【C++初阶】string类的常见基本使用

👦个人主页:@Weraphael
✍🏻作者简介:目前学习C++和算法
✈️专栏:C++航路
🐋 希望大家多多支持,咱一起进步!😁
如果文章对你有帮助的话
欢迎 评论💬 点赞👍🏻 收藏 📂 加关注✨
目录
- 一、什么是STL
- 二、string类概念总结
- 三、string类的常用接口(重点)
- 3.1 常见的四种构造(初始化)
- 3.2 常见容量操作
- 3.2.1 size
- 3.2.2 empty
- 3.2.3 clear
- 四、string类对象的修改操作
- 4.1 push_back
- 4.2 append
- 4.3 运算符重载+=
- 4.4 insert
- 4.5 erase
- 4.6 swap
- 4.7 c_str
- 4.8 find
- 4.9 pop_back
- 4.10 substr
- 4.11 rfind
- 4.12 operator+
- 五、迭代器iterator
- 5.1 什么是迭代器
- 5.2 常见的string类迭代器
- 5.2.1 begin
- 5.2.2 end
- 5.2.3 rbegin + rend --- 反向迭代器
- 5.2.4 const修饰的对象
- 六、string类遍历操作
- 6.1 string的底层重载operator[]
- 6.2 迭代器遍历
- 6.3 语法糖(范围for)
- 6.4 补充:迭代器的意义
- 七、string的读入与输出
- 7.1 getline - 输入
- 7.2 puts - 输出
- 八、string转化为其他类型
- 九、其他类型转string
一、什么是STL
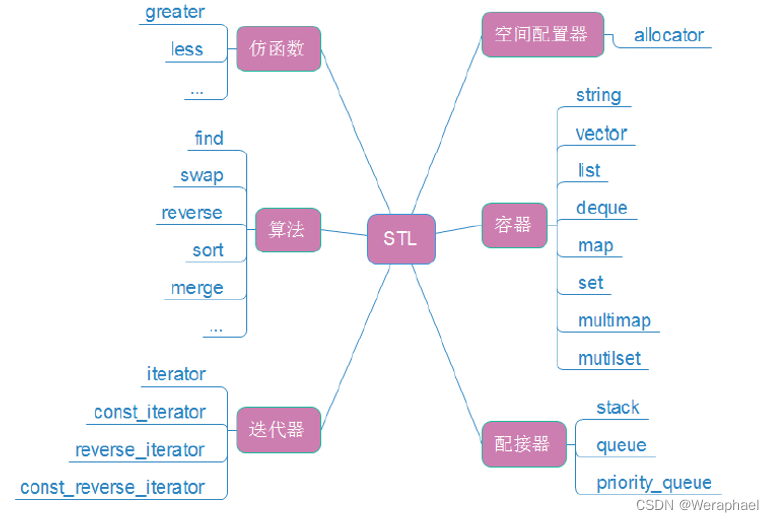
STL(standard template libaray - 标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的组件库,而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架。
STL的六大组件:
二、string类概念总结
-
string是一个管理字符数组的类 -
该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门的函数用来操作
string的常规操作。例如:push_back等(后面会详细介绍) -
string在底层实际是:basic_string;模板类的别名:typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string -
在使用
string类时,必须包含头文件#include <string>
三、string类的常用接口(重点)
3.1 常见的四种构造(初始化)
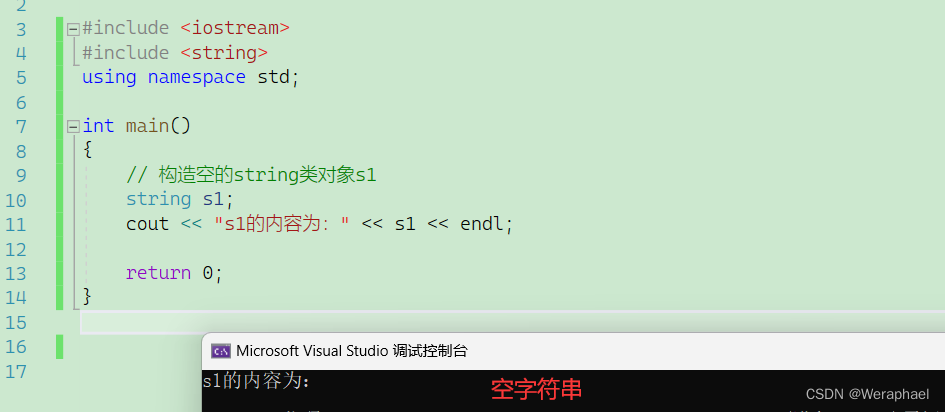
- 构造空的
string类对象,即空字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 构造空的string类对象s1string s1;cout << "s1的内容为:" << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
- 用
C语言的格式字符串来构造string类对象
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
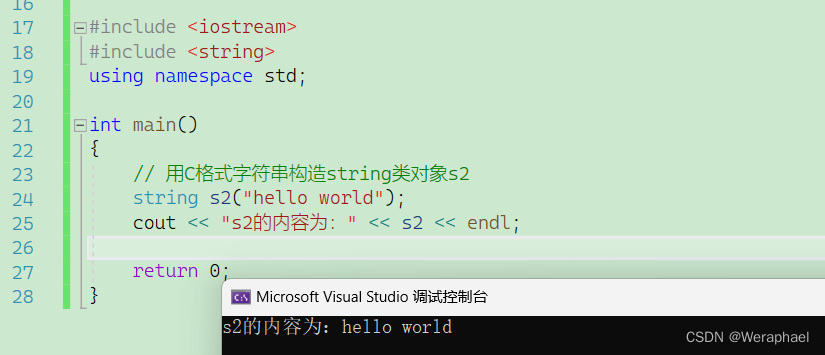
{// 用C格式字符串构造string类对象s2string s2("hello world");cout << "s2的内容为:" << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
- 拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
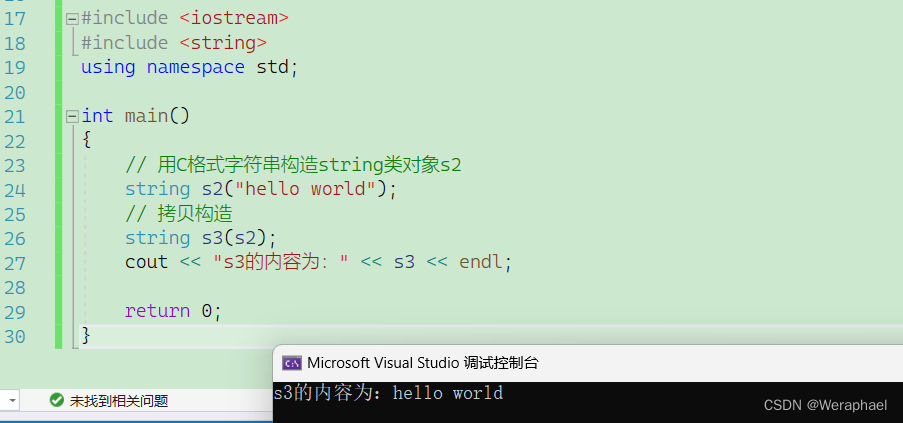
{// 用C格式字符串构造string类对象s2string s2("hello world");// 拷贝构造string s3(s2);cout << "s3的内容为:" << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
string类支持赋值运算符重载=
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
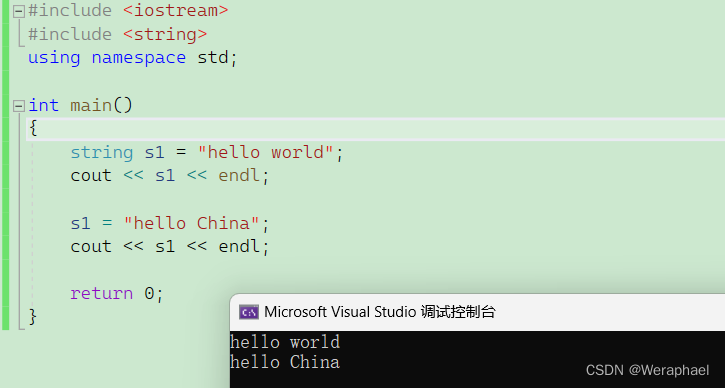
{string s1 = "hello world";cout << s1 << endl;s1 = "hello China";cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
3.2 常见容量操作
3.2.1 size
返回字符串的有效长度(不包含
'\0')
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
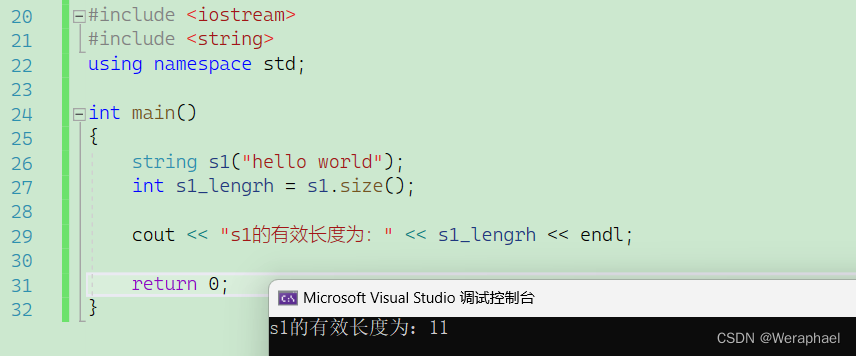
{string s1("hello world");int s1_lengrh = s1.size();cout << "s1的有效长度为:" << s1_lengrh << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
注意:
'\0’是标识字符串结束的特殊字符,不算有效字符!
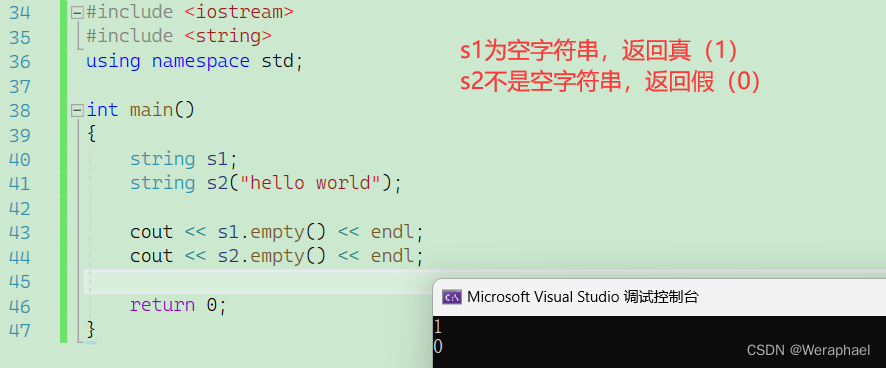
3.2.2 empty
检测字符是否为空字符串。如果是空字符串返回
true,否则返回false
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;string s2("hello world");cout << s1.empty() << endl;cout << s2.empty() << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
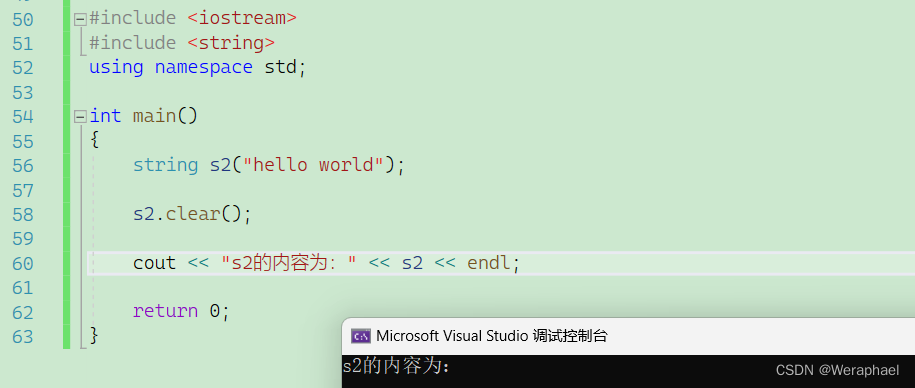
3.2.3 clear
清空有效字符
clear
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s2("hello world");s2.clear();cout << "s2的内容为:" << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
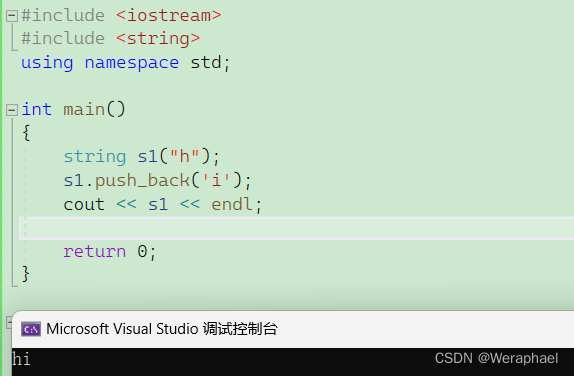
四、string类对象的修改操作
4.1 push_back
功能:尾插一个字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("h");s1.push_back('i');cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
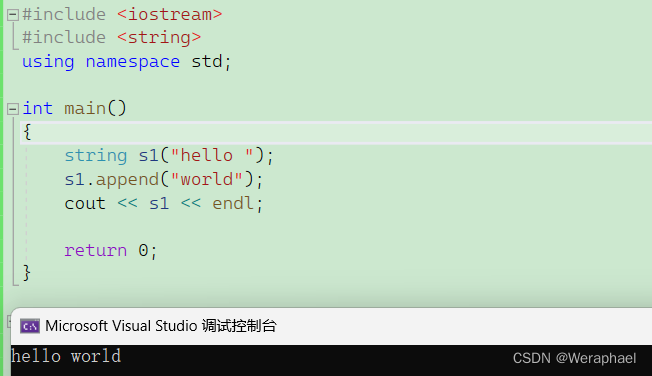
4.2 append
功能:尾插字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello ");s1.append("world");cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
4.3 运算符重载+=
既可以尾插一个字符,也能尾插一个字符串。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
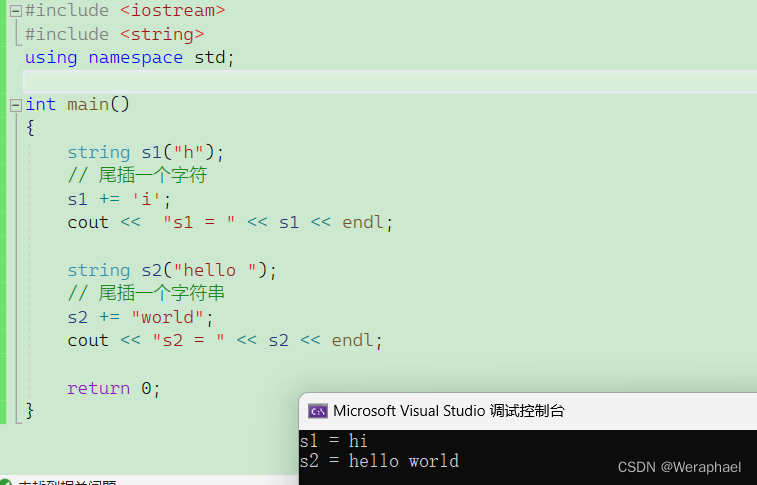
{string s1("h");// 尾插一个字符s1 += 'i';cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;string s2("hello ");// 尾插一个字符串s2 += "world";cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
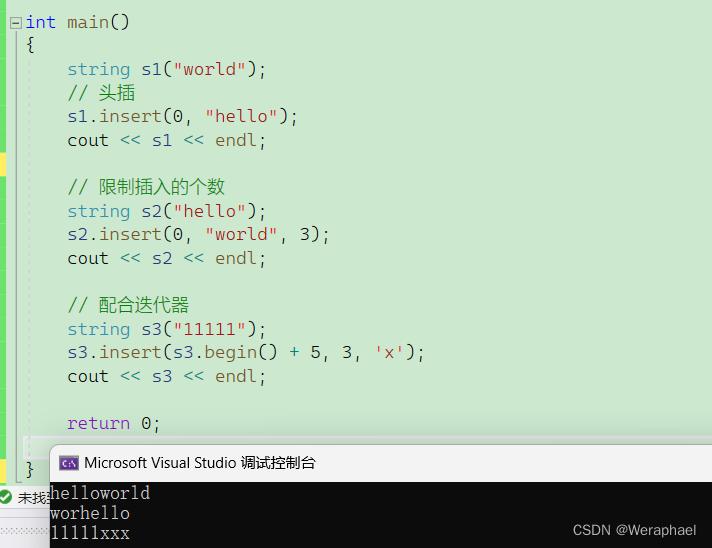
4.4 insert
- 功能:插入字符或者字符串
- 缺点:效率低,特别是头插
【代码示例】
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("world");// 头插s1.insert(0, "hello");cout << s1 << endl;// 限制插入的个数string s2("hello");s2.insert(0, "world", 3);cout << s2 << endl;// 配合迭代器string s3("11111");// 尾插3个xs3.insert(s3.begin() + 5, 3, 'x');cout << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
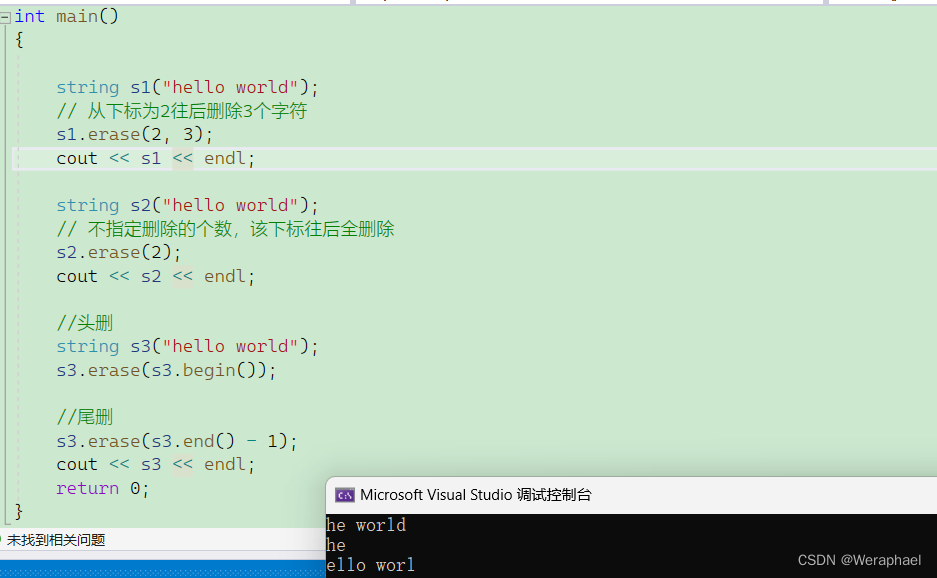
4.5 erase
功能:删除某个位置的字符或者字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");// 从下标为2往后删除3个字符s1.erase(2, 3);cout << s1 << endl;string s2("hello world");// 不指定删除的个数,该下标往后全删除s2.erase(2);cout << s2 << endl;//头删string s3("hello world");s3.erase(s3.begin());//尾删s3.erase(s3.end() - 1);cout << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
4.6 swap
功能:交换
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello");string s2("world");s1.swap(s2);cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】

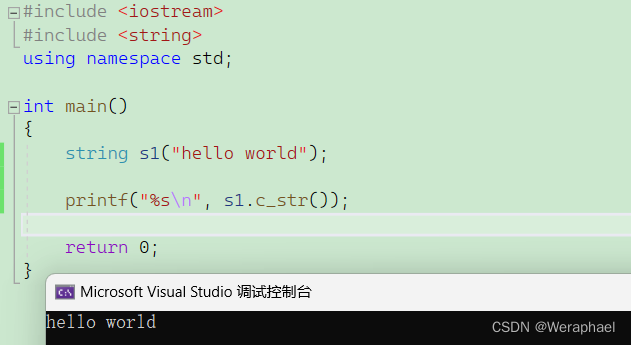
4.7 c_str
功能:将
string转化为C字符串。
比如printf只能打印内置类型,如果想打印string类型,需要使用c_str
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");printf("%s\n", s1.c_str());return 0;
}
【输出结果】
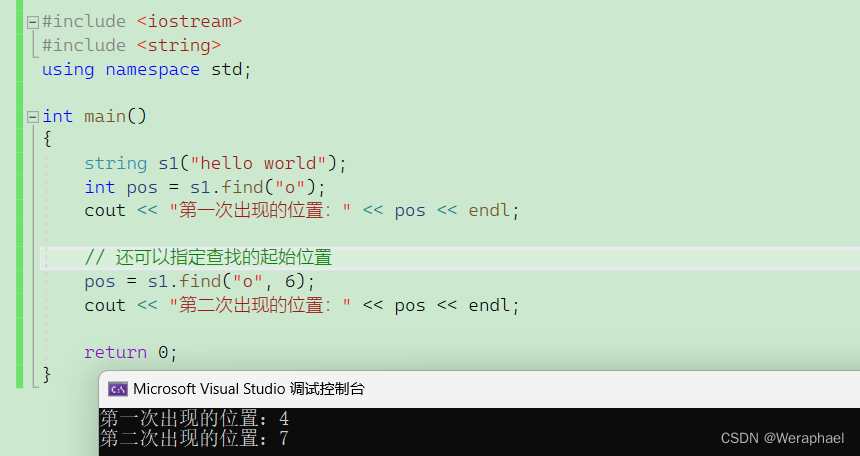
4.8 find
功能:查找字符。找到第一次出现的字符下标,如果没有找到会返回
npos,本质就是-1。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");int pos = s1.find("o");cout << "第一次出现的位置:" << pos << endl;// 还可以指定查找的起始位置pos = s1.find("o", 6);cout << "第二次出现的位置:" << pos << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
4.9 pop_back
功能:尾删一个字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1.pop_back();cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】

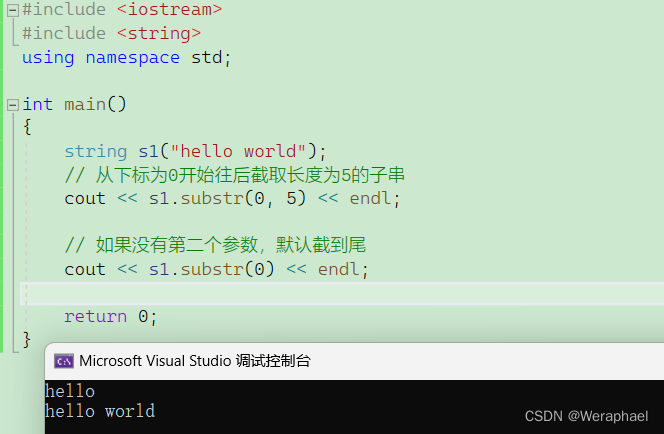
4.10 substr
功能:截取子串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");// 从下标为0开始往后截取长度为5的子串cout << s1.substr(0, 5) << endl;// 如果没有第二个参数,默认截到尾cout << s1.substr(0) << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
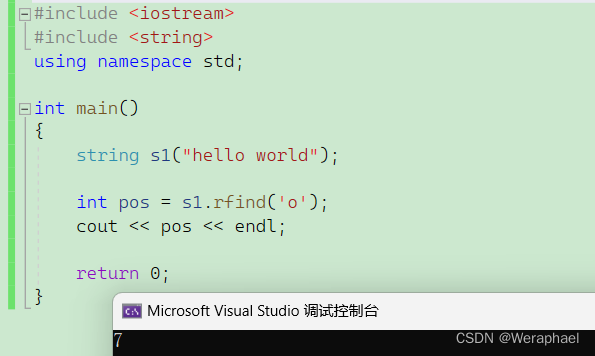
4.11 rfind
功能:从字符串的后面开始往前找第一次出现的字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");int pos = s1.rfind('o');cout << pos << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
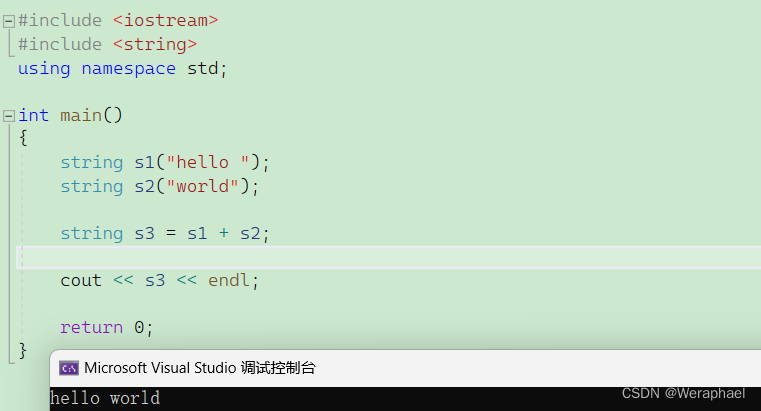
4.12 operator+
string类重载了运算符+,可以拼接2个字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello ");string s2("world");string s3 = s1 + s2;cout << s3 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
五、迭代器iterator
5.1 什么是迭代器
现阶段可以理解迭代器是像指针一样的类型,但也有可能是指针,也有可能不是指针。
string迭代器的语法形式:
// string::iterator是类型
// it是变量名
string::iterator it = xxx;
5.2 常见的string类迭代器
5.2.1 begin
【文档描述】

【代码演示】
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
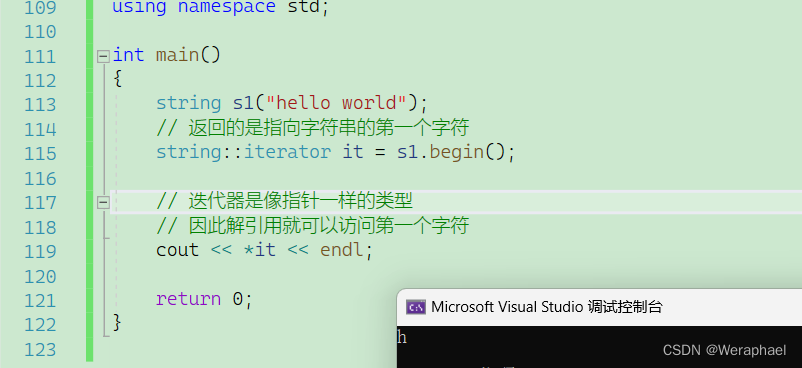
{string s1("hello world");// 返回的是指向字符串的第一个字符string::iterator it = s1.begin();// 迭代器是像指针一样的类型// 因此解引用就可以访问第一个字符cout << *it << endl;return 0;
}
【程序结果】
5.2.2 end
【文档描述】

【代码示例】
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
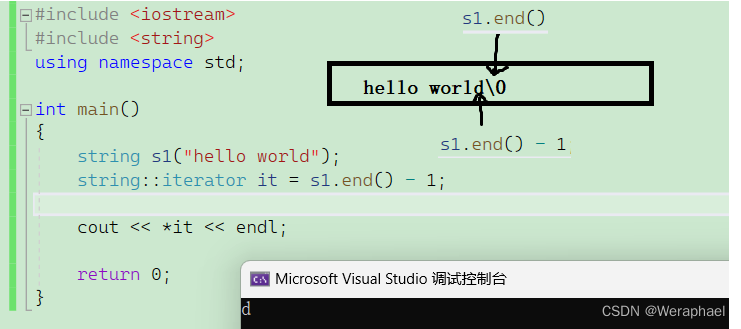
{string s1("hello world");string::iterator it = s1.end() - 1;cout << *it << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
5.2.3 rbegin + rend — 反向迭代器
【文档描述】

【代码示例】
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();while (rit != s1.rend()){cout << *rit;rit++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】

注:如果觉得
string::reverse_iterator太长,可以使用auto代替。
5.2.4 const修饰的对象
注:
const修饰的对象不能用普通迭代器
看看以下代码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;void print(const string& s)
{string::iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit;sit++;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{string s1("hello world");//封装print函数来打印print(s1);return 0;
}
【错误报告】

const修饰的对象只能用const的迭代器
【正确代码】
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;void print(const string& s)
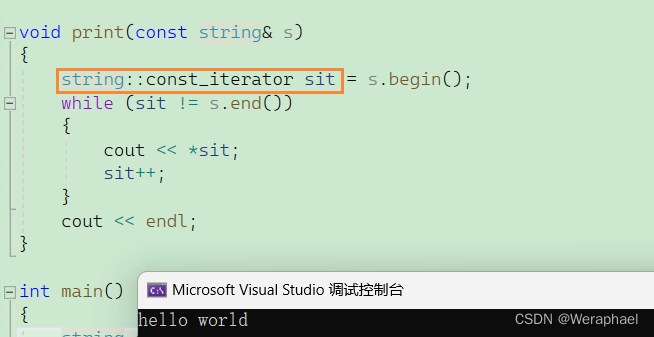
{string::const_iterator sit = s.begin();while (sit != s.end()){cout << *sit;sit++;}cout << endl;
}int main()
{string s1("hello world");//封装print函数来打印print(s1);return 0;
}
【输出结果】
六、string类遍历操作
因为
string底层是支持流提取>>,用cout就可以直接打印string字符串的内容,但是打印的结果比较固定。因此以下三种方式既可以访问遍历,也可以对其内容修改打印。
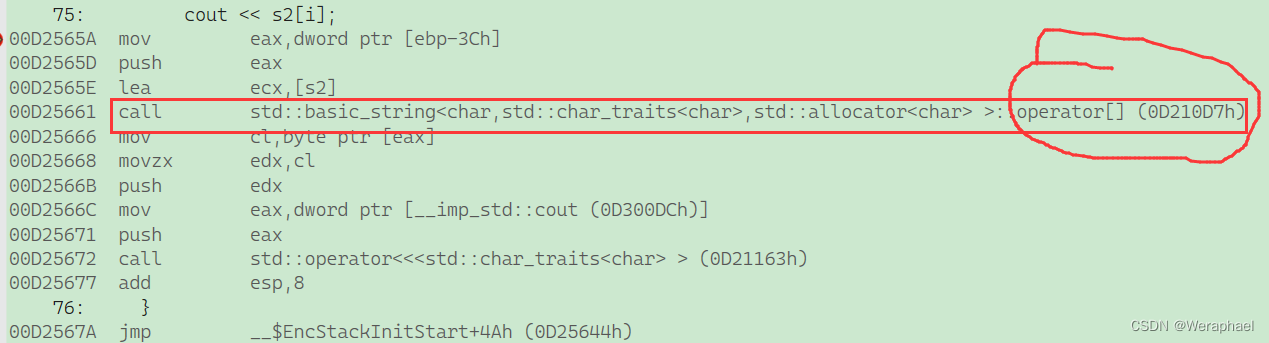
6.1 string的底层重载operator[]
相当于数组下标的访问
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
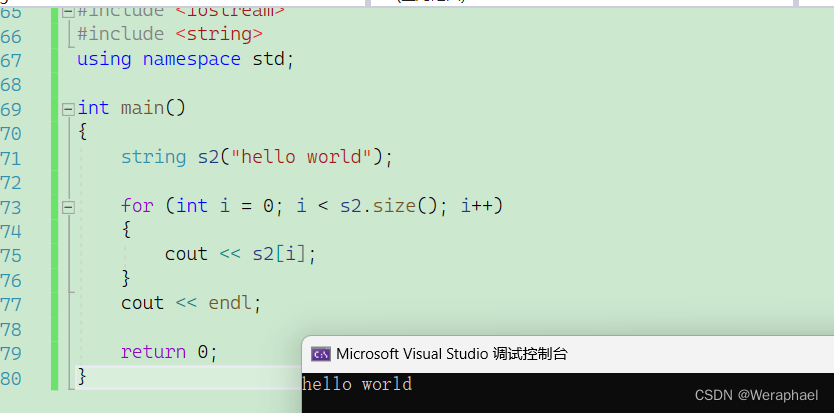
{string s2("hello world");for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){// 遍历string字符串cout << s2[i];}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
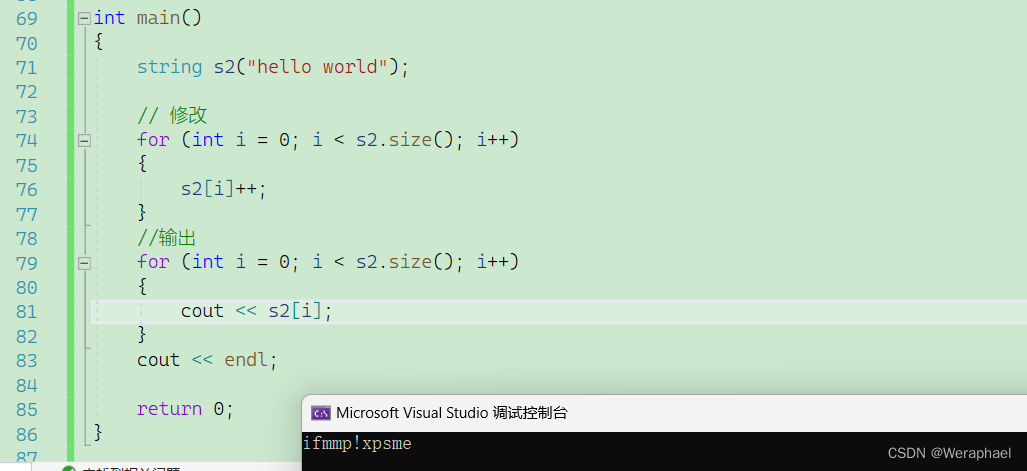
当然还可以对字符串进行修改
以下是将字符串的内容都+1
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s2("hello world");// 修改for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){s2[i]++;}// 输出for (int i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){cout << s2[i];}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
注意:这里需要区分
string和普通数组
s2[i]的底层是调用s2.operator[](i)函数
- 普通数组的底层是解引用操作
char ch1[] = "abcdef";ch1[0];// 访问下标为0的元素
ch1[0]的底层含义是:*(ch1 + 0)
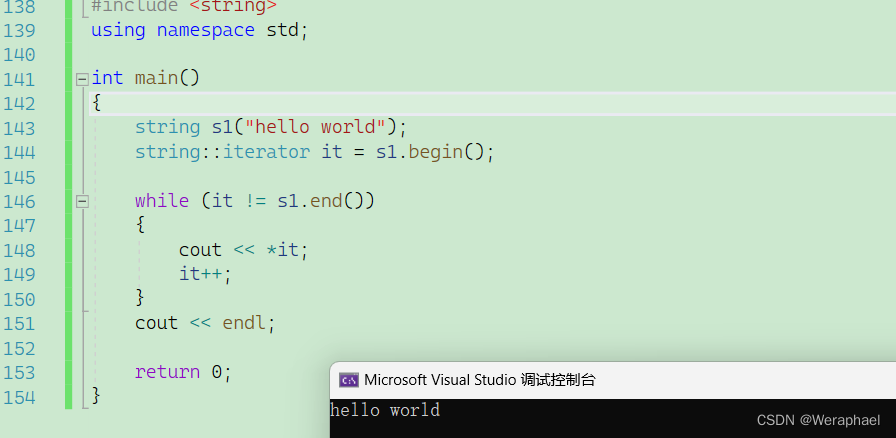
6.2 迭代器遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it;it++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【程序结果】
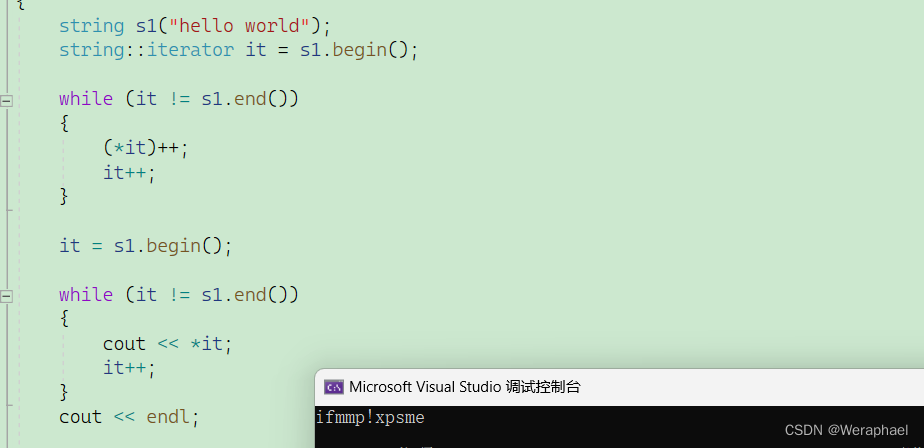
当然也可以对字符串的内容进行修改
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::iterator it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){(*it)++;it++;}it = s1.begin();while (it != s1.end()){cout << *it;it++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
在这里就有的人想,迭代器的代码要写这么多,还不如用下标来访问。所以,迭代器的意义是什么呢? 让我们接着往下看
6.3 语法糖(范围for)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
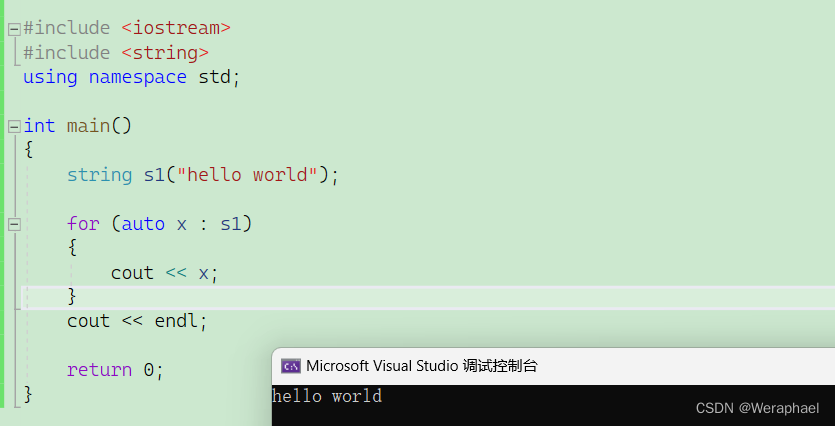
{string s1("hello world");for (auto x : s1){cout << x;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
范围for同样支持修改
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");// 修改for (auto& x : s1){x++;}// 输出结果for (auto x : s1){cout << x;}cout << endl;return 0;
}【输出结果】
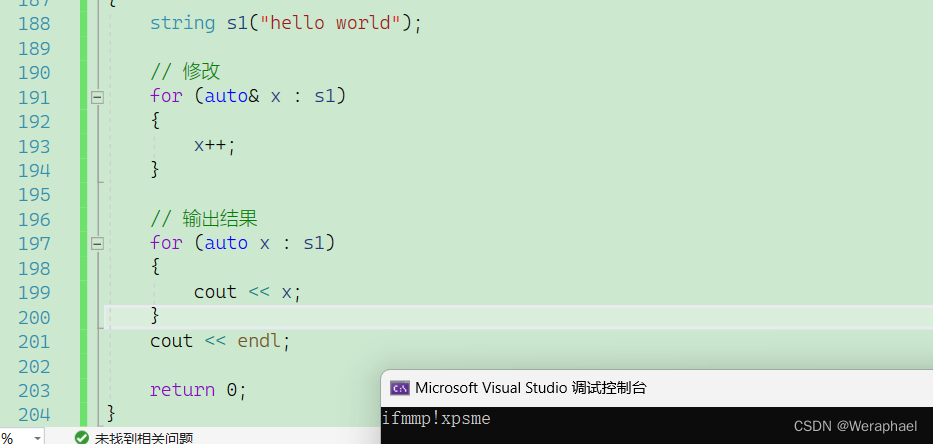
范围
for虽然很香,但是有个致命的缺点:**不能倒着遍历,只有反向迭代器可以倒着遍历。 **
6.4 补充:迭代器的意义
范围for又和迭代器有啥关系呢?迭代器的意义又是什么呢?
- 其实,范围
for代码短,之所以是这么好用是因为:范围for的底层就是用迭代器实现的!!!
我们可以利用反汇编来看看代码底层:
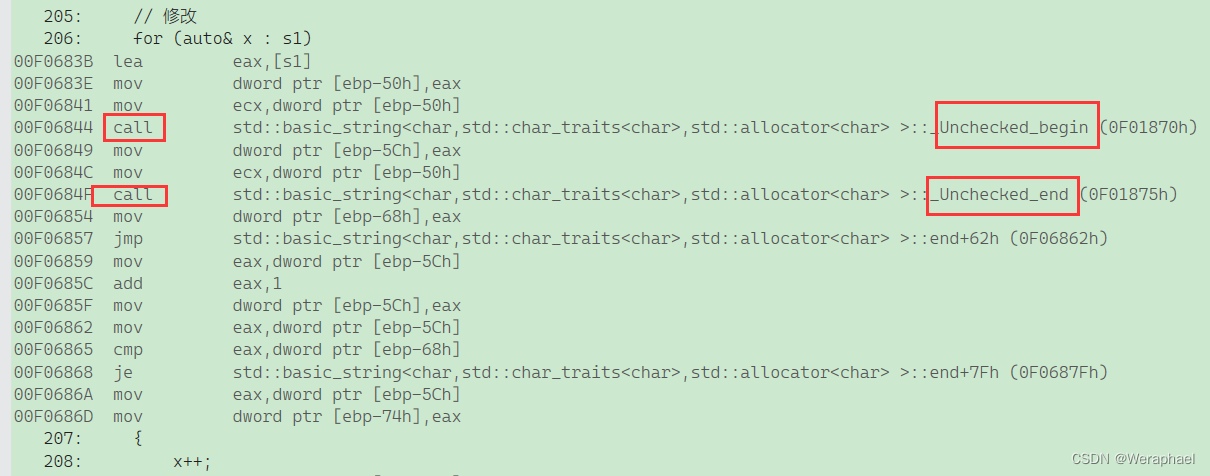
范围for的底层就是调用了begin和end。
- 迭代器提供了一种统一的方式访问和修改容器的数据
以下以vector容器为例
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v;// 尾插数据v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);// 迭代器vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin();while (vit != v.end()){cout << *vit << ' ';vit++;}cout << endl;// 范围forfor (auto e : v){cout << e << ' ';}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
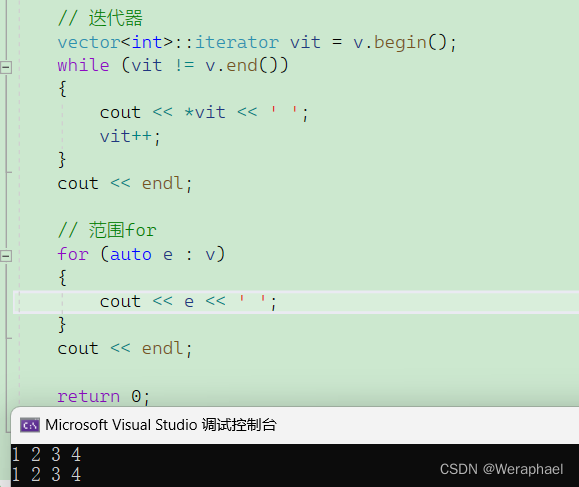
如果一个容器支持迭代器,那么它必定支持访问
for,反之就不一定了。
这里再提一嘴,很多人认为下标访问是主流,但是使用下标访问的空间必须是连续的,所以当我拿出链表,阁下又该如何应对呢?因此迭代器是可以访问链表的。
- 迭代器可以和算法配合使用
这里给大家介绍一个浅浅介绍一个算法(后序会补充),-- sort
【文档描述】

【代码演示】
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> // 算法库头文件
using namespace std;int main()
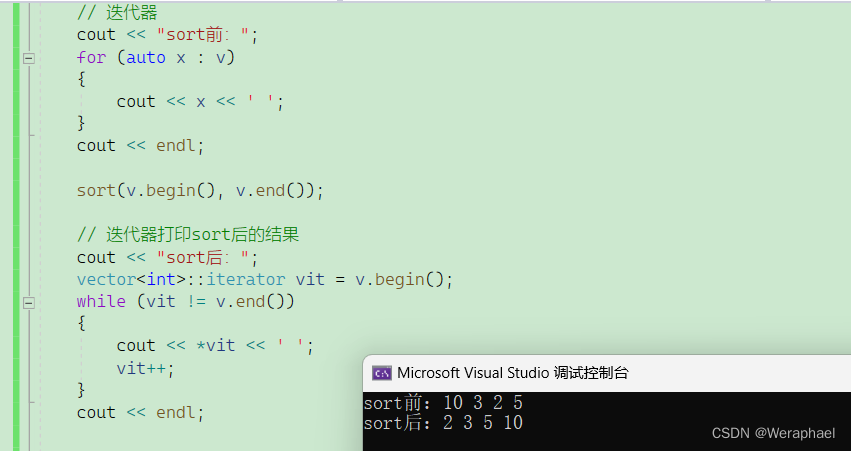
{vector<int> v;// 尾插数据v.push_back(10);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(5);// 迭代器cout << "sort前:";for (auto x : v){cout << x << ' ';}cout << endl;sort(v.begin(), v.end());// 迭代器打印sort后的结果cout << "sort后:";vector<int>::iterator vit = v.begin();while (vit != v.end()){cout << *vit << ' ';vit++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
【程序结果】
七、string的读入与输出
7.1 getline - 输入
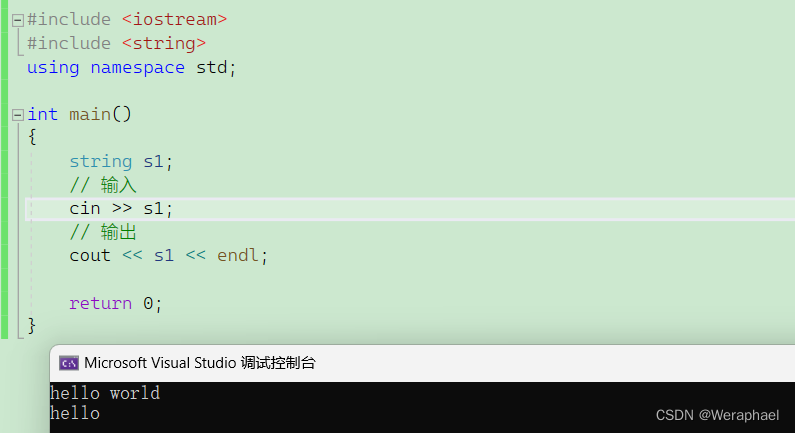
注意:cin和scanf读取到空格或者回车就不再往后读取了
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;// 输入cin >> s1;// 输出cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
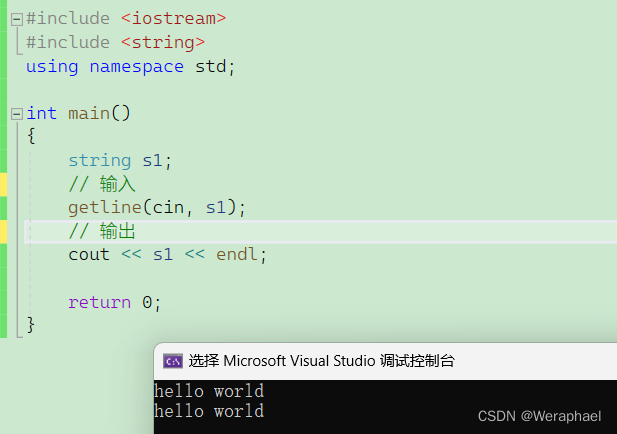
而getline可以读入空格
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;// 输入getline(cin, s1);// 输出cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
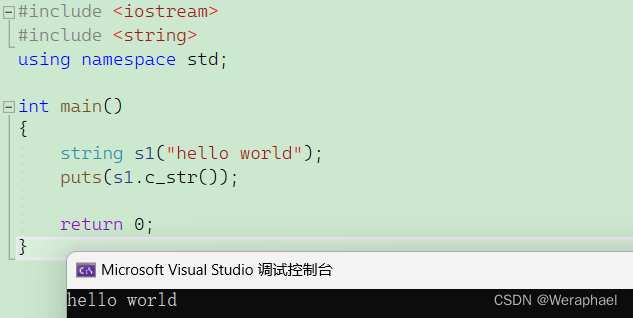
7.2 puts - 输出
因为
string类重载了流插入<<和流提取>>,因此可以支持cin和cout的输入输出。除此之外还能用puts来输出string类的字符串(自带换行的)。注意:puts和printf只能打印内置类型的字符串,因此可以用c_str转化为C语言的字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{string s1("hello world");puts(s1.c_str());return 0;
}
【输出结果】
八、string转化为其他类型
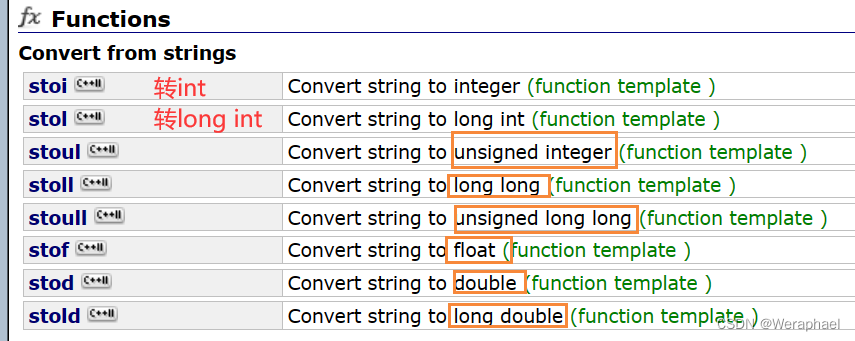
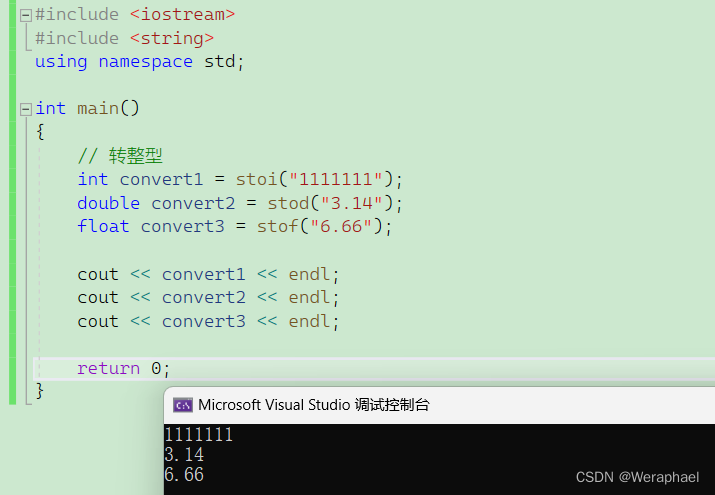
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 转整型int convert1 = stoi("1111111");double convert2 = stod("3.14");float convert3 = stof("6.66");cout << convert1 << endl;cout << convert2 << endl;cout << convert3 << endl;return 0;
}
【输出结果】
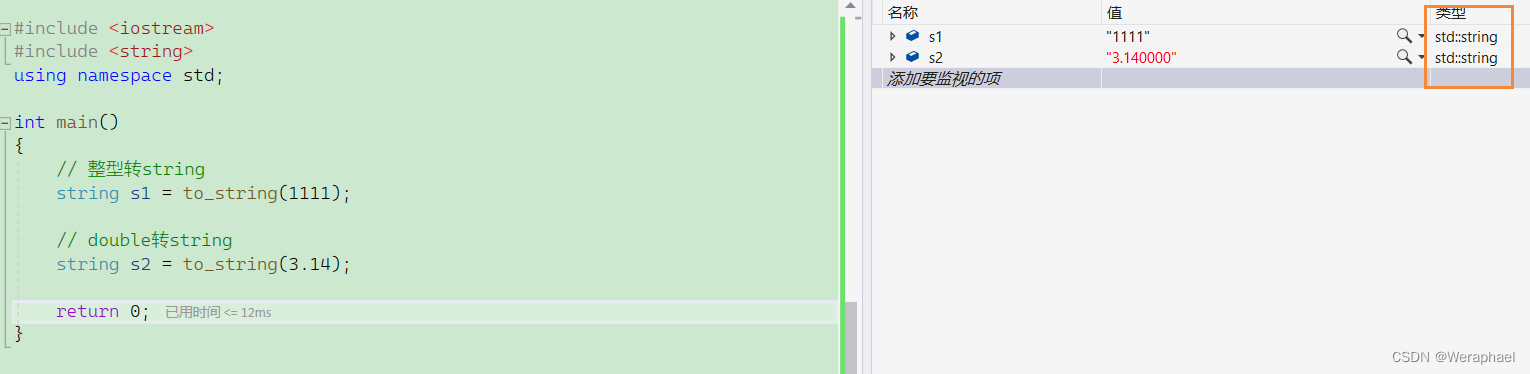
九、其他类型转string

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 整型转stringstring s1 = to_string(1111);// double转string string s2 = to_string(3.14);return 0;
}
【输出结果】