Google Guice 5:AOP
1. AOP
1.1 实际开发中面临的问题
-
在实际开发中,经常需要打印一个方法的执行时间,以确定是否存在慢操作
-
最简单的方法,直接修改已有的方法,在
finnally语句中打印耗时@Override public Optional<Table> getTable(String databaseName, String tableName) {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {... // 省略关键代码return result;}... // 省略catch语句finally {long consumedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;logger.info("getTable() -- databaseName: %s, tableName: %s, consumed time: %dms", databaseName, tableName, consumedTime);} } -
随着打印耗时的需求增多,你会发现整个应用程序中存在很多打印耗时的代码
-
这些代码如果按照OOP(
Object Oriented Programming)编程的思想,是无法抽象出来复用的,因为它与方法的执行是紧耦合的 -
而且随着需求的增多,安全检查、权限校验、审计日志等附加功能的代码,会使得整个方法越来越臃肿,以致难以阅读
-
同时,如果附加功能的逻辑发生变化,将牵一发而动全身
1.2 AOP编程
-
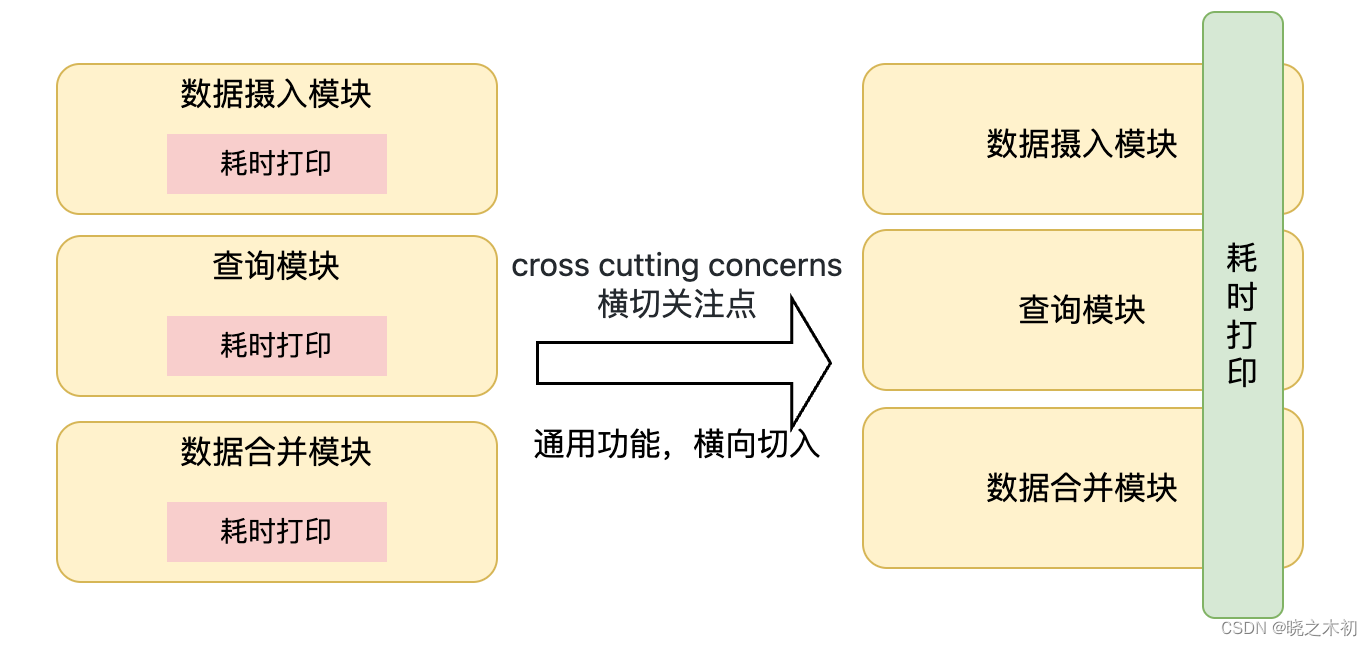
这时,我们希望有一种编程范例,能将这些公共的代码从方法中剥离出来,并切入到有需要的方法中
-
这种范例叫做AOP(
Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向切面编程) -
它将问题划分成了不同的面(
Aspect),在程序编译或运行阶段可以将这些面插入到需要的地方,以实现辅助功能与核心逻辑的解耦以及代码的复用 -
维基百科对AOP的描述如下:
- In computing, aspect-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns.
在计算机领域,AOP是一种允许横切关注以增加代码模块化的编程范例 - It does so by adding behavior to existing code (an advice) without modifying the code itself, instead separately specifying which code is modified via a “pointcut” specification, such as “log all function calls when the function’s name begins with ‘set’”.
它可以在不修改代码本身的情况下,向已有的代码添加行为(an advice),通过 "pointcut"规范来单独指定修改哪些代码,例如:记录所有以set开头的函数的调用 - This allows behaviors that are not central to the business logic (such as logging) to be added to a program without cluttering the code core to the functionality.
这样可以允许将不属于业务核心逻辑的行为(如日志打印)添加到程序中,并不会导致功能的代码核心紊乱
- In computing, aspect-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns.
-
上述的第二点,笔者觉得维基百科的描述可能存在一定问题:
- advice,通知,是对被拦截到的方法需要执行的代码(又叫增强),可以是前置、后置、最终、异常、环绕通知五类。以环绕通知为例,就是在方法执行前后需要执行的代码
- pointcut: joint point是连接点的意思,即可能需要注入切面的地方;而pointcut用于定义需要特殊处理的连接点
1.3 Srping AOP的常见术语
-
使用过Spring进行AOP编程的小伙伴,可能会注意到Aspect、Pointcut、Advice(Before、After、AfterReturning、AfterThrowing、Around)这些类似的关键字
-
在Spring AOP中,有很多术语,但最常使用的还是上面三种术语
-
下面是一段打印controller请求参数的AOP代码
@Component @Aspect // 表示这是一个切面 public class ControllerParamsLogAspect {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ControllerParamsLogAspect.class);// 定义切点,匹配com.sunrise.controller包下所有的public方法,方法的参数任意@Pointcut("execution(public * com.sunrise.controller..*.*(..))")public void logAspect() {}// 前置通知,在执行controller方法前,打印方法入参@Before("logAspect()")public void doBefore(JoinPoint point) {// 构建打印内容JSONObject content = new JSONObject();try {... // 省略核心代码logger.error("API请求信息:{}", CommonUtils.jsonObjectToString(content));} catch (Exception exception) {... // 省略异常处理代码}} } -
以上与AOP有关的注解,需要的maven依赖如下:
<dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId><version>1.8.14</version> </dependency> -
其余术语概念可以参考:
- Spring AOP详解
- Spring 学习笔记(四):Spring AOP
-
PS: 阅读理论知识如果让你觉得迷糊,可以尝试直接看一段代码或者写一个小demo
2. AOP的实现方法
2.1 笔者的理解
-
通过对AOP基础知识的学习,在笔者心中AOP的实现方法,就应该像动态代理一样:以某种方式调用方法(如反射),并在方法的执行前后添加一些代码,从而可以在不修改已有业务逻辑的情况下增强方法
-
这是使用JDK动态代理实现的,打印方法耗时的核心代码:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {return method.invoke(animal, args);} finally {long diff = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;System.out.printf("%s() called, consumed %dms\n", method.getName(), diff);} } -
然而,动态代理是有针对性的,AOP应该是有普适性的
- cglib动态代理虽然能代理一个类,但是后续对该类的访问,都需要转为对proxy的访问
- AOP则可以在满足特定规则的所有方法上使用,例如,只要对方法添加指定注解,Aspect则可以应用到这些方法上;又或者,所以以
set开头的方法,都可以打印审计日志以记录数据的变化
-
让笔者不认同的是,有些博客宣称可以使用动态代理实现AOP,这明显是忽略了AOP的普适性
-
当然,这也可能是笔者对动态代理的理解不够深入 🤣 🤣 🤣
-
Guice使用拦截器机制实现AOP,笔者也比较赞同这种思想
2.2. Guice对AOP的支持
-
使用AOP实现一个打印方法耗时的功能,在目标方法执行结束后,系统会自动打印该方法的耗时
-
定义一个注解,使用该注解的方法,都将获得耗时打印的附加能力
@Target({METHOD}) @Retention(RUNTIME) public @interface PrintExecutionTime { } -
定义一个打印方法耗时的拦截器,它实现了
org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor接口public class ExecutionTimePrinter implements MethodInterceptor {@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();try {return invocation.proceed();} finally {long consumedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;System.out.printf("call %s() and consumed %dms\n", invocation.getMethod().getName(), consumedTime);}} } -
将拦截器应用到计算器的某些方法上
public class Calculator {private static final Random random = new Random();@PrintExecutionTimepublic int add(int a, int b) throws Throwable {// 随机休眠一段时间Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(2000));return a + b;}public int sub(int a, int b) {return a - b;}@PrintExecutionTimepublic int div(int a, int b) throws Throwable {// 随机休眠一段时间Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(2000));return a / b;}public long mul(int a, int b) {return a * b;} } -
在Module中定义pointcut,即拦截器将作用到满足什么规则的方法上
public class AopModule extends AbstractModule {@Overrideprotected void configure() {// ExecutionTimePrinter将作用到任意类的、使用了@PrintExecutionTime的方法上bindInterceptor(Matchers.any(), Matchers.annotatedWith(PrintExecutionTime.class),new ExecutionTimePrinter());} } -
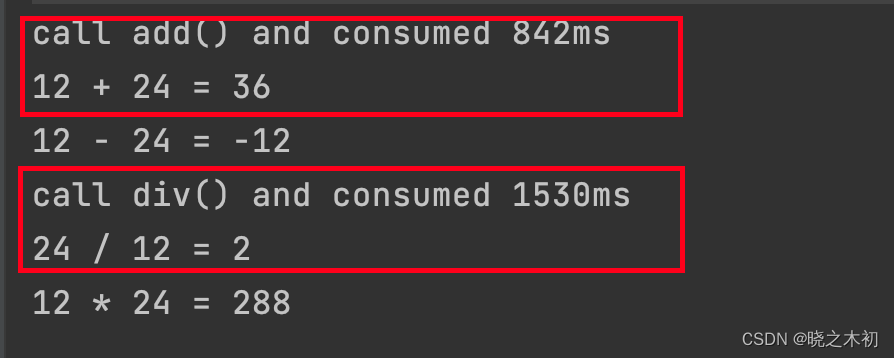
从Guice中获取一个计算器实例,执行其方法以验证拦截器是否生效
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {Injector injector = Guice.createInjector(new AopModule());Calculator calculator = injector.getInstance(Calculator.class);int a = 12, b = 24;System.out.printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, calculator.add(a, b));System.out.printf("%d - %d = %d\n", a, b, calculator.sub(a, b));System.out.printf("%d / %d = %d\n", b, a, calculator.div(b, a));System.out.printf("%d * %d = %d\n", a, b, calculator.mul(a, b)); } -
最终,添加了@PrintExecutionTime的
add()和div()方法执行结束后将打印耗时