【二进制安全】堆漏洞:Double Free原理
参考:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/241598
次要参考:https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6342
malloc_chunk 的源码如下:
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /*前一个chunk的大小*/
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /*当前chunk的大小*/
struct malloc_chunk * fd; /*指向前一个释放的chunk*/
struct malloc_chunk * bk; /*指向后一个释放的chunk*/
}
释放的chunk 会以单向链表的形式回收到fastbin 里面。
fastbin 是 LIFO 的数据结构,使用单向链表实现。
示例代码:
// https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/241598#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int main(void)
{puts("The goal of this is to show how we can edit a freed chunk using a Double Free bug.");puts("Editing freed chunks will allow us to overwrite heap metadata, which is crucial to a lot of heap attacks.");puts("However a bug to edit the heap metadata is often just one piece of the exploitation process.\n");printf("So we start off by allocating three chunks of memory. Let's also write some data to them.\n\n");char *ptr0, *ptr1, *ptr2;ptr0 = malloc(0x30);ptr1 = malloc(0x30);ptr2 = malloc(0x30);char *data0 = "00000000";char *data1 = "11111111";char *data2 = "22222222";memcpy(ptr0, data0, 0x8);memcpy(ptr1, data1, 0x8); memcpy(ptr2, data2, 0x8);printf("Chunk0: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr0, ptr0);printf("Chunk1: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr1, ptr1);printf("Chunk2: @ %p\t contains: %s\n\n", ptr2, ptr2);printf("Now is where the bug comes in. We will free the same pointer twice (the first chunk pointed to by ptr0).\n");printf("In between the two frees, we will free a different pointer. This is because in several different versions of malloc, there is a double free check \n(however in libc-2.27 it will hit the tcache and this will be fine).\n");printf("It will check if the pointer being free is the same as the last chunk freed, and if it is the program will cease execution.\n");printf("To bypass this, we can just free something in between the two frees to the same pointer.\n\n");free(ptr0); //-----------------------> b1free(ptr1);free(ptr0); //-----------------------> b2printf("Next up we will allocate three new chunks of the same size that we freed, and write some data to them. This will give us the three chunks we freed.\n\n");char *ptr3, *ptr4, *ptr5;ptr3 = malloc(0x30); //--------------> b3ptr4 = malloc(0x30);ptr5 = malloc(0x30);memcpy(ptr3, data0, 0x8);memcpy(ptr4, data1, 0x8); memcpy(ptr5, data2, 0x8);printf("Chunk3: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr3, ptr3); //-------------> b4printf("Chunk4: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr4, ptr4);printf("Chunk5: @ %p\t contains: %s\n\n", ptr5, ptr5);printf("So you can see that we allocated the same pointer twice, as a result of freeing the same pointer twice (since malloc will reuse freed chunks of similar sizes for performance boosts).\n");printf("Now we can free one of the pointers to either Chunk 3 or 5 (ptr3 or ptr5), and clear out the pointer. We will still have a pointer remaining to the same memory chunk, which will now be freed.\n");printf("As a result we can use the double free to edit a freed chunk. Let's see it in action by freeing Chunk3 and setting the pointer equal to 0x0 (which is what's supposed to happen to prevent UAFs).\n\n");free(ptr3);ptr3 = 0x0;printf("Chunk3: @ %p\n", ptr3);printf("Chunk5: @ %p\n\n", ptr5);printf("So you can see that we have freed ptr3 (Chunk 3) and discarded it's pointer. However we still have a pointer to it. Using that we can edit the freed chunk.\n\n");char *data3 = "15935728";memcpy(ptr5, data3, 0x8);printf("Chunk5: @ %p\t contains: %s\n\n", ptr5, ptr5);printf("Just like that, we were able to use a double free to edit a free chunk!\n");}
需要使用glibc 2.27编译。
Linux下更换glibc版本的方法:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44864859/article/details/107237134
使用glibc-all-in-one和patchelf对编译好的二进制文件直接替换其ld和libc的链接库地址,指向2.27版本的再次进行调试。
下面进行解释。
首先是申请三段内存,并填入数据:
ptr0 = malloc(0x30);
ptr1 = malloc(0x30);
ptr2 = malloc(0x30);char *data0 = "00000000";
char *data1 = "11111111";
char *data2 = "22222222";memcpy(ptr0, data0, 0x8);
memcpy(ptr1, data1, 0x8);
memcpy(ptr2, data2, 0x8);
然后依次释放ptr0、ptr1、ptr0
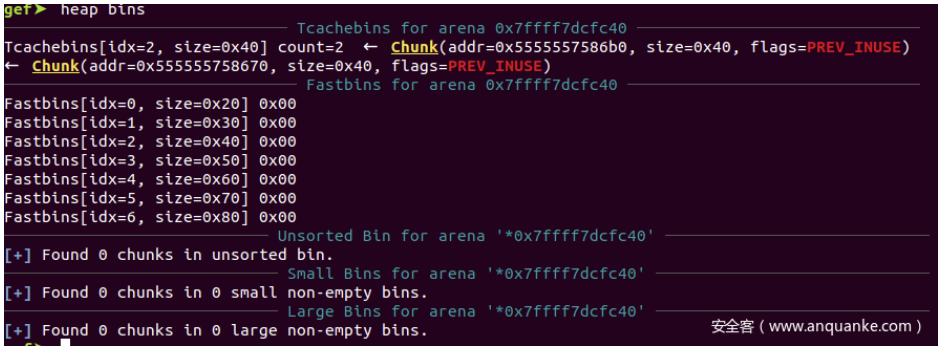
释放ptr0和ptr1之后的Tcachebin:
再释放ptr0之后的Tcachebin:
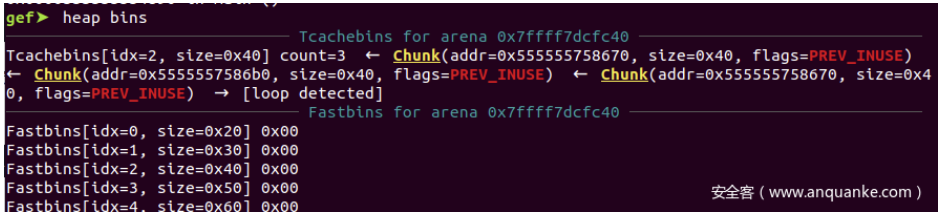
可以看到addr=0x555555758670这个chunk被放到了tcache 0x40 大小的链表上两次
之后再申请ptr3、ptr4、ptr5(同样大小)
char *ptr3, *ptr4, *ptr5;ptr3 = malloc(0x30); //--------------> b3ptr4 = malloc(0x30);ptr5 = malloc(0x30);memcpy(ptr3, data0, 0x8);memcpy(ptr4, data1, 0x8); memcpy(ptr5, data2, 0x8);printf("Chunk3: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr3, ptr3); //-------------> b4printf("Chunk4: @ %p\t contains: %s\n", ptr4, ptr4);printf("Chunk5: @ %p\t contains: %s\n\n", ptr5, ptr5);
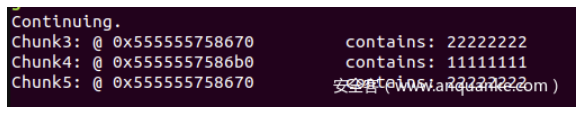
可以看出来,ptr3和ptr5实际上是返回的同一块地址。
因此,在之后,即便我们释放ptr3,并且把ptr3的值指向0x0,我们还是可以操作这个已经被释放的chunk。
free(ptr3);
ptr3 = 0x0;printf("Chunk3: @ %p\n", ptr3);
printf("Chunk5: @ %p\n\n", ptr5);char *data3 = "15935728";
memcpy(ptr5, data3, 0x8);
printf("Chunk5: @ %p\t contains: %s\n\n", ptr5, ptr5);

总结就是2次free,2次malloc,一次free,最终得到可用的空闲块指针。
我们先不用管 修改已被释放的空闲块中的内容到底有什么用,
我们现在只需要知道Double free可以实现这个目标 就可以了
