拿到目标对象后,下面进入plugin方法,再进入wrap方法:
这里会判断是不是需要被代理的接口:如果不是(这里paramPlugin插件拦截的是StatementHandler所以不会进入if)就直接return。
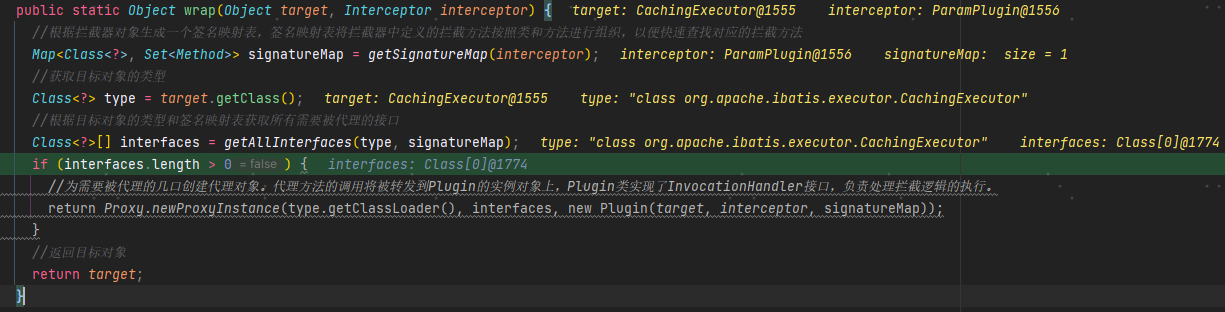
如果需要被代理:则创建代理对象
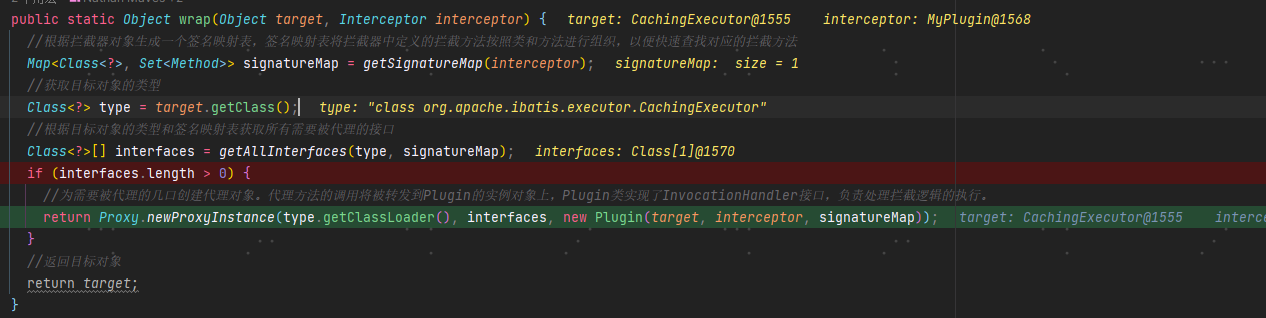
代理对象处理逻辑:
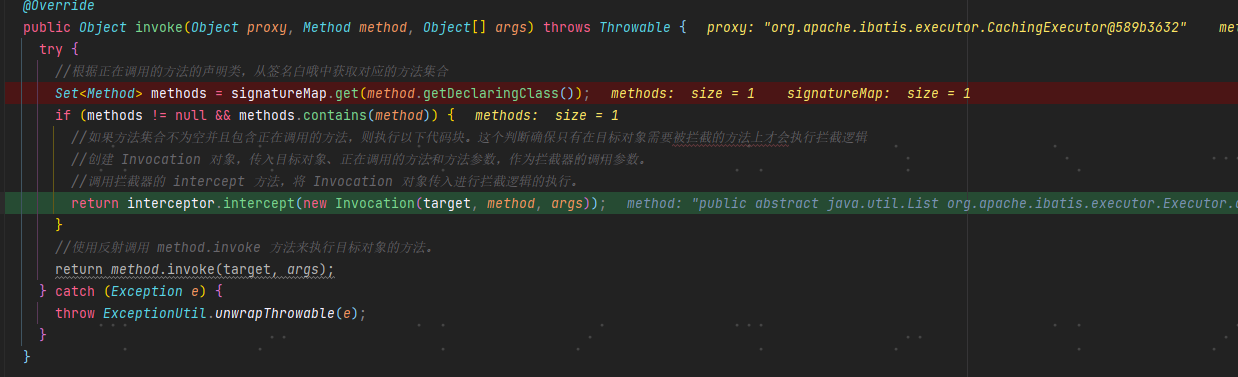
进入intercept方法,可以看到进入了我们自定义的插件中:

到此为止,插件的执行与应用流程就分析完毕了。多个插件会继续从pluginAll中进入循环。