安卓源码分析(10)Lifecycle实现组件生命周期管理
参考:
https://developer.android.google.cn/topic/libraries/architecture/lifecycle?hl=zh-cn#java
https://developer.android.google.cn/reference/androidx/lifecycle/Lifecycle
文章目录
- 1、概述
- 2、LifeCycle类
- 3、LifecycleOwner类
- 4、LifecycleObserver类
1、概述
Android Lifecycle 是一种用于管理 Android 组件(如 Activity 和 Fragment)生命周期的架构组件。Lifecycle 提供了一种在组件生命周期变化时触发相应操作的方式,以帮助开发者编写更加健壮和可维护的代码。
Android 组件的生命周期包括多个阶段,如创建(Create)、启动(Start)、恢复(Resume)、暂停(Pause)、停止(Stop)和销毁(Destroy)。在每个阶段,组件可以执行特定的操作,如初始化界面、加载数据、保存状态等。例如,经典的Activity组件的生命周期图:

使用 Lifecycle 可以将与组件生命周期相关的操作集中到一个地方,并确保这些操作在正确的时机被调用。说白了,就是将生命周期的管理和业务实现分离,抽象成通用的公共组件,以实现代码复用和抽象。
在 Android 框架中定义的大多数应用组件都存在生命周期。生命周期由操作系统或进程中运行的框架代码管理。它们是 Android 工作原理的核心,应用必须遵循它们。如果不这样做,可能会引发内存泄漏甚至应用崩溃。
Lifecycle 提供了以下主要的元素和功能:
- LifecycleOwner: 一个实现了 LifecycleOwner 接口的对象,通常是 Activity 或 Fragment。它负责提供生命周期的状态。
- Lifecycle : 表示一个组件的生命周期状态,如 CREATED、STARTED、RESUMED 等。可以通过 Lifecycle 对象来观察和监听生命周期状态的变化。
- LifecycleObserver: 一个实现了 LifecycleObserver 接口的类,用于观察和响应生命周期事件。
通过使用 Lifecycle,开发者可以避免常见的生命周期相关问题,如内存泄漏、UI 更新异常、数据不一致等。它提供了一种结构化的方式来管理生命周期,并使代码更易于理解、测试和维护。
总之,Android Lifecycle 是一种用于管理 Android 组件生命周期的架构组件,它提供了一套机制和工具来观察、响应和管理组件的状态变化,使开发者能够编写更加可靠和健壮的代码。
2、LifeCycle类
Lifecycle 是一个类,用于存储有关组件(如 activity 或 fragment)的生命周期状态的信息,并允许其他对象观测此状态。
Lifecycle 使用两种主要枚举跟踪其关联组件的生命周期状态:
事件
从框架和 Lifecycle 类分派的生命周期事件。这些事件映射到 activity 和 fragment 中的回调事件。
状态
Lifecycle 对象所跟踪的组件的当前状态。
跟踪生命周期的流程如下:
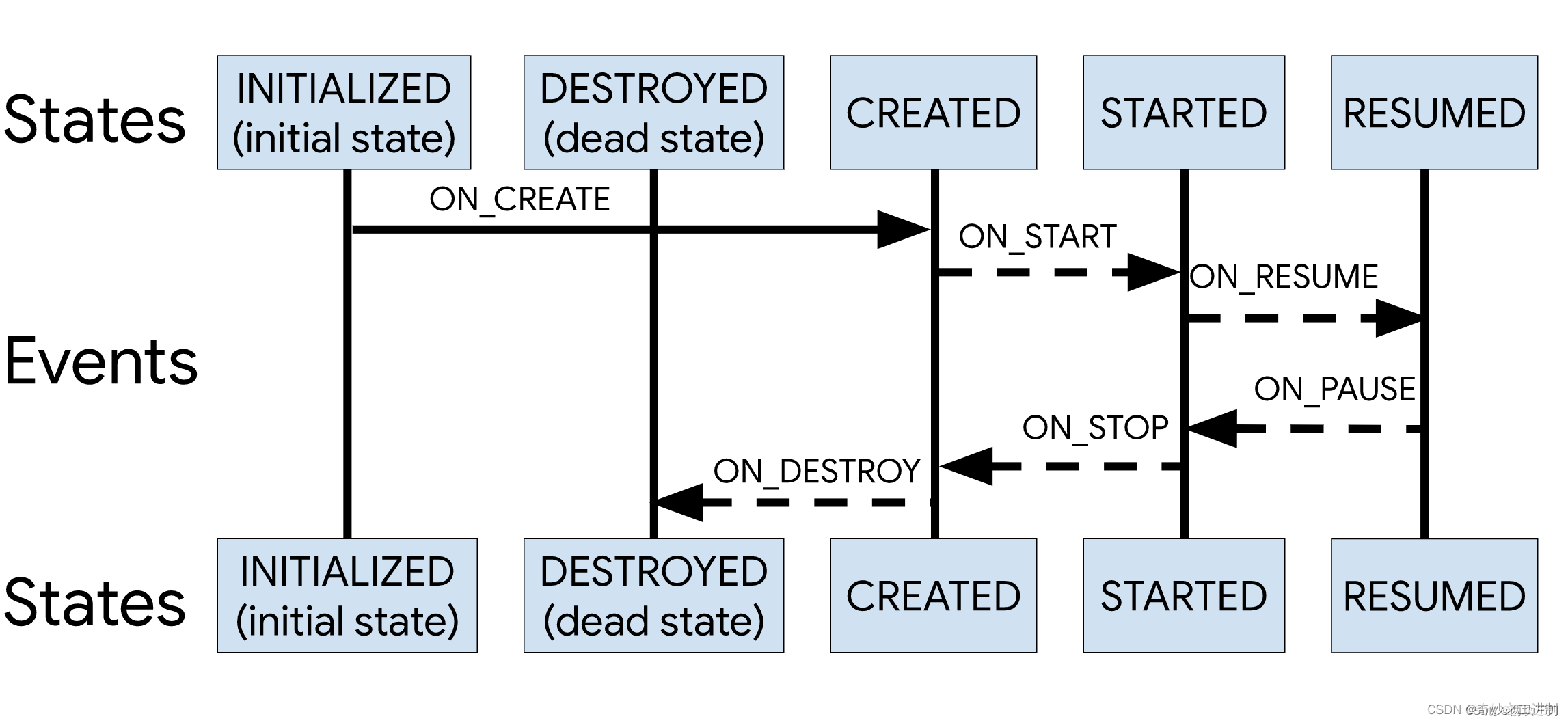
熟悉状态机的同学很容易理解,状态在发生某些事情时就会跃迁到另一个状态,上图的箭头就描述了某些事件发生时状态的跃迁。
LifeCycle定义了以下几种状态:
public enum State {/*** Destroyed state for a LifecycleOwner. After this event, this Lifecycle will not dispatch* any more events. For instance, for an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state is reached* <b>right before</b> Activity's {@link android.app.Activity#onDestroy() onDestroy} call.*/DESTROYED,/*** Initialized state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this is* the state when it is constructed but has not received* {@link android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle) onCreate} yet.*/INITIALIZED,/*** Created state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state* is reached in two cases:* <ul>* <li>after {@link android.app.Activity#onCreate(android.os.Bundle) onCreate} call;* <li><b>right before</b> {@link android.app.Activity#onStop() onStop} call.* </ul>*/CREATED,/*** Started state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state* is reached in two cases:* <ul>* <li>after {@link android.app.Activity#onStart() onStart} call;* <li><b>right before</b> {@link android.app.Activity#onPause() onPause} call.* </ul>*/STARTED,/*** Resumed state for a LifecycleOwner. For an {@link android.app.Activity}, this state* is reached after {@link android.app.Activity#onResume() onResume} is called.*/RESUMED;/*** Compares if this State is greater or equal to the given {@code state}.** @param state State to compare with* @return true if this State is greater or equal to the given {@code state}*/public boolean isAtLeast(@NonNull State state) {return compareTo(state) >= 0;}}
定义的事件如下:
public enum Event {/*** Constant for onCreate event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_CREATE,/*** Constant for onStart event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_START,/*** Constant for onResume event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_RESUME,/*** Constant for onPause event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_PAUSE,/*** Constant for onStop event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_STOP,/*** Constant for onDestroy event of the {@link LifecycleOwner}.*/ON_DESTROY,/*** An {@link Event Event} constant that can be used to match all events.*/ON_ANY;
LifeCycle除了提供了生命周期的记录,还提供了观测的方法,采用了设计模式观察者模式,
/*** Adds a LifecycleObserver that will be notified when the LifecycleOwner changes* state.* <p>* The given observer will be brought to the current state of the LifecycleOwner.* For example, if the LifecycleOwner is in {@link State#STARTED} state, the given observer* will receive {@link Event#ON_CREATE}, {@link Event#ON_START} events.** @param observer The observer to notify.*/@MainThreadpublic abstract void addObserver(@NonNull LifecycleObserver observer);/*** Removes the given observer from the observers list.* <p>* If this method is called while a state change is being dispatched,* <ul>* <li>If the given observer has not yet received that event, it will not receive it.* <li>If the given observer has more than 1 method that observes the currently dispatched* event and at least one of them received the event, all of them will receive the event and* the removal will happen afterwards.* </ul>** @param observer The observer to be removed.*/@MainThreadpublic abstract void removeObserver(@NonNull LifecycleObserver observer);
想要观测该状态,需要被Lifecycle添加为观察者,当然也可以移除解除通知。
同时提供了一个供外部查询当前状态的接口:
/*** Returns the current state of the Lifecycle.** @return The current state of the Lifecycle.*/@MainThread@NonNullpublic abstract State getCurrentState();
3、LifecycleOwner类
LifecycleOwner只是个简单的接口类,定义了一个获取Lifecycle的方法。
public interface LifecycleOwner {/*** Returns the Lifecycle of the provider.** @return The lifecycle of the provider.*/@NonNullLifecycle getLifecycle();
}
想要拥有生命周期管理的组件只要实现该接口即可。
像ComponentActivity就继承于该接口。
4、LifecycleObserver类
Lifecycle是一个被观测对象,自然要有观察者,即关心生命周期变化的人。提供了LifecycleObserver 类用于观测Lifecycle,学java的都知道,java就喜欢极度抽象,LifecycleObserver 是个空接口类,啥都没有。
public interface LifecycleObserver {}
观察者的接口自然是观测Lifecyle状态变化,onXXX习惯用于表达XXX事件发生时的回调。
表达事件/状态变化可以有两种表达方式,一种是穷举出所有的事件,一种是通过形参表达,android两种形式都提供了:
FullLifecycleObserver 穷举定义了所有事件回调:
interface FullLifecycleObserver extends LifecycleObserver {void onCreate(LifecycleOwner owner);void onStart(LifecycleOwner owner);void onResume(LifecycleOwner owner);void onPause(LifecycleOwner owner);void onStop(LifecycleOwner owner);void onDestroy(LifecycleOwner owner);
}
通过函数形参区分不同事件的接口定义LifecycleEventObserver :
/*** Class that can receive any lifecycle change and dispatch it to the receiver.* <p>* If a class implements both this interface and* {@link androidx.lifecycle.DefaultLifecycleObserver}, then* methods of {@code DefaultLifecycleObserver} will be called first, and then followed by the call* of {@link LifecycleEventObserver#onStateChanged(LifecycleOwner, Lifecycle.Event)}* <p>* If a class implements this interface and in the same time uses {@link OnLifecycleEvent}, then* annotations will be ignored.*/
public interface LifecycleEventObserver extends LifecycleObserver {/*** Called when a state transition event happens.** @param source The source of the event* @param event The event*/void onStateChanged(@NonNull LifecycleOwner source, @NonNull Lifecycle.Event event);
}
注释里提到,如果一个Observer同时实现了这两种形式的接口,FullLifecycleObserver的相应接口会先被调用,其次才是onStateChanged这个接口。
同时还定义了一个空实现的DefaultLifecycleObserver,这样我们可以根据需要,override部分接口。
在最后,我们补全一张类图:
