vue-router 源码解析(二)-创建路由匹配对象
文章目录
- 基本使用
- 导语
- createRouterMatcher 创建匹配路由记录
- addRoute 递归添加matcher
- createRouteRecordMatcher 创建matcher
- tokenizePath 解析path
- tokensToParser 记录打分
- insertMatcher 将matcher排序
- 总结
基本使用
const routes = [{path:"/",component: Demo2,name:'root',beforeEnter: (to, from) => {console.log('ddd')return true;},beforeLeave:(to, from) => {console.log('aa')return true;},},{ path: '/d0/d01?p0=jeff', component: App,name:'n0',alias:'/a0',beforeEnter: (to, from) => {return true;},},{ path: '/d1/:d11', component: Demo1 ,name:'n1',beforeEnter:[ (to, from) => {return true;},(to, from) => {return true;}],},{ path: '/d2/d21', component: Demo2,name:'n2',redirect:'/r2'},{path: '/d3',name: 'n3',component: Demo1,children: [{ path: 'd31', name: 'n31', component: Demo2,alias:'a31' }],},]const router = VueRouter.createRouter({history: VueRouter.createWebHashHistory(), // 创建对应的路由对象routes,
})导语
- 在上文中介绍了三种模式下路由对象的创建,而本文将深入createRouter,解析如何将传入的routes配置,转换成未来进行导航时对应的一个个matcher,当开发者通过push 等API进行导航时,会查找到对应path|name 的matcher记录,进而拿到需要的路由记录信息
- matcher的创建过程,会根据routes中的信息,转换出一条条具有分数(或者理解为权重)的matcher,匹配时会根据分数优先匹配
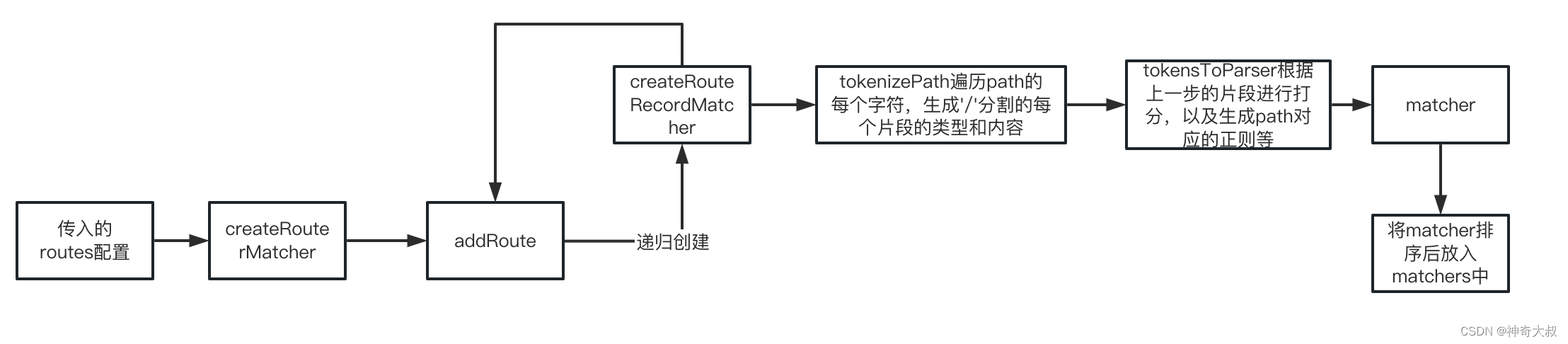
createRouterMatcher 创建匹配路由记录
//router.ts
export function createRouter(options: RouterOptions): Router { //options就为传入的配置// 这里返回的matcher是操作路由记录的API,非路由记录对应的匹配matcherconst matcher = createRouterMatcher(options.routes, options)// ...
}
- 会递归调用addRoutes方法,将配置的routes全部转换成matcher
export function createRouterMatcher(routes: Readonly<RouteRecordRaw[]>,globalOptions: PathParserOptions
): RouterMatcher {// 存储所有routes配置转换而成的路由记录const matchers: RouteRecordMatcher[] = []// 存储原始路由记录(非原始记录:设置了alias的别名路由会再创建一条记录,但该记录不会加入matcherMap中)const matcherMap = new Map<RouteRecordName, RouteRecordMatcher>()// 合并开发者传递的strict、end和sensitive这些约定路由匹配模式的属性globalOptions = mergeOptions({ strict: false, end: true, sensitive: false } as PathParserOptions,globalOptions)function addRoute(route){ //将routes配置转换成matcher,过程会递归调用创建子路由matcher// ...} // 创建一级路由记录routes.forEach(route => addRoute(route));return { addRoute, resolve, removeRoute, getRoutes, getRecordMatcher };
}
addRoute 递归添加matcher
- 普通路由:
- 会为每一个route创建一个matcher
- 别名路由:
- 如果存在别名路由时,会再创建一条matcher,matcher.path为别名设置的名称
- 别名路由的matcher.aliasOf会指向原始路由记录的matcher
- 原始路由的matcher.alias[],会存放对应的所有别名路由记录matcher
- 子路由:
- 当存在子路由时,会递归创建
- 子路由matcher.path会拼接上父路由的路径
- 子路由matcher.parent属性会指向父路由matcher
- 最终所有的matcher会存入matchers,整个创建出来的matchers是一个平级结构(一维数组)
function addRoute(record: RouteRecordRaw, // 原始的route记录(开发者传入的)parent?: RouteRecordMatcher,// 当存在子路由时,parent才会有,第一次因为是创建一级路由,所以为空originalRecord?: RouteRecordMatcher // alais别名路由对应的原始记录) {// 首次添加originalRecord为空,表明是添加第一层根路由const isRootAdd = !originalRecord// 将单个路由配置转换成规定格式,格式如下/**{path: record.path,redirect: record.redirect,name: record.name,meta: record.meta || {},aliasOf: undefined, // 别名记录才会有值,执行原始记录beforeEnter: record.beforeEnter,props: normalizeRecordProps(record),children: record.children || [],instances: {},//路由组件实例,复用时使用leaveGuards: new Set(), // setup中使用的守卫updateGuards: new Set(),// setup中使用的守卫enterCallbacks: {},components:'components' in record? record.components || null: record.component && { default: record.component },}*/const mainNormalizedRecord = normalizeRouteRecord(record)// 让个是别名路由,originalRecord会指向原始路由,为别名路由添加引用mainNormalizedRecord.aliasOf = originalRecord && originalRecord.record// 合并route记录中存在的strict、end和sensitive这些约定路由匹配模式的属性const options: PathParserOptions = mergeOptions(globalOptions, record)// 将转换后的路由变成数组格式,因为可能存在别名,将别名记录添加进去const normalizedRecords: typeof mainNormalizedRecord[] = [mainNormalizedRecord,]// 处理别名情况if ('alias' in record) {// 别名可以是一个字符串或数组,统一变成数组格式const aliases =typeof record.alias === 'string' ? [record.alias] : record.alias!// 将alias变成path,有多少个alias就会添加多少条记录for (const alias of aliases) {normalizedRecords.push(assign({}, mainNormalizedRecord, {components: originalRecord? originalRecord.record.components: mainNormalizedRecord.components,// 别名作为pathpath: alias,// 别名路由指向的原始路由记录aliasOf: originalRecord? originalRecord.record: mainNormalizedRecord,// the aliases are always of the same kind as the original since they// are defined on the same record}) as typeof mainNormalizedRecord)}}// route对应的matcherlet matcher: RouteRecordMatcher// 别名对应的原始matcherlet originalMatcher: RouteRecordMatcher | undefinedfor (const normalizedRecord of normalizedRecords) {const { path } = normalizedRecord// 当存在parent时,说明正在处理子路由// 添加子路由:处理alias没有加'/',且父路由没有以'/'结尾的情况,会拼接父路由路径作为pathif (parent && path[0] !== '/') {const parentPath = parent.record.pathconst connectingSlash =parentPath[parentPath.length - 1] === '/' ? '' : '/'normalizedRecord.path =parent.record.path + (path && connectingSlash + path)}// 现在的版本必须用正则代替'*'匹配所有路由if (__DEV__ && normalizedRecord.path === '*') {throw new Error('Catch all routes ("*") must now be defined using a param with a custom regexp.\n' +'See more at https://next.router.vuejs.org/guide/migration/#removed-star-or-catch-all-routes.')}// 创建出matchermatcher = createRouteRecordMatcher(normalizedRecord, parent, options)if (__DEV__ && parent && path[0] === '/')checkMissingParamsInAbsolutePath(matcher, parent)// 当设置了别名alias,会再次生成一条别名对路由记录// 当第一次遍历原始路由记录后,originalRecord为上次原始记录,将别名路由记录放进原始记录的alias中if (originalRecord) {// 原始记录中添加别名记录originalRecord.alias.push(matcher)if (__DEV__) {checkSameParams(originalRecord, matcher)}} else {// 没有originalMatcher说明没有设置alias别名,或者正在处理原始路由记录originalMatcher = originalMatcher || matcher// 处理别名路由中,往alias中添加别名路由if (originalMatcher !== matcher) originalMatcher.alias.push(matcher)// 检查删除掉之前添加的相同name路由if (isRootAdd && record.name && !isAliasRecord(matcher))removeRoute(record.name)}// 如果存在子路由if (mainNormalizedRecord.children) {const children = mainNormalizedRecord.childrenfor (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {addRoute(children[i],matcher,originalRecord && originalRecord.children[i])}}originalRecord = originalRecord || matcherif ((matcher.record.components &&Object.keys(matcher.record.components).length) ||matcher.record.name ||matcher.record.redirect) {// 将matcher根据分数排序,添加进matchers中insertMatcher(matcher)}}// 最终返回删除当前matcher的方法return originalMatcher? () => {// since other matchers are aliases, they should be removed by the original matcherremoveRoute(originalMatcher!)}: noop
}
createRouteRecordMatcher 创建matcher
最主要的是tokenizePath和tokensToParser两个方法
- tokenizePath:解析每一个片段(指按照’/'分割的路径)的类型和内容
- tokensToParser:根据上一步结果进行打分和生成正则等
export function createRouteRecordMatcher(record: Readonly<RouteRecord>, // 路由记录parent: RouteRecordMatcher | undefined, // 父路由记录options?: PathParserOptions // strict、end和sensitive这些约定路由匹配模式的属性
): RouteRecordMatcher {// 通过tokenizePath解析每一个片段(指按照'/'分割的路径)类型和内容,tokensToParser根据上一步结果进行打分和生成正则等const parser = tokensToParser(tokenizePath(record.path), options)const matcher: RouteRecordMatcher = assign(parser, {record,parent,// these needs to be populated by the parentchildren: [],alias: [],})if (parent) {if (!matcher.record.aliasOf === !parent.record.aliasOf)parent.children.push(matcher)}return matcher}
tokenizePath 解析path
- 会遍历path的每一个字符,根据path中的‘/’进行分割,返回[[{type: 0, value: ‘’}],[{type: 0, value: ‘d01?p0=jeff’}]]类似结果
const enum TokenizerState {Static, // 静态路径Param, // 动态路径,比如:idParamRegExp, // custom re for a paramParamRegExpEnd, // check if there is any ? + *EscapeNext,
}
export function tokenizePath(path: string): Array<Token[]> {//...while (i < path.length) {char = path[i++]if (char === '\\' && state !== TokenizerState.ParamRegExp) {previousState = statestate = TokenizerState.EscapeNextcontinue}switch (state) {case TokenizerState.Static: //如果匹配到的是静态路径if (char === '/') {if (buffer) {consumeBuffer()}finalizeSegment()} else if (char === ':') { // 解析到':',说明遇到了动态路径,走动态路径的解析分支consumeBuffer()state = TokenizerState.Param} else {addCharToBuffer()}breakcase TokenizerState.Param: // 动态路径的解析if (char === '(') {state = TokenizerState.ParamRegExp} else if (VALID_PARAM_RE.test(char)) { // 字母或数字addCharToBuffer()} else {consumeBuffer()state = TokenizerState.Static// go back one character if we were not modifyingif (char !== '*' && char !== '?' && char !== '+') i--}break//...
}
- 如果路径为:‘/d0/d01?p0=jeff’,那么将会返回 [ [ {type: 0, value: ‘d0’} ], [ { type: 0, value: ‘d01?p0=jeff’ } ]]
- 如果路径为:‘/d1/:d11’,那么将会返回 [ [ {type: 0, value: ‘d1’} ], [ { type: 1, value: ‘d11’} ] ]
tokensToParser 记录打分
- 根据上一步分割的片段,进行打分以及生成正则
// 打分规则
const enum PathScore {_multiplier = 10,Root = 9 * _multiplier, // just /Segment = 4 * _multiplier, // /a-segmentSubSegment = 3 * _multiplier, // /multiple-:things-in-one-:segmentStatic = 4 * _multiplier, // /staticDynamic = 2 * _multiplier, // /:someIdBonusCustomRegExp = 1 * _multiplier, // /:someId(\\d+)BonusWildcard = -4 * _multiplier - BonusCustomRegExp, // /:namedWildcard(.*) we remove the bonus added by the custom regexpBonusRepeatable = -2 * _multiplier, // /:w+ or /:w*BonusOptional = -0.8 * _multiplier, // /:w? or /:w*// these two have to be under 0.1 so a strict /:page is still lower than /:a-:bBonusStrict = 0.07 * _multiplier, // when options strict: true is passed, as the regex omits \/?BonusCaseSensitive = 0.025 * _multiplier, // when options strict: true is passed, as the regex omits \/?
}
export function tokensToParser(segments: Array<Token[]>,extraOptions?: _PathParserOptions
): PathParser {const score: Array<number[]> = []// 针对动态path等会抽取出来,用于后续判断是否重复出现相同的path,开发环境会提示const keys: PathParserParamKey[] = []for (const segment of segments) {// ...// 如果配置了sensitive的分数let subSegmentScore: number =PathScore.Segment +(options.sensitive ? PathScore.BonusCaseSensitive : 0)// 如果是静态路径的分数 if (token.type === TokenType.Static) {// prepend the slash if we are starting a new segmentif (!tokenIndex) pattern += '/'pattern += token.value.replace(REGEX_CHARS_RE, '\\$&')subSegmentScore += PathScore.Static} // ...}
}
- 如果路径为’/d1/:d11’,最终会返回这样的结果
{"re": {},"score": [[80],[60]],"keys": [{"name": "d11","repeatable": false,"optional": false}],"record": {// ...},"children": [],"alias": []
}
insertMatcher 将matcher排序
function addRoute(record: RouteRecordRaw, // 原始的route记录(开发者传入的)parent?: RouteRecordMatcher,// 当存在子路由时,parent才会有,第一次因为是创建一级路由,所以为空originalRecord?: RouteRecordMatcher // alais别名路由对应的原始记录) {// ...matcher = createRouteRecordMatcher(normalizedRecord, parent, options)// ...if ((matcher.record.components &&Object.keys(matcher.record.components).length) ||matcher.record.name ||matcher.record.redirect) {insertMatcher(matcher)}
}
insertMatcher
function insertMatcher(matcher: RouteRecordMatcher) {let i = 0// 对路由记录根据score进行排序,i代表该路由记录排序后的位置while (i < matchers.length &&comparePathParserScore(matcher, matchers[i]) >= 0 && // comparePathParserScore 是个比较器// 子路由为空路径时,排序应该在父路由前面(matcher.record.path !== matchers[i].record.path ||!isRecordChildOf(matcher, matchers[i])))i++// 将路由记录插入matchers中matchers.splice(i, 0, matcher)// matcherMap 中只存放原始记录if (matcher.record.name && !isAliasRecord(matcher))matcherMap.set(matcher.record.name, matcher)}
总结
- vue-router会将开发者传入的routes配置转换成一条条matcher,而matcher会根据你path的类型进行打分排序,后续匹配时会优先匹配分数高的
