黑马程序员2024新版C++笔记 第2章 语句
1.if逻辑判断语句

语法主体:
if(要执行的判断,结果是bool型){判断结果是true会执行的代码;
}2.AI大模型辅助编程

在Clion中搜索并安装对应插件:

右上角齿轮点击后找到插件(TRONGYI LINGMA和IFLYCODE)安装后重启ide即可。
重启后会有通义登录引导,点击会跳转到阿里云账号登陆界面,可以直接登录或注册一个。点击右侧的图标就可以使用了。

不想写注释可以全选代码->右键->选择通义灵码->生成注释

生成后的代码选择“插入”即可完成当前代码的注释。
讯飞灵火类似的操作不再整理。
3.if逻辑判断语句练习

答案:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 提示用户输入年龄cout << "欢迎来到黑马儿童游乐场,儿童免费,成人收费!" << endl;cout << "请输入你的年龄:";int age;cin >> age;// 根据年龄判断并输出相应内容if (age < 18) {cout << "您未成年,免费游玩,欢迎您小朋友!" << endl;}cout << "祝您游玩愉快!!!" << endl;return 0;
}
4.if_else语句
程序判断语法:
if(条件判断)
{判断条件为true会执行的代码;
}
else(条件判断)
{判断结果为false会执行的代码;
}5.if_else语句练习

#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main() {// 欢迎语cout << "欢迎来到黑马动物园。" << endl;cout << "请输入您的身高(cm):";int height; // 定义变量 height 用于存储用户输入的身高cin >> height; // 使用 cin 获取用户输入的身高// 根据身高判断并输出相应内容if (height > 120) {cout << "您的身高超出120cm,游玩需要购票10元。" << endl;} else {cout << "您的身高未超出120cm,可以免费游玩。" << endl;}cout << "祝您游玩愉快。" << endl;return 0;
}
6.else if语句

7.逻辑判断语句的嵌套
有很多场景不仅是多个并列条件,还会有满足前置条件才会有第二次判断的多层次需求。对于这种需求嵌套判断语句可以实现。


8.逻辑判断语句的嵌套练习

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // 用于 rand() 和 srand()
#include <ctime> // 用于 time()using namespace std;int main() {// 1. 定义一个变量,数字类型,内容在 1~10 范围内int target;cin >> target;// 提供三次猜测的机会for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i) {int guess;cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 次猜测的数字(1~10):";cin >> guess;// 判断猜测是否正确if (guess == target) {cout << "第 " << i << " 次就猜对了。你真棒!" << endl;return 0; // 猜对了,程序结束} else {cout << "不对,请再猜一次。" << endl;}}// 如果三次都未猜对cout << "Sorry,全部猜错啦,我想的是:" << target << endl;return 0;
}
9.逻辑判断的综合案例

提示:随机数可通过C++中的random库得到。
将下方代码放置在main函数之前即可调用
#include<random>//将下方代码放置于main()函数之前即可调用
int get_random_num(int min, int max)
{//创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());//定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);//生成一个随机数并输出int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;}随机数范围可通过调用函数的2个参数控制
int num = get_random_num(1,10);#include <iostream>
#include<random>using namespace std;/** 案例需求(填补页牌):* 随机产出3份信息:* 第一份信息:1~10的数字,代表扑克牌1~10* 第二份信息:字符串,红色或黑色,代表扑克牌的花色* 第三份信息:字符串,如果是红色产出红桃或方块,如果是黑色产出黑桃或梅花* 案例要求:* 通过该套判断,并结合判断语句猜测上述信息,如* 先猜数字,成功后猜颜色,再成功猜测具体的花型*///将下方代码放置于main()函数之前即可调用
int get_random_num(int min, int max)
{//创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());//定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);//生成一个随机数并输出int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;}int main() {// 第一份信息:1~10的数字,代表扑克牌1~10int num = get_random_num(1,10);// 第二份信息:字符串,红色或黑色,代表扑克牌的花色string color = get_random_num(0,1) ? "红色" : "黑色";// 第三份信息:字符串,如果是红色产出红桃或方块,如果是黑色产出黑桃或梅花string suit;if (color == "红色") {suit = get_random_num(0,1) ? "红桃" : "方块" ;}elsesuit = get_random_num(0,1) ? "黑桃" : "梅花" ;//目前检查一下输出变量,没有问题cout << "数字:" << num << " 花色:" << color << " 花型:" << suit << endl;// 先猜数字,成功后猜花色,再成功后猜具体的花型int guess_num;cout << "请输入数字:" << endl;cin >> guess_num;if (guess_num == num) {// 数字猜对了要继续猜花色int guess_color;cout << "请猜测花色,红色输入1,黑色输入0:" << endl;cin >> guess_color;if ((guess_color ? "红色" : "黑色") == color) {// 颜色猜对了int suit_num;if (color == "红色") {// 猜测是否是红桃还是方块cout << "请猜测花型,红桃输入1,方块输入0" << endl;cin >> suit_num;if ((suit_num ? "红桃" : "方块") == suit) {cout << "花型正确,恭喜你游戏成功,游戏的花型是" << suit << endl;}else {cout << "花型错误,游戏失败。正确的花型是: " << suit << endl;}}// 花色是黑色// 猜测是黑桃或梅花else{cout << "请猜测花型,黑桃输入1,梅花输入0" << endl;cin >> suit_num;if ((suit_num ? "黑桃" : "梅花") == suit){cout << "花型正确,恭喜你游戏成功,游戏的花型是" << suit << endl;}else {cout << "花型错误,游戏失败。正确的花型是: " << suit << endl;}}}// 颜色猜错了else cout << "花色错误,游戏结束" << endl;}else cout << "数字错误,游戏结束" << endl;return 0;
}输出答案:
数字:5 花色:红色 花型:红桃
请输入数字:
5
请猜测花色,红色输入1,黑色输入0:
1
请猜测花型,红桃输入1,方块输入0
1
花型正确,恭喜你游戏成功,游戏的花型是红桃10.基于逻辑运算符完成复杂判断

11.switch控制语句
switch控制语句适用于多条件判断的场景,它在功能上和if 、elseif功能一致,语法更简洁接。

switch仅做值匹配(相等判断)。break语句可以中断switch语句,否则向下执行其他case段(包括default段),直至执行完或遇到break为止。示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// 输入数字1-7 输出星期几int num;cout << "请输入数字来自知是星期几(1-7):" << endl;cin >> num;switch(num){case 1:cout << "今天是星期一" << endl;break;case 2:cout << "今天是星期二" << endl;break;case 3:cout << "今天是星期三" << endl;break;case 4:cout << "今天是星期四" << endl;break;case 5:cout << "今天是星期五" << endl;break;case 6:cout << "今天是星期六" << endl;break;case 7:cout << "今天是星期日" << endl;break;default:cout << "输入错误,请输入1-7之间的数字!" << endl;}return 0;
}老师还讲了break的巧妙(多重)用法:
-
case一旦匹配成功,从该处开始执行后续语句,若未遇到break,则会继续执行后续所有 case 的语句(称为“穿透”)。也就是说多个case可连续书写,不写语句或break,共享同一段代码。例如9分和10分都是优秀可以写成case10:case9:cout<<"优秀"<<endl;break; -
break的作用是跳出 switch 语句,防止继续执行后续 case。 -
default相当于“兜底选项”,不匹配任何 case 时执行。
12.枚举类型
枚举本质上是一个被命名的整型常数的集合。因为枚举可以将一些数字或字符串符号化,以此增强程序的可读性和可维护性。

枚举语法:
enum 枚举名{枚举元素1;枚举元素2;...枚举元素n;
}; //分号不能省略枚举类型每个元素都有整数标号,默认从0开始,以此类推。起始标号也可以自行设置,例如“
enum Season {spring = 3;summer;autumn;winter;
};从3开始递增,即:spring为3,sutumn为5,winter为6.示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;// 定义颜色枚举类型
enum Color {RED, // 默认是0YELLOW, // 默认是1BLUE // 默认是2
};int main() {int num;cout << "小朋友们你们喜欢什么颜色?0红色,1黄色,2蓝色" << endl;cin >> num;switch (num) {case RED:cout << "小朋友喜欢红色!" << endl;break;case YELLOW:cout << "小朋友喜欢黄色!" << endl;break;case BLUE:cout << "小朋友喜欢蓝色!" << endl;break;default:cout << "输入无效,请输入0、1或2。" << endl;break;}return 0;
}
13.while循环语句

14.while循环语句练习题讲解

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {// 求1-100的和// 在循环外部定义循环控制变量和累计和int i = 1, sum = 0;while ( i<=100 ) {sum += i;i++;}// 输出累计和cout << "1-100的和为:" << sum << endl;return 0;
}
15.while循环猜数字案例
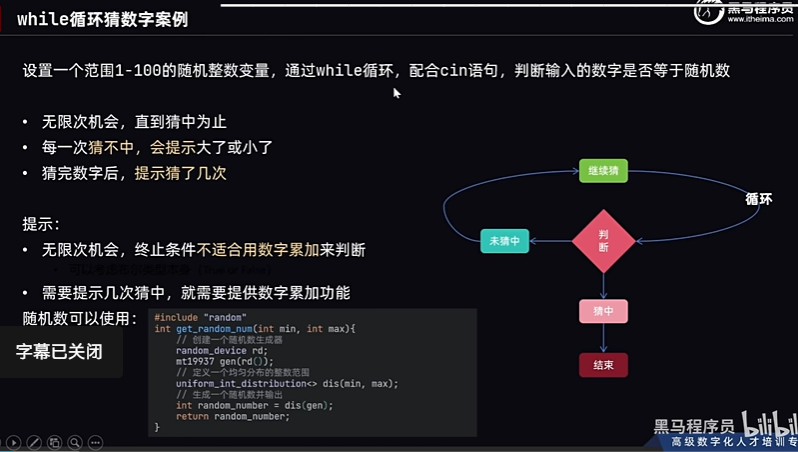
随机数可以使用:
#include<random>
int get_random_number(int min, int max){//创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());//定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);//生成一个随机数并输出int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;
}答案:
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;#include<random>
int get_random_number(int min, int max){//创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());//定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);//生成一个随机数并输出int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;
}int main() {/** 1.无限次机会* 2.提示大了或小了* 提示总共猜了多少次*/// 得到一个随机数1~100范围int random_number = get_random_number(1, 100);// 提示用户输入数字进行猜测cout << "请输入一个1~100的数字进行猜测:" << endl;int input_number;cin >> input_number;int guess_count = 1;// 循环判断用户输入的数字是否正确while (input_number != random_number) {//true表示为猜错// 1.判断条件上面就是// 2.循环控制因子就是input_number// 3.循环控制因子更新是来源于如果猜错,继续要求用户输入新的数字cout << "不好意思你猜错了" << endl;// 提示大了或小了if (input_number > random_number) {cout << "您输入的数字大了,请重新猜测" << endl;cin >> input_number; //控制因子的更新}else {cout << "您输入的数字小了,请重新猜测" << endl;cin >> input_number; //控制因子的更新}// 提示总共猜了多少次guess_count++;}cout << "恭喜你猜对了,总共猜了" << guess_count << "次" << endl;return 0;
}
16.do_while 循环语句
do while 循环是 while 循环的一个变换形式。和while循环在功能上有一个不同:while循环至少执行0次(条件判断不成立),do while循环至少会执行一次循环体的代码。
语法:
do{// 循环体,至少执行一次code;```
} while(条件表达式)用do while循环解决上一个练习题:
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;#include<random>
int get_random_number(int min, int max){//创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());//定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);//生成一个随机数并输出int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;
}int main() {/** 1.无限次机会* 2.提示大了或小了* 提示总共猜了多少次*/// 得到一个随机数1~100范围int random_number = get_random_number(1, 100);int input_number;// 提示用户输入数字进行猜测do{cout << "请输入一个1~100的数字进行猜测:" << endl;cin >> input_number;int guess_count = 1;cout << "不好意思你猜错了" << endl;// 提示大了或小了if (input_number > random_number) {cout << "您输入的数字大了,请重新猜测" << endl;cin >> input_number; //控制因子的更新// 提示总共猜了多少次guess_count++;}else if (input_number < random_number) {cout << "您输入的数字小了,请重新猜测" << endl;cin >> input_number; //控制因子的更新// 提示总共猜了多少次guess_count++;}else cout << "恭喜你猜对了" << endl;cout << "恭喜你猜对了,总共猜了" << guess_count << "次" << endl;return 0;} while (input_number != random_number);
}17.while循环嵌套

18.while循环嵌套练习题讲解

🏋️♀️ 练习:坚持瘦身
小明有点儿胖,决定想要减肥,请通过嵌套循环,描述小明的心态,实现如下输出:
(输出效果大致如下,每天进行3次400米冲刺训练,每做完一次输出当前进展,做完3次后减重1斤并更新体重,持续5天),例如:
今天是减肥的第1天!
开始做减肥第1天的第1个俯卧撑!
开始做减肥第1天的第2个俯卧撑!
开始做减肥第1天的第3个俯卧撑!
减重第1天的3次共400米冲刺跑完,体重减少1斤,目前累计减掉体重:1斤!今天是减肥的第2天!
开始做减肥第2天的第1个俯卧撑!
...
减重第2天的3次共400米冲刺跑完,体重减少1斤,目前累计减掉体重:2斤!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;/*** 细节点:* 1. 外层循环完成5天的减肥* 2. 内层循环进行:三次俯卧撑(三次完成减少1斤体重)、三次400米冲刺(三次完成减少1斤体重)* 3. 过程中要累计其体重减少*/int main()
{cout << "有点胖需要减掉10斤体重,计划5天,每天目标2斤体重。加油!" << endl;// 外层循环完成5天的减肥int day = 1; // 减肥日的周期int sum = 0; // 累计体重减少while (day <= 5) { //减肥控制5天cout << "今天是减肥的第" << day << "天" << endl;// 俯卧撑三次控制int sport = 1;while (sport <= 3) {cout << "今天做减肥第" << day << "天的第" << sport << "次俯卧撑\t" ;sport++;}cout << endl;sum+=1;cout << "减肥第" << day << "天的3个俯卧撑做完,体重减少1斤,累计减少" << sum << "斤" << endl;// 400米冲刺三次控制int sprint = 1;while (sprint <= 3) {cout << "今天做减肥第" << day << "天的第" << sprint << "次400米冲刺\t" ;sprint ++;}sum += 1;cout << endl;cout << "减肥第" << day << "天的3个400米冲刺做完,体重减少1斤,累计减少" << sum << "斤" << endl;cout << endl;day++; // 循环控制因子更新,每一天完事day+1}return 0;
}
19.while循环嵌套案例(九九乘法表)

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;/** 打印九九乘法表* 1. 外层循环控制行,内层控制列* 2. \t分隔内层循环的输出,行和行之间有换行分隔* 1x1=1* 1x2=2 2x2=4* 1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9* 1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16* 1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25* 1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36* 1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49* 1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64* 1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81*/int main() {// 1.通过外层循环输出9行int line = 1; // 外层循环控制因子,从1开始while (line <=9) {// 2.内层循环int column = 1; // 内层循环控制因子while (column <= line) {cout << column << "x" << line << "=" << column*line << "\t"; // \t对齐效果column++;}cout << endl; // 内循环结束换行line ++; // 外层循环控制因子更新}return 0;
}输出:
1x1=1
1x2=2 2x2=4
1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9
1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16
1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25
1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36
1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49
1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64
1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81
20.for循环语句
语法:

执行顺序:(与while循环对比学习)

条件判断语句可省略(但是不建议这么做),写法示例:
for (int i = 1; ; i += 2) {cout << i << " ";}循环控制因子的创建也可以省略,写法如下:
int num = 0;
for (; i<= 20 ; i += 2) {cout << i << " ";}循环控制因子的更新也可以省略(但是可能造成无限循环,不建议省略),示例:
for (int i = 1; i<= 20 ; ) {cout << i << " ";}21.for循环的嵌套

示例:99乘法表for循环写法:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main() {for (int i = 1; i<=9; i++) {for (int j = 1; j<=i; j++) {cout << j << "x" << i << "=" << i*j << "\t";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}22.for循环练习题讲解

#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;/*** for循环猜数字,提供无限次机会,猜错了提示大了或小了* 使用bool型作为条件判断依据,猜对了置为false,猜错了依旧是true* 不需要循环因子更新语句 (在循环体内,通过if判断来修改)*/
int get_random_num(int min, int max)
{// 创建一个随机数生成器random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());// 定义一个均匀分布的整数范围uniform_int_distribution<> dis(min, max);// 生成一个随机数并输出 (注:原注释中是“并输出”,但代码中是返回)int random_number = dis(gen);return random_number;
}int main()
{// 获取一个随机数字int num = get_random_num(1, 10);// 要求用户猜测(第一次)int guess_num;cout << "请输入一个数字:";cin >> guess_num;// for循环判断并继续执行猜测流程for (bool is_continue = true; is_continue;) {if (guess_num == num) {cout << "恭喜你,猜对了!" << endl;is_continue = false; // 手动更改循环因子的值并结束循环}else if (guess_num > num) {cout << "你猜的数字太大了,请重新输入:";cin >> guess_num;}else {cout << "你猜的数字太小了,请重新输入:";cin >> guess_num;}}return 0;
}23.变量的作用域


24.循环中断语句continue和break


// 程序会输出0-9,字符串一次都不会输出,因为遇到continue会跳过本次循环,并继续下一次循环for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << i << ' ';continue;cout << "This will not be printed" << endl;}// 程序会输出0,字符串和其余数字不会被输出,因为break直接跳出循环,不再执行后续代码for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {cout << i << ' ';break;cout << "This will not be printed" << endl;}return 0;continue和break的作用范围都仅对当前循环语句起作用,嵌套的循环也一样。
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;int main() {// 通过for循环输出1到20之间的奇数for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i ++) {if (i % 2 == 0) {continue; // 跳过本次循环,进入下一次}cout << i << " ";}cout << endl;// 通过for循环输出1-20for (int i = 1; true; i ++) {if (i > 20)break;cout << i << " ";}return 0;
}25.循环综合案例-发工资

答案:
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;// 随机数生成器函数
int get_random_num(int min, int max) {random_device rd;mt19937 gen(rd());uniform_int_distribution<> distrib(min, max);return distrib(gen);
}int main() {// 1.定义一个变量记录余额int money = 10000;// 2.for循环进入发工资流程for (int id = 0; id <= 20; id++) {// 如果工资发完了,结束发工资if (money <= 0) {cout << "工资发完了,请下个月再来" << endl;break;}// 随即得到绩效分int score = get_random_num(0, 10);if (score < 5) {cout << "不好意思,员工:" << id << ",绩效分" << score << ",小于5分,不发工资" << endl;continue;}// 未跳过即为满足条件,开始发放工资money -= 1000;cout << "员工:" << id <<"," << "领取工资1000,当前余额:" << money << "元" << endl;}return 0;
}26.goto语句

#include <iostream>
#include <random>
using namespace std;/** label A:*** label B:*** label C:*** goto A/B/C***/int main() {int i = 1;loop:i++;if (i <= 10) {goto loop;}cout << i << endl;return 0;
}输出:
11