day26 SpringBootWeb案例(二)
目录
SpringBootWeb案例
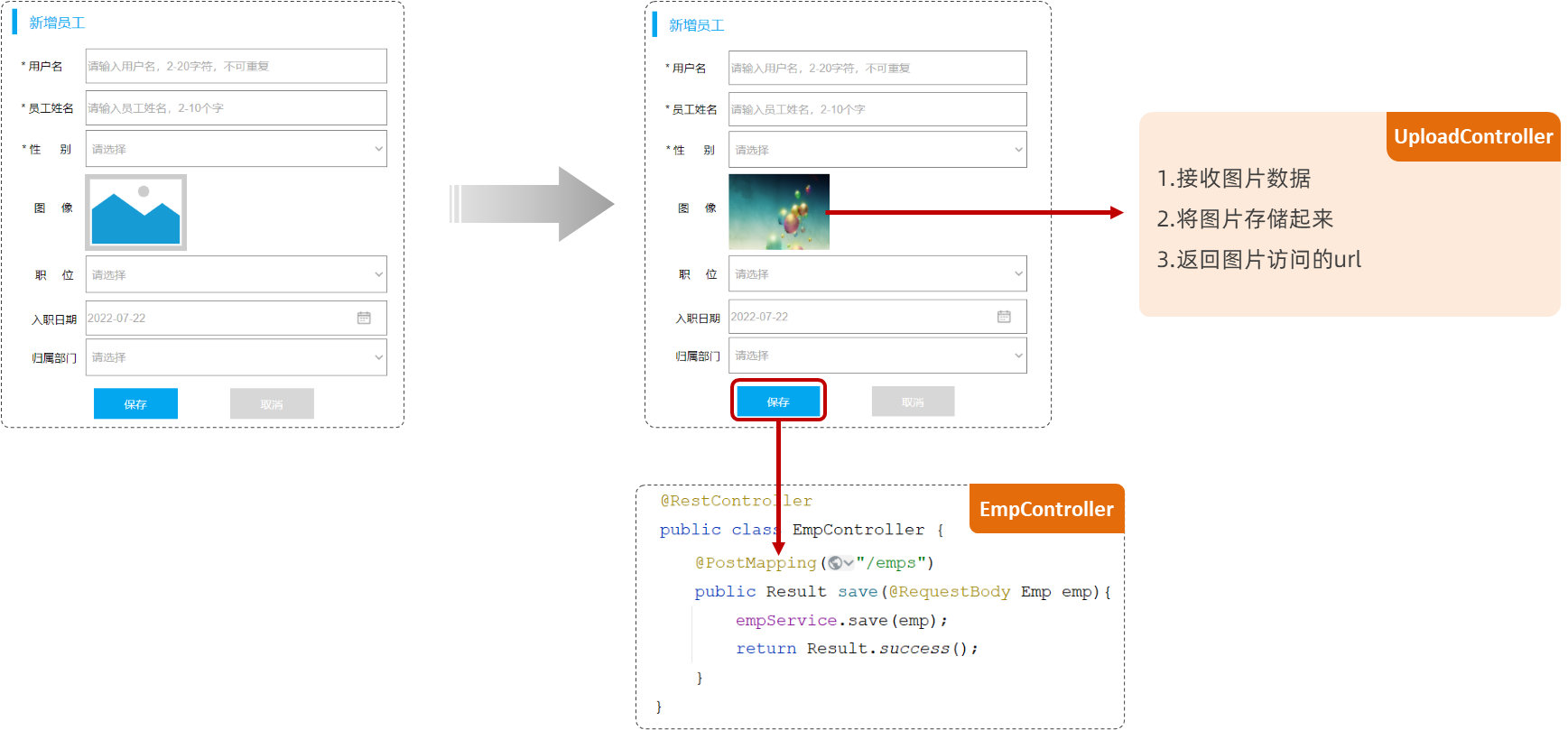
1. 新增员工
1.1 需求
1.2 开发
1.3 测试
2. 文件上传
2.1 简介
2.2 本地存储
2.3 阿里云OSS
3. 配置文件
3.1 @Value
3.2 yml配置
3.3 @ConfigurationProperties
4. 修改员工
4.1 需求
4.2 查询回显
4.3 保存修改
SpringBootWeb案例
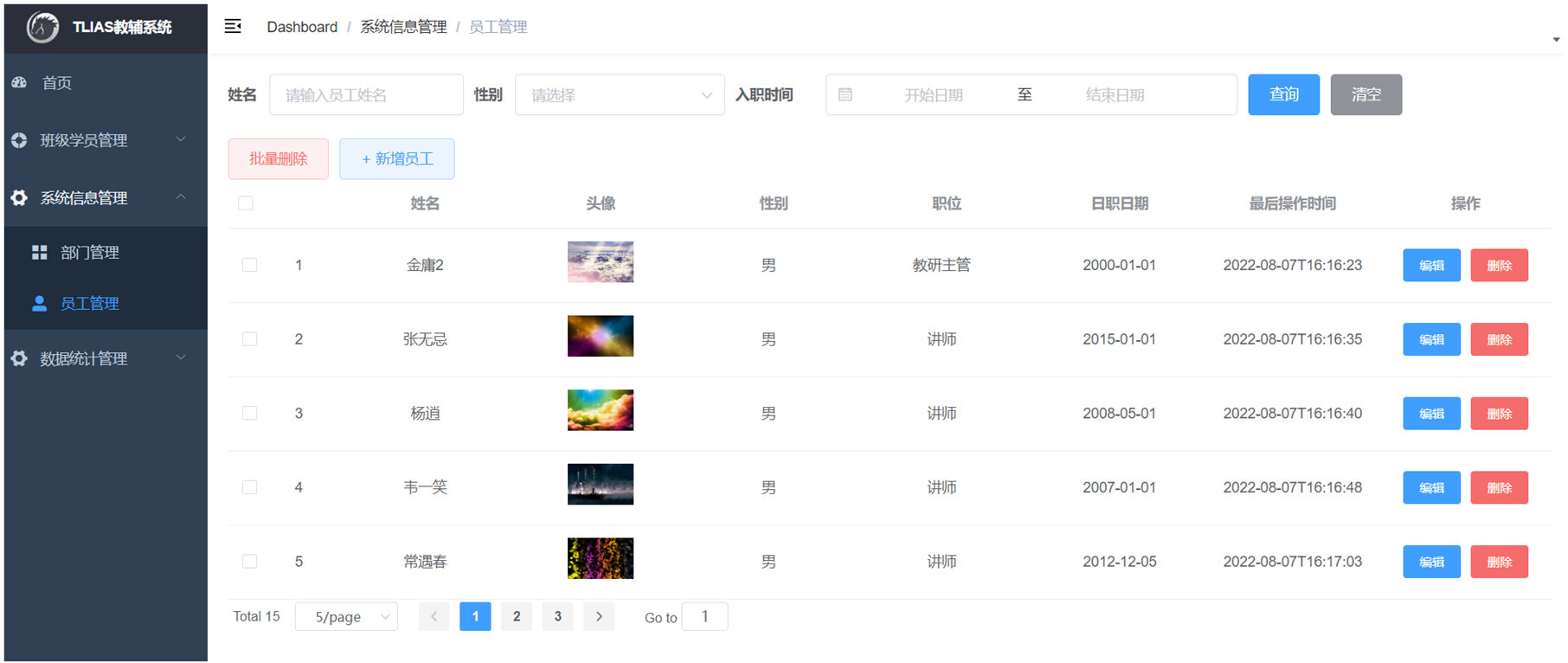
前面我们已经实现了员工信息的条件分页查询 以及 删除操作。 关于员工管理的功能,还有两个需要实现:
- 新增员工
- 修改员工
今天我们的内容包括以下四个部分的内容:
- 新增员工
- 文件上传
- 配置文件
- 修改员工
1. 新增员工
1.1 需求

在新增用户时,我们需要保存用户的基本信息,并且还需要上传的员工的图片,目前我们先完成第一步操作,保存用户的基本信息。
我们可以看一下接口文档,参照接口文档,进行功能的开发。
1.2 开发
新增员工,最终呢,我们就是需要往数据库表结构中插入数据。具体的流程为:

1). EmpMapper
//保存员工信息
@Insert("insert into emp (username, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time) " +
"values (#{username}, #{name}, #{gender}, #{image}, #{job}, #{entrydate}, #{deptId}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime});")
void save(Emp emp);2). EmpService / EmpServiceImpl
EmpService
/**
* 保存员工信息
* @param emp
*/
void save(Emp emp);EmpServiceImpl
@Override
public void save(Emp emp) {emp.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());emp.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());empMapper.save(emp);
}3). EmpController
//新增
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody Emp emp){empService.save(emp);return Result.success();
}1.3 测试
代码编写完毕后,启动服务器,打开Postman发送 POST 请求,请求连接:http://localhost:8080/emps

新增员工基本信息,我们已经保存到数据库了。那接下来,我们要来完成的是员工图像的上传。

2. 文件上传
2.1 简介
- 文件上传,也称为upload,是指将本地图片、视频、音频等文件上传到服务器上,可以供其他用户浏览或下载的过程。
- 文件上传在项目中应用非常广泛,我们经常发微博、发微信朋友圈都用到了文件上传功能。
2.1.1 前端代码
在resources文件夹中创建一个fileupload.html网页文件,如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>文件上传</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">姓名: <input type="text" name="name"/><br/>年龄: <input type="text" name="age"/></br>图片: <input type="file" name="image"/><br/><br/><input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form></body>
</html>上传文件的原始form表单,要求表单必须具备以下三点(上传文件页面三要素):
- 表单必须有 file 域,用于选择要上传的文件。
- 表单提交方式必须为 POST。
- 表单的编码类型enctype必须要设置为 multipart/form-data。
如果我们加上 enctype="multipart/form-data",代表的是我们请求的数据是多部分的,通过浏览器的开发者工具( firefox浏览器 ),我们也可以看到请求的数据:

请求体的数据,也是分为多个部分:

2.1.2 后端代码
在服务端,我们要想接收上传上来的文件,需要使用Spring给我们提供的一个,专门接收文件的API : MultipartFile。
import com.itheima.pojo.Result;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;@RestController
public class UploadController {@PostMapping("/upload")public Result upload(MultipartFile image) throws IOException {System.out.println(image.getName)return Result.success();}}上传上来的文件,其实呢,是暂存在系统的临时文件中了。 我们可以通过debug,就可以看出来。
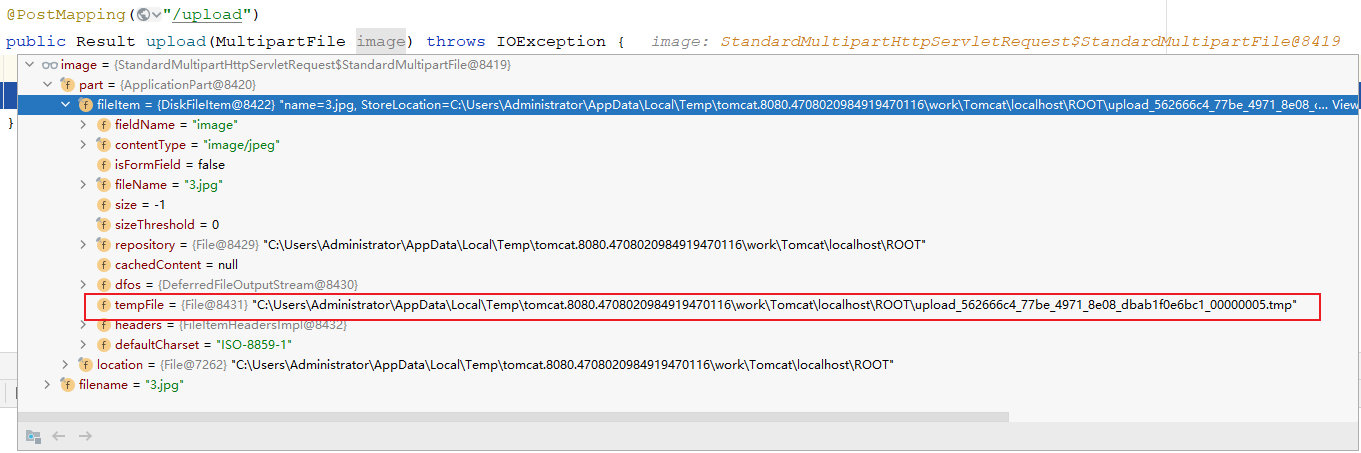
当我们,程序运行完毕之后,这个临时文件会自动删除。
所以,我们如果想上传文件,需要将这个临时文件,要转存到我们的磁盘目录中。
2.2 本地存储
对于这个图片上传功能呢,主要分为两部操作:
- 选择文件,进行图片上传,将图片文件上传到服务器存储起来,然后返回图片访问的URL。
- 当点击保存时,除了页面的基本表单数据需要提交到服务端,图片访问的URL,也需要提交到服务端。
2.2.1 代码实现
我们先来完成第一部分,将上传的图片保存在本地磁盘目录。
package com.itheima.controller;import com.itheima.pojo.Result;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.UUID;@RestController
public class UploadController {@Autowiredprivate AliOSSUtils aliOSSUtils;//上传至本地服务器@PostMapping("/upload")public Result upload(MultipartFile image) throws IOException {//获取原始文件名String originalFilename = image.getOriginalFilename();//构建新的文件名String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));//将文件保存在服务器端 E:/images/ 目录下image.transferTo(new File("E:/images/"+newFileName));return Result.success();}}MultipartFile 常见方法:
getOriginalFilename():获取原始文件名
getContentType():获取文件的类型
getInputStream():获取文件的输入流
transferTo(File dest) :将上传的文件保存到目标文件中(Mac中测试有问题,可以使用流获取数据拷贝方式)
getBytes():获取文件的字节数组
如果transferTo方法在Mac中测试会报错,提示找不到临时文件:

此时可以使用获取流的方式,通过流来拷贝。流的操作可以使用commons-io框架,依赖如下:
<dependency><groupId>commons-io</groupId><artifactId>commons-io</artifactId><version>2.11.0</version>
</dependency>示例如下:
import com.itheima.tlias.pojo.Result;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestPart;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;@RestControllerpublic class FileUploadController {/*** 文件商城api* @param image 接收文件* @param name 接收前端传过来的name* @param age 接收前端端传过来的age* @return*/@PostMapping("/upload")public Result uploadFile(@RequestPart("image") MultipartFile image, String name, Integer age) {//获取原始名称String originalFilename = image.getOriginalFilename();//目标文件File dest = new File("tlias/serverfile", originalFilename);try {//使用commons-io框架进行文件拷贝FileUtils.copyInputStreamToFile(image.getInputStream(),dest);return Result.success("提交成功:"+originalFilename + "," + name + "," + age);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();return Result.error(e.getMessage());}}}2.2.2 测试
可以直接使用我们准备好的文件上传的页面进行测试。
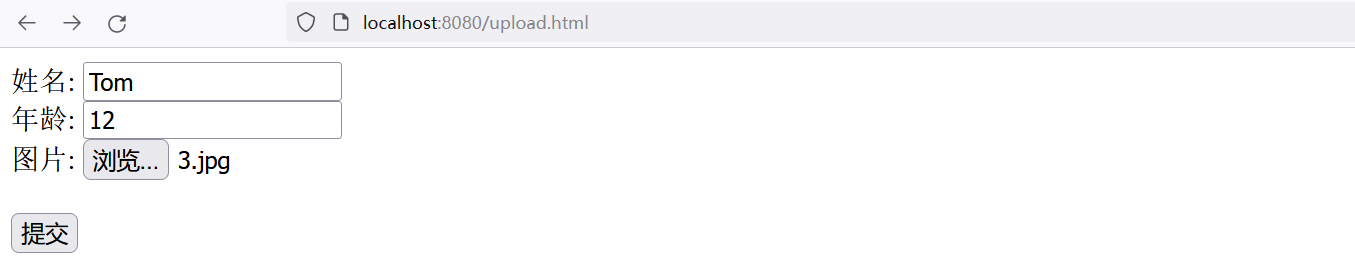
我们也可以使用postman来进行测试。

2.2.3 配置
在我们进行图片上传的测试中,我们发现,有时候可以上传成功,而有时候呢,又不能上传成功,报出如下错误。

报错我原因呢,是因为:在SpringBoot中,文件上传,默认单个文件允许最大大小为 1M,如果需要上传大文件,可以在application.properties进行如下配置:
#配置单个文件的最大上传大小
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB#配置单个请求最大上传大小(一次请求可以上传多个文件)
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB2.2.4 问题分析
我们现在上传的文件呢都是存储在本地电脑上的,将来程序部署到服务器之后,那这些图片就存在服务器的本地磁盘中。

如果直接存储在服务器的磁盘目录中,存在以下缺点:
- 不安全:磁盘如果损坏,所有的文件就会丢失。
- 容量有限:如果存储大量的图片,磁盘空间有限(磁盘不可能无限制扩容)。
- 无法直接访问
为了解决上述问题呢,一般有两种解决方案:
- 自己搭建文件存储系统,如:fastDFS
- 自己搭建对象存储服务,如:MinIO
- 使用现成的云服务,如:阿里云,腾讯云,华为云

2.3 阿里云OSS
2.3.1 介绍
阿里云对象存储OSS(Object Storage Service)是一款海量、安全、低成本、高可靠的云存储服务,提供99.9999999999% (12个9)的数据持久性,99.995%的数据可用性。多种存储类型供选择,全面优化存储成本。

2.3.2 步骤

SDK:Software Development Kit 的缩写,软件开发工具包。这是一个覆盖面相当广泛的名词,辅助开发某一类软件的相关文档、范例和工具的集合都可以叫做SDK。
注册完账号之后,就可以登录阿里云:

点击控制台,然后找到 对象存储OSS 服务。

如果是第一次访问,还需要开通 对象存储服务OSS。


开通之后,就可以进入到阿里云对象存储的控制台。

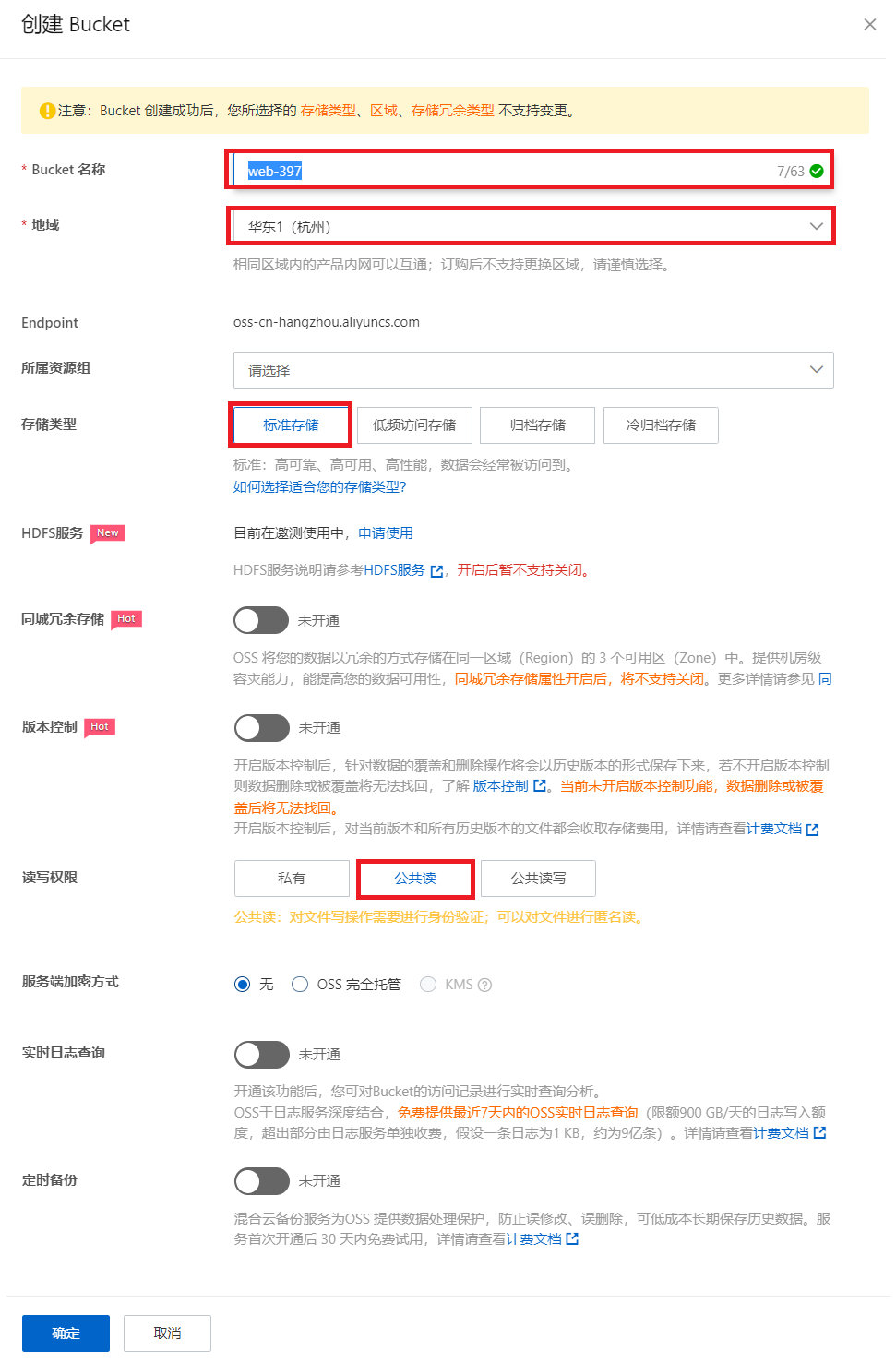
点击左侧的 "Bucket列表",然后创建一个Bucket。

2.3.3 文件上传
参照官方提供的SDK,改造一下,即可实现文件上传功能。
1). pom.xml
<dependency><groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId><artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId><version>3.15.0</version>
</dependency>2). 测试文件上传
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientException;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSException;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;public class AliOssTest {@Testpublic void testOss(){// Endpoint以华东1(杭州)为例,其它Region请按实际情况填写。String endpoint = "换成自己的";// 阿里云账号AccessKey拥有所有API的访问权限,风险很高。强烈建议您创建并使用RAM用户进行API访问或日常运维,请登录RAM控制台创建RAM用户。String accessKeyId = "换成自己的";String accessKeySecret = "换成自己的";// 填写Bucket名称,例如examplebucket。String bucketName = "换成自己的";// 填写Object完整路径,完整路径中不能包含Bucket名称,例如exampledir/exampleobject.txt。String objectName = "0001.jpg";// 填写本地文件的完整路径,例如D:\\localpath\\examplefile.txt。// 如果未指定本地路径,则默认从示例程序所属项目对应本地路径中上传文件流。String filePath= "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Pictures\\Saved Pictures\\10.jpg";// 创建OSSClient实例。OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);try {InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);// 创建PutObject请求。ossClient.putObject(bucketName, objectName, inputStream);} catch (OSSException oe) {System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());} catch (Exception ce) {System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "+ "such as not being able to access the network.");System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());} finally {if (ossClient != null) {ossClient.shutdown();}}}
}在上述的代码中,需要替换的内容为:
- accessKeyId:阿里云账号AccessKey
- accessKeySecret:阿里云账号AccessKey对应的秘钥
- bucketName:Bucket名称
- objectName:对象名称,在Bucket中存储的对象的名称
- filePath:文件路径
2.3.4 案例集成OSS
1). 引入阿里云OSS文件上传工具类(由官方SDK改造而来) -- 资料中已提供
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;/*** 阿里云 OSS 工具类*/
@Component
public class AliOSSUtils {private String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";private String accessKeyId = "替代为自己的accessKeyId";private String accessKeySecret = "替代为自己的accessKeySecret";private String bucketName = "替代为自己的bucketName";/*** 实现上传图片到OSS*/public String upload(MultipartFile multipartFile) throws IOException {// 获取上传的文件的输入流InputStream inputStream = multipartFile.getInputStream();// 避免文件覆盖String fileName = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss")) + multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();//上传文件到 OSSOSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);ossClient.putObject(bucketName, fileName, inputStream);//文件访问路径String url = endpoint.split("//")[0] + "//" + bucketName + "." + endpoint.split("//")[1] + "/" + fileName;// 关闭ossClientossClient.shutdown();return url;// 把上传到oss的路径返回}}2). 上传图片功能升级改造
在原有的UploadController的基础上进行升级改造
@RestController
public class UploadController {@Autowiredprivate AliOSSUtils aliOSSUtils;//上传至本地服务器/*@PostMapping("/upload")public Result upload(MultipartFile image) throws IOException {//获取原始文件名String originalFilename = image.getOriginalFilename();//构建新的文件名String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));//将文件保存在服务器端 E:/images/ 目录下image.transferTo(new File("E:/images/"+newFileName));return Result.success();}*/@PostMapping("/upload")public Result upload(MultipartFile image) throws IOException {String url = aliOSSUtils.upload(image);return Result.success(url);}}3). 测试


4). 联调测试

3. 配置文件
3.1 @Value
在上述的案例中,关于阿里云的相关配置信息,我们是直接写死在java代码中了,这样做,功能虽然实现了,但是是不便于维护和管理的。 为了解决这个问题呢,我们可以将其配置在properties的配置文件中。如下:
#自定义的阿里云OSS配置信息
aliyun.oss.endpoint=替换为自己的
aliyun.oss.accessKeyId=替换为自己的
aliyun.oss.accessKeySecret=替换为自己的
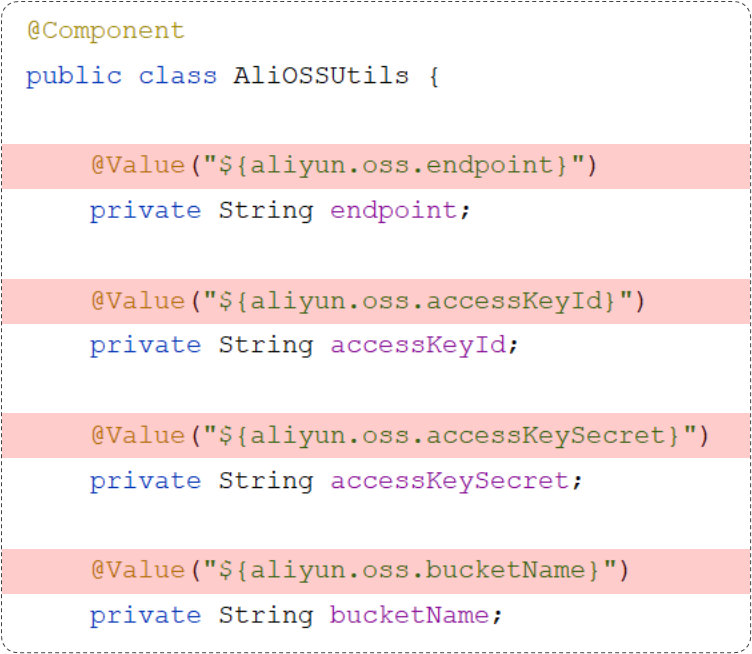
aliyun.oss.bucketName=替换为自己的配置在了配置文件之后,如果我们想在java代码中使用。 我们可以直接通过@Value注解,就可以加载并读取配置文件中的配置项,具体形式为:@Value("${key}")
@Component
public class AliOSSUtils {// private String endpoint = "替换为自己的";
// private String accessKeyId = "替换为自己的";
// private String accessKeySecret = "替换为自己的";
// private String bucketName = "替换为自己的";@Value("${aliyun.oss.endpoint}")private String endpoint;@Value("${aliyun.oss.accessKeyId}")private String accessKeyId;@Value("${aliyun.oss.accessKeySecret}")private String accessKeySecret;@Value("${aliyun.oss.bucketName}")private String bucketName;//其他代码省略}- @Value 注解通常用于外部配置的属性注入,具体用法为: @Value("${配置文件中的key}")
3.2 yml配置
3.2.1 介绍
前面我们一直使用springboot项目创建完毕后自带的application.properties进行属性的配置,那其实呢,在springboot项目中提供了多种属性的配置方式:
- application.properties
server.port=8080
server.address=127.0.0.1- application.yml
server:port: 8080address: 127.0.0.1- application.yaml
server:port: 8080address: 127.0.0.1我们看到,配置同样的数据信息,yml格式的数据呢,有以下特点:
- 容易阅读
- 容易与脚本语言交互
- 以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
yml 格式的配置文件,后缀名有两种:
- yml (推荐)
- yaml
3.2.2 基本语法
- 大小写敏感
- 数值前边必须有空格,作为分隔符
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,缩进时,不允许使用Tab键,只能用空格(idea中会自动将Tab转换为空格)
- 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
- 表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略

3.2.3 基本格式
- 对象/Map集合
user:name: zhangsanage: 18password: 123456- 数组/List/Set集合
hobby: - java- game- sport3.2.4 配置改造
将原来使用的application.properties 改名为 _application.properties(名字随便一换,springboot就加载不到了)。然后创建新的配置文件 application.yml,然后再将application.properties 改造称为 application.yml。
改造后效果如下:
spring:datasource:driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tliasusername: rootpassword: rootservlet:multipart:max-file-size: 10MBmax-request-size: 100MBmybatis:configuration:log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplmap-underscore-to-camel-case: truealiyun:oss:endpoint: 替换为自己的accessKeyId: 替换为自己的accessKeySecret: 替换为自己的bucketName: 替换为自己的3.2.5 问题分析
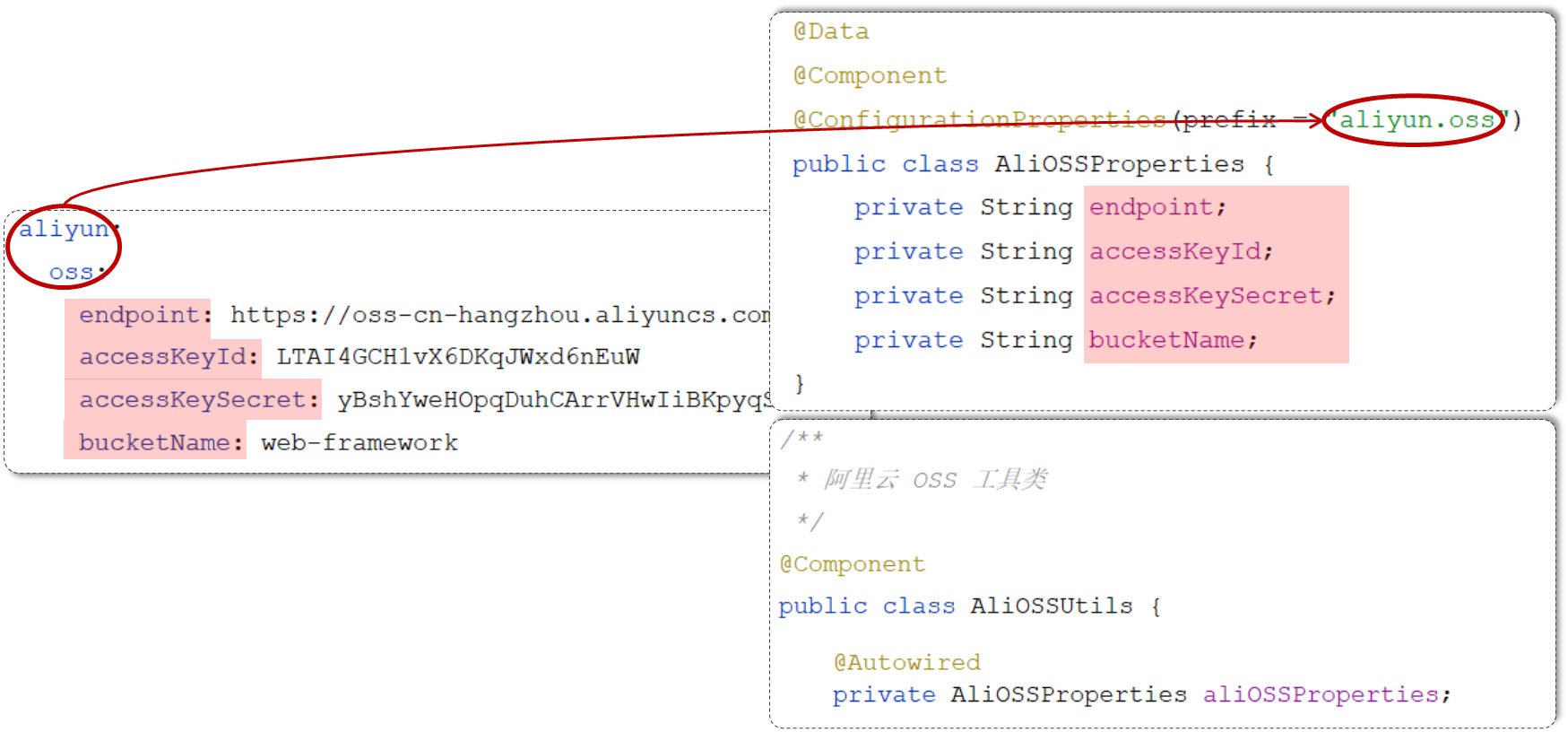
我们在 application.properties 或者 application.yml 中配置了自定义的信息之后,如果需要在 java 需要注入这些属性,我们直接直接通过@Value注解来进行注入,这种方式没有问题。 但是如果说需要注入的属性较多,我们写起来会比较繁琐,此时我们可以通过 @ConfigurationProperties 来简化。
3.3 @ConfigurationProperties
1). 定义实体类,用于封装需要注入的属性。
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "aliyun.oss") //指定配置文件
public class AliOSSProperties {private String endpoint;private String accessKeyId;private String accessKeySecret;private String bucketName;
}2). 在工具类中,注解注入上述的bean对象,然后调用get方法就可以获取到各个属性
4. 修改员工
4.1 需求


在进行修改员工信息的时候,我们首先先要根据员工的ID查询员工的信息用于页面回显展示,然后用户修改员工数据之后,点击保存按钮,就可以将修改的数据提交到服务端,保存到数据库。 所以呢,分为两部操作:
- 根据ID查询员工信息
- 保存修改
4.2 查询回显
查询回显,就是根据ID查询员工的信息,用于页面回显展示。接下来,我们就需要参考接口文档进行开发:

1). EmpMapper
//根据ID查询员工信息
@Select("select * from emp where id = #{id}")
Emp getById(Integer id);2). EmpService / EmpServiceImpl
EmpService
/**
* 根据ID查询员工
* @param id
* @return
*/
Emp getById(Integer id);EmpServiceImpl
@Override
public Emp getById(Integer id) {return empMapper.getById(id);
}3). EmpController
//根据id查询
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Integer id){Emp emp = empService.getById(id);return Result.success(emp);
}4). 测试
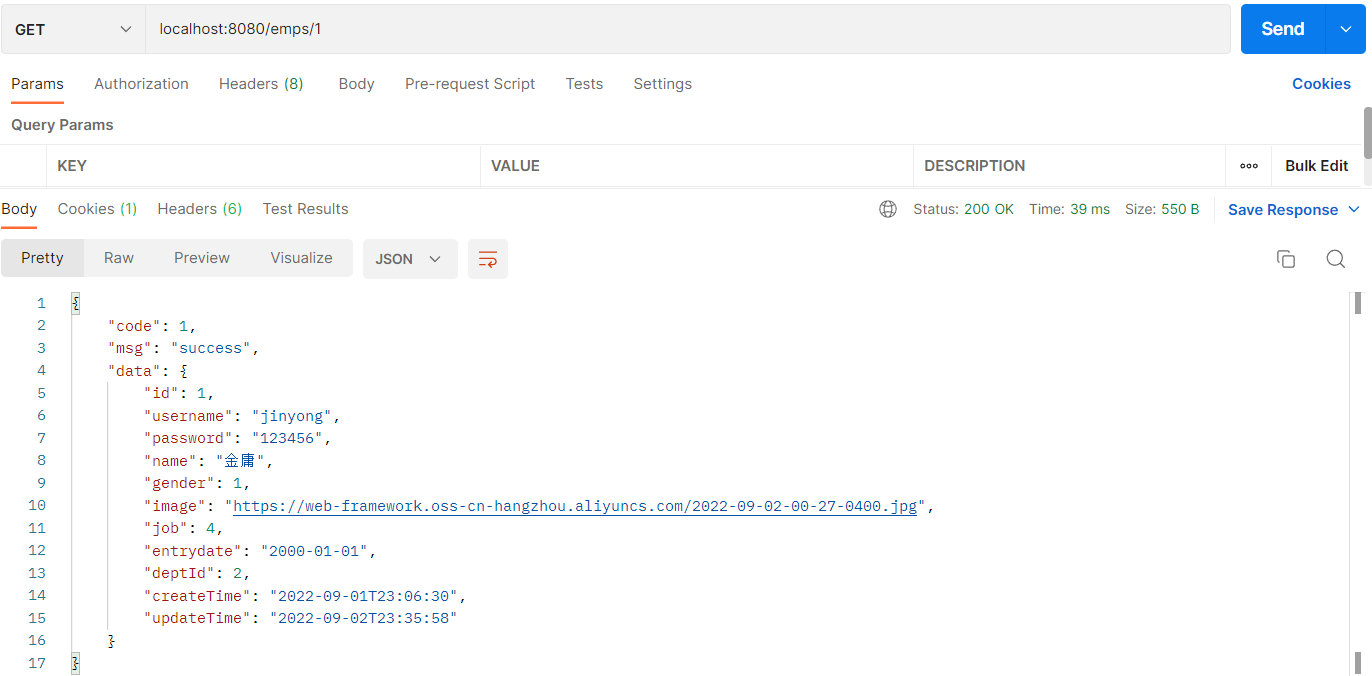
代码编写完毕后,启动服务器,打开Postman发送 GET 请求,请求连接:http://localhost:8080/emps/1
4.3 保存修改

当用户修改完数据之后,点击保存按钮,就需要将数据提交到服务端,然后服务端需要将数据保存到数据库中。 具体的执行流程为:

接下来,我们就可以根据接口文档进行功能开发了。
1). EmpMapper
EmpMapper接口
//修改员工信息
void update(Emp emp);EmpMapper.xml
<update id="update">update emp<set><if test="username != null and username != ''">username = #{username},</if><if test="password != null and password != ''">password = #{password},</if><if test="name != null and name != ''">name = #{name},</if><if test="gender != null">gender = #{gender},</if><if test="image != null and image != ''">image = #{image},</if><if test="job != null">job = #{job},</if><if test="entrydate != null">entrydate = #{entrydate},</if><if test="deptId != null">dept_id = #{deptId},</if><if test="updateTime != null">update_time = #{updateTime}</if></set>where id = #{id}
</update>2). EmpService / EmpServiceImpl
EmpService
/**
* 更新员工
* @param emp
*/
void update(Emp emp);EmpServiceImpl@Override
public void update(Emp emp) {emp.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); //更新修改时间为当前时间empMapper.update(emp);
}3). EmpController
//修改
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Emp emp){empService.update(emp);return Result.success();
}4). 测试

5). 联调测试