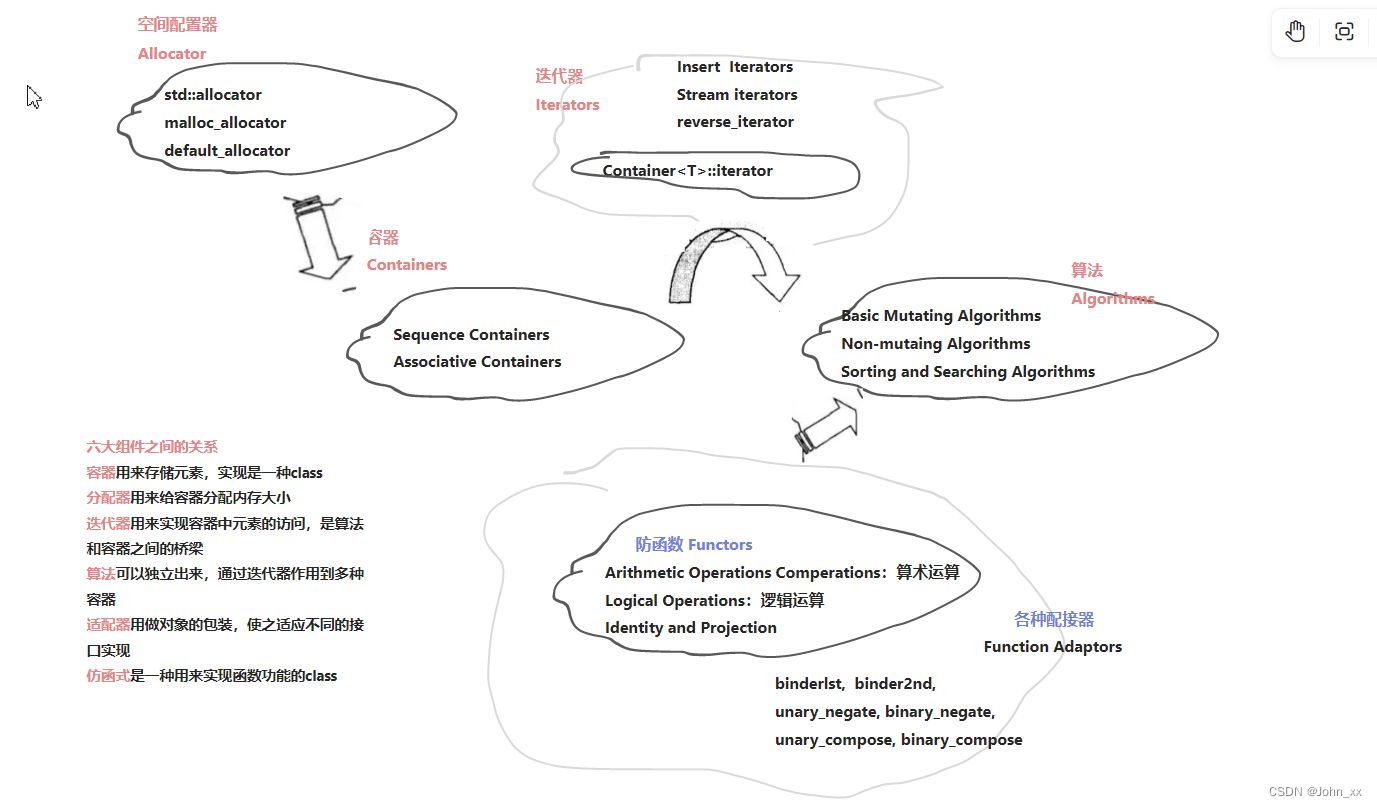
C++:STL架构图
STL架构图
- 1:仿函数
- 2:算法
架构图
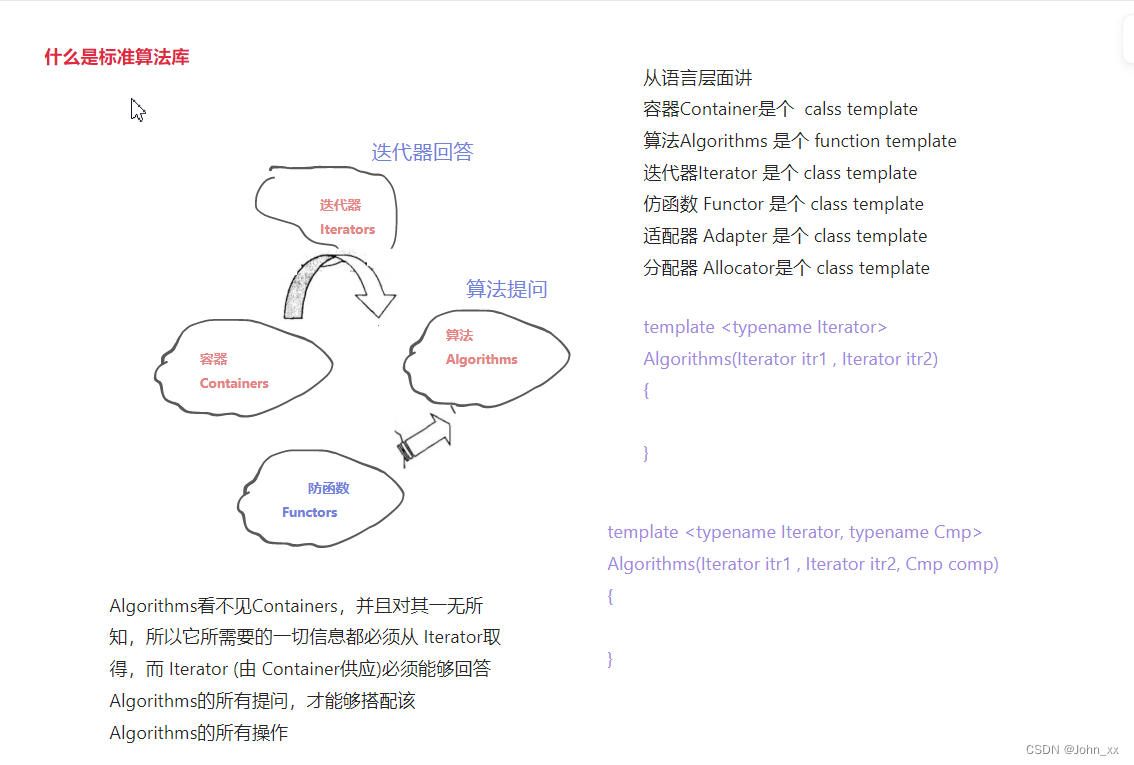
算法库
再看一下这个实例
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{int i[6] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};vector<int,allocator<int>> vec (i,i+6);for (auto& elem : vec){std::cout << elem << " ";}cout <<endl;// 相当于x<6是否成立,用于判定那些小于6的元素cout<< "there are " << count_if(vec.begin(),vec.end(),bind2nd(less<int>(), 6)) << " elements that are less than 6" <<endl;// 相当于3<x是否成立,用于判定那些大于3的元素cout << "there are " << count_if(vec.begin(),vec.end(),bind1st(less<int>(), 3)) << " elements that are not less than 3" << endl;return 0;
}
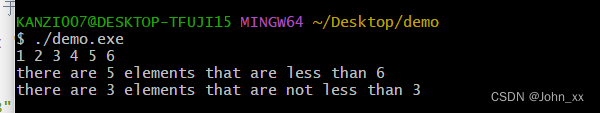
- vector 通过数组构建,container的使用
- allocator 是容器构建中使用的分配器
- count_if 是算法一种,符合if 条件则计数
- vec.begin(),vec.end()调用的是迭代器
- bind1st,bind2nd 是一种 function adapter
- less() 获取一个 function object (仿函数)
容器的基础
容器中的元素在 [ c.begin(), c.end()) 之间,当迭代器遍历到 c.end()时候,实际已经脱离了容器的元素区间。
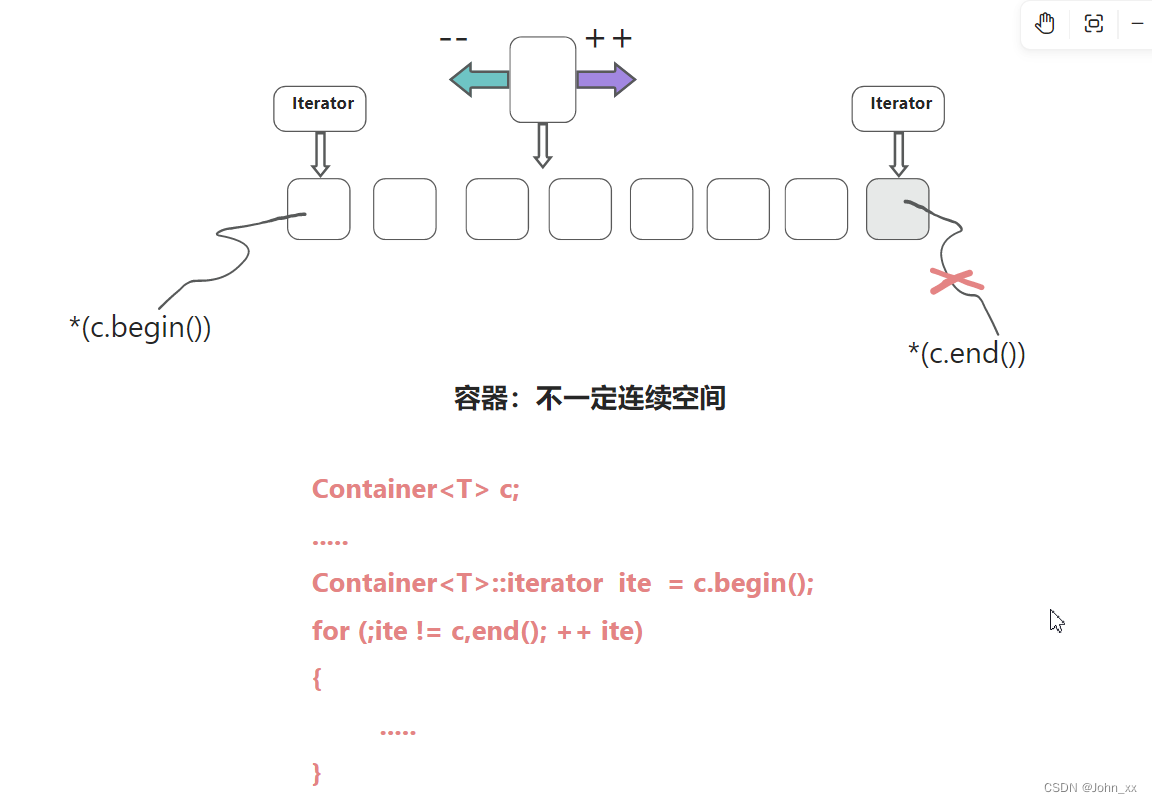
基本遍历
使用for 循环进行遍历
std::vector<double> vec;
for (auto& elem : vec){std::cout << elem << std::endl;
}
1:仿函数
🚀定义
所谓的仿函数(functor),是通过重载()运算符模拟函数形为的类。因此,这里需要明确两点:
- 仿函数不是函数,它是个类;
- 仿函数重载了()运算符,使得它的对你可以像函数那样子调用(代码的形式好像是在调用函数)。
2:算法
STL算法特征
🚀🚀🚀
- STL算法本身是一种函数模版
- 通过迭代器获得输入数据
- 通过函数对象对数据进行处理
- 通过迭代器将结果输出
- STL算法是通用的,独立于具体的数据类型、容器类型。
