【ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码】十分钟带你深入ConcurrentHashMap并发解析
ConcurrentHashMap1.7源码
四个核心要点
- 初始化
- PUT
- 扩容
- GET
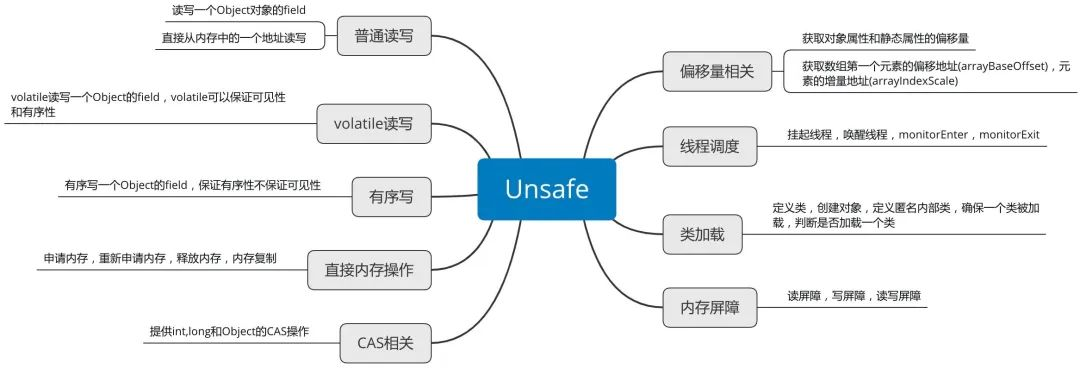
Unsafe
初始化
五个构造方法
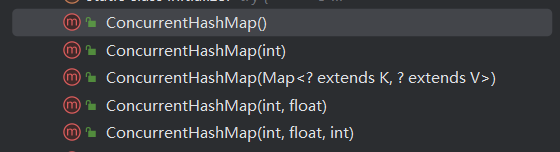
/*** Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).*/public ConcurrentHashMap() {}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need* to dynamically resize.** @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal* sizing to accommodate this many elements.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of* elements is negative*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));this.sizeCtl = cap;}/*** Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.** @param m the map*/public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;putAll(m);}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,* given the specified load factor.* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for* establishing the initial table size* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive** @since 1.6*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);}/*** Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).** @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,* given the specified load factor.* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for* establishing the initial table size* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as* a sizing hint.* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are* nonpositive*/public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many binsinitialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threadslong size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);this.sizeCtl = cap;}
无参构造方法
/*** Creates a new, empty map with a default initial capacity (16),* load factor (0.75) and concurrencyLevel (16).*/public ConcurrentHashMap() {this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);}
四个参数
- initialCapacity-初始容量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
- loadFactor-加载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
- concurrencyLevel-并发等级(最大支持线程)
static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16;
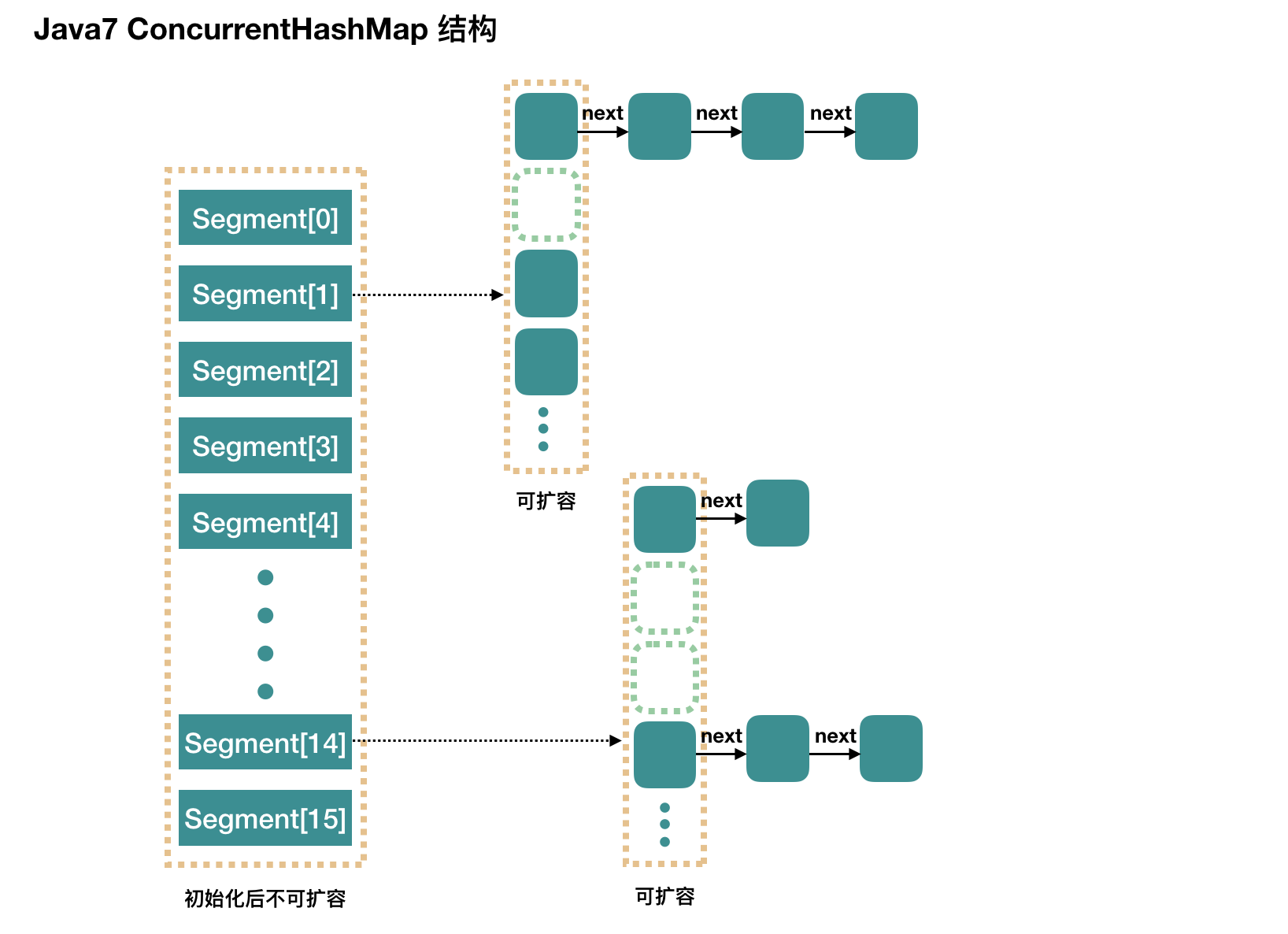
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {// 参数校验if (!(loadFactor > 0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS)concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS;// Find power-of-two sizes best matching argumentsint sshift = 0;// 关键int ssize = 1;// 1 < 16 2 < 16 4 < 16 8 < 16 最后ssize=16// 假如传入concurrencyLevel = 9 ,ssize = 16// 也就是找一个大于concurrencyLevel的2次幂数给ssizewhile (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {++sshift;ssize <<= 1;}this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;// 以默认值为例c=16/16=1int c = initialCapacity / ssize;// 如果是initialCapacity=9,concurrencyLevel=8// 下面是向上取整,要确保要这么多容量if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)++c;// static final int MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY = 2;// cap = 2,所以初始化的时候cap=2int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;// 保证cap容量是2的幂次方数while (cap < c)cap <<= 1;// create segments and segments[0]Segment<K, V> s0 =new Segment<K, V>(loadFactor, (int) (cap * loadFactor),(HashEntry<K, V>[]) new HashEntry[cap]);Segment<K, V>[] ss = (Segment<K, V>[]) new Segment[ssize];// 默认先在Segment数组里放了一个segments[0],里面是一个new HashEntry[cap]// 后面会以这个默认进行扩容UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); // ordered write of segments[0]this.segments = ss;}
注意:默认初始化的时候,HashEntry数组默认是16x2=32个,而不是16个
Segment
继承了ReentrantLock,方便lock
static final class Segment<K, V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L;/*** The maximum number of times to tryLock in a prescan before* possibly blocking on acquire in preparation for a locked* segment operation. On multiprocessors, using a bounded* number of retries maintains cache acquired while locating* nodes.*/static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;/*** The per-segment table. Elements are accessed via* entryAt/setEntryAt providing volatile semantics.*/transient volatile HashEntry<K, V>[] table;/*** The number of elements. Accessed only either within locks* or among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.*/transient int count;/*** The total number of mutative operations in this segment.* Even though this may overflows 32 bits, it provides* sufficient accuracy for stability checks in CHM isEmpty()* and size() methods. Accessed only either within locks or* among other volatile reads that maintain visibility.*/transient int modCount;/*** The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold.* (The value of this field is always <tt>(int)(capacity ** loadFactor)</tt>.)*/transient int threshold;/*** The load factor for the hash table. Even though this value* is same for all segments, it is replicated to avoid needing* links to outer object.** @serial*/final float loadFactor;Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry<K, V>[] tab) {this.loadFactor = lf;this.threshold = threshold;this.table = tab;}
PUT方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public V put(K key, V value) {Segment<K, V> s;if (value == null)throw new NullPointerException();// 计算hash值int hash = hash(key);// segmentMask = ssize - 1// 下面算segment的下标int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;// 判断segment是不是nullif ((s = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegments = ensureSegment(j);// segment不为空直接putreturn s.put(key, hash, value, false);}
创建segment
只需要一个线程来创建segment,另一个线程也是得到同一个Segment
/*** Returns the segment for the given index, creating it and* recording in segment table (via CAS) if not already present.** @param k the index* @return the segment*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private Segment<K, V> ensureSegment(int k) {final Segment<K, V>[] ss = this.segments;long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; // raw offsetSegment<K, V> seg;// 只有一个线程拿到ss是null,一个线程进入ifif ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {// 原型模式Segment<K, V> proto = ss[0]; // use segment 0 as prototypeint cap = proto.table.length;float lf = proto.loadFactor;// 0.75x16 = 12int threshold = (int) (cap * lf);HashEntry<K, V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K, V>[]) new HashEntry[cap];// DCLif ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))== null) { // recheck// 创建Segment对象Segment<K, V> s = new Segment<K, V>(lf, threshold, tab);while ((seg = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))== null) {// 把新segment放入数组if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))break;}}}return seg;}
PUT
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {// 两个线程进来,tryLock(),拿到锁就可以走下面流程放入元素,没有的话就可以走scanAndLockForPut流程// 在等待锁的过程中可以执行相关代码,也就是自旋// lock是阻塞,trylock是非阻塞HashEntry<K, V> node = tryLock() ? null :scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);V oldValue;try {HashEntry<K, V>[] tab = table;// 计算HashEntry tab的下标int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;HashEntry<K, V> first = entryAt(tab, index);// 以下就是hashmap的代码for (HashEntry<K, V> e = first; ; ) {if (e != null) {K k;if ((k = e.key) == key ||(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent) {e.value = value;++modCount;}break;}e = e.next;} else {if (node != null)node.setNext(first);elsenode = new HashEntry<K, V>(hash, key, value, first);int c = count + 1;if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)rehash(node);elsesetEntryAt(tab, index, node);++modCount;count = c;oldValue = null;break;}}} finally {unlock();}return oldValue;}
scanAndLockForPut
保证一定要Segment加上锁
/*** Scans for a node containing given key while trying to* acquire lock, creating and returning one if not found. Upon* return, guarantees that lock is held. UNlike in most* methods, calls to method equals are not screened: Since* traversal speed doesn't matter, we might as well help warm* up the associated code and accesses as well.** @return a new node if key not found, else null*/private HashEntry<K, V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {HashEntry<K, V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);HashEntry<K, V> e = first;HashEntry<K, V> node = null;int retries = -1; // negative while locating node// 自旋锁,等待的过程可以执行其他流程// 下面可以创建HashEntry node对象while (!tryLock()) {HashEntry<K, V> f; // to recheck first belowif (retries < 0) {// e 是头节点,如果e==null,表示遍历到链表最后if (e == null) {if (node == null) // speculatively create nodenode = new HashEntry<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);retries = 0;// 如果key已经存在,则不创建node对象} else if (key.equals(e.key))retries = 0;else// 相当于遍历链表e = e.next;// static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES =// Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1;} else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {// 超过阈值就会保证加上锁lock();break;// retries & 1 保证偶数次重试的时候,判断头节点是不是一样的// 如果头节点不一样表示头节点被修改,插入了元素} else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {// 保证是最新的头节点e = first = f; // re-traverse if entry changedretries = -1;}}return node;}
GET方法
/*** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.** <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code key.equals(k)},* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)** @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null*/public V get(Object key) {Segment<K, V> s; // manually integrate access methods to reduce overheadHashEntry<K, V>[] tab;int h = hash(key);long u = (((h >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask) << SSHIFT) + SBASE;if ((s = (Segment<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(segments, u)) != null &&(tab = s.table) != null) {for (HashEntry<K, V> e = (HashEntry<K, V>) UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long) (((tab.length - 1) & h)) << TSHIFT) + TBASE);e != null; e = e.next) {K k;if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == h && key.equals(k)))return e.value;}}return null;}
Size方法
本质上是遍历每一个segment,加上所有的node节点
public int size() {// Try a few times to get accurate count. On failure due to// continuous async changes in table, resort to locking.final Segment<K, V>[] segments = this.segments;int size;boolean overflow; // true if size overflows 32 bitslong sum; // sum of modCountslong last = 0L; // previous sumint retries = -1; // first iteration isn't retrytry {for (; ; ) {if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)ensureSegment(j).lock(); // force creation}sum = 0L;size = 0;overflow = false;// 遍历每一个segmentsfor (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {Segment<K, V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);if (seg != null) {sum += seg.modCount;int c = seg.count;if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)overflow = true;}}if (sum == last)break;last = sum;}} finally {if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();}}return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;}
总结
ConcurrentHashMap采用了分段锁的设计,当需要put元素的时候,并不是对整个hashmap进行加锁,而是先通过hashcode来知道要放在哪一个分段中,然后对这个分段进行加锁,所以当多线程put的时候,只要不是放在一个分段中,就没有锁竞争,实现真正的并行插入。相比于对整个Map加锁的设计,分段锁大大的提高了高并发环境下的处理能力。但同时,由于不是对整个Map加锁,导致一些需要扫描整个Map的方法(如size(), containsValue())需要使用特殊的实现,另外一些方法(如clear())甚至放弃了对一致性的要求(ConcurrentHashMap是弱一致性的)。
假如new ConcurrentHashMap(32, 0.75, 16)就是新建了一个ConcurrentHashMap,他的容量是32,分段锁的个数是16,也就是每个Segment里面HashEntry[]数组的长度是2。但是new ConcurrentHashMap()时,每个Segment里面HashEntry[]数组的长度也是2,因为ConcurrentHashMap规定了Segment数组中HashEntry数组的长度是2。