C++---list常用接口和模拟实现
list---模拟实现
- list的简介
- list函数的使用
- 构造函数
- 迭代器的使用
- list的capacity
- list element access
- list modifiers
- list的模拟实现
- 构造函数,拷贝构造函数和=
- 迭代器
- begin和end
- insert和erase
- clear和析构函数
- 源码
list的简介
list是用双向带头联表实现的一个容器,双向联表中每个元素存在互不相关的独立节点中,再节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素,并且可以再常数范围内再任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器。
list函数的使用
构造函数
| 构造函数( (constructor)) | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list |
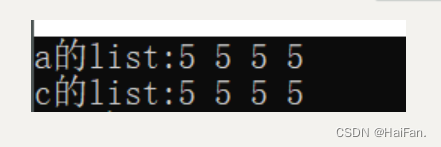
void ListTest2()
{std::list<int> a(4, 5);std::cout << "a的list" << ':';for (auto& e : a){std::cout << e << ' ';}std::cout << std::endl;std::list<int> b;//Emptystd::list<int> c(a.begin(), a.end());std::cout << "c的list" << ':';for (auto& e : c){std::cout << e << ' ';}}
迭代器的使用
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| begin + end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的 reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |
std::list<int> a(4, 5);std::cout << "a的list" << ':';std::list<int>::iterator it = a.begin();while (it != a.end()){std::cout << *it << ' ';++it;}
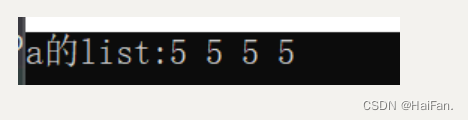
list的capacity
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| empty | 检测list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点的个数 |
list element access
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| front | 返回list的第一个节点中值的引用 |
| back | 返回list的最后一个节点中值的引用 |
list modifiers
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list中第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |
list的模拟实现
要想模拟实现list,首先我们可以定义一个节点类。为什么要定义一个节点类呢,想想数据结构中的双链表,每个元素都在独立的节点中,通过节点的前驱指针和后继指针指向前后位置。
list的模拟实现跟vector和string实现是不一样的,vector本质上是一个数组,数组本身就是一个迭代器,而list是一个个的节点,通过指针联系在一起,所以vector类不用对迭代器进行封装,可以直接使用,list不一样,节点++是什么是不清楚的,这个时候可以使用运算符重载,对++,–,*等进行重载。
template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;list_node(const T& val = T()):_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr),_val(val){}};
再定义一个list类,再这个类中,完成其他函数的实现
template<class T>class list{public:private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
构造函数,拷贝构造函数和=
list的构造函数实现,跟双链表中的初始化是一样的,将next指针和prev指针都指向头节点,形成一个环。
void EmptyInit(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
拷贝构造函数再拷贝之前,要先开一个头节点的空间,然后再头节点后面依次把值进行尾插即可。
list(const list<T>& it){EmptyInit();for (auto& e : it){push_back(e);}}
赋值重载=和vector里面的写法是一样的。
list<T>& operator=(list<T> it){swap(it);return *this;}
通过传参创建出一个临时变量,然后将其交换。
迭代器
要想实现list的迭代器,需要将原生态指针进行封装。
list是由一个个的节点组成,节点++,解引用,–,等操作是找不到对应的数据的,所以需要用自定义类型对指针进行封装,从而完成一系列操作。
迭代器有一个const类型的迭代器,有一个无const类型的,再实现一个无const类型的迭代器之后,把代码赋值粘贴,也可以改成带const类型的迭代器,但这样显然是代码冗余的,重复的太多,这个时候,那些大佬们就通过增加模板参数,来解决代码冗余,根据参数的类型,实列化出不同的类。
//typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
//typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;//构造方法__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}//对节点解引用,是找不到我们存储的数据的,因为节点里面存的是val,next和prev,重载的目是使其对迭代器解引用可以找到有效数据Ref operator*(){return _node->_val;}Ptr operator->(){return &(_node->val);}//指针++,到下一个位置,其实就是让节点向后移动self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}//将节点向前移动self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->prev;return *this;}bool operator !=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}};
以上就是用自定义的类,对指针进行封装。
begin和end
对指针进行封装之后,就可以实现begin和end了。
begin只要返回头节点的下一个节点即可
end就是头节点
iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}
insert和erase
有一个insert,就可以完成再任意位置插入。
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;return newnode;}
先找到当前节点cur和当前节点的上一个节点prev,再new出一个要插入的节点newnode,使得cur和newnode进行双向连接,prev和newnode进行双向连接。
删除一个节点,只需要让当前节点的上一个节点和下一个节点完成双向连接即可。
iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--_size;return next;}
clear和析构函数
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = earse(it);}_size = 0;}~list(){}
源码
#pragma once#include <assert.h>
#include <algorithm>namespace HaiFan
{template<class T>struct list_node{list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;T _val;list_node(const T& val = T()):_next(nullptr),_prev(nullptr),_val(val){}};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct __list_iterator{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;Node* _node;__list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_val;}T* operator->(){return &(_node->val);}T& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}T operator++(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}T& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}T operator--(int){self tmp(*this);_node = _node->prev;return *this;}bool operator !=(const self& it) const{return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const self& it) const{return _node == it._node;}};template<class T>class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}list(){EmptyInit();}list(const list<T>& it){EmptyInit();for (auto& e : it){push_back(e);}}list<T>& operator=(list<T> it){swap(it);return *this;}void swap(list<T>& it){std::swap(_head, it._head);std::swap(_size, it._size);}void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = earse(it);}_size = 0;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;return newnode;}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;--_size;return next;}size_t size(){return _size;}void EmptyInit(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}~list(){}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}
