系统编程之文件IO(四)——初级IO(open、close、write、lseek)
文章目录
- 1.open和close
- open的注意事项
- 2. write
- 3.read
- 问题产生:无法读到数据
- 当时程序
- 当时结果
- 原因分析
- 4.Iseek
- 附 man1、2、3的解释
1.open和close
原型:
int open (const char *pathname, int flags)
pathname 是文件名
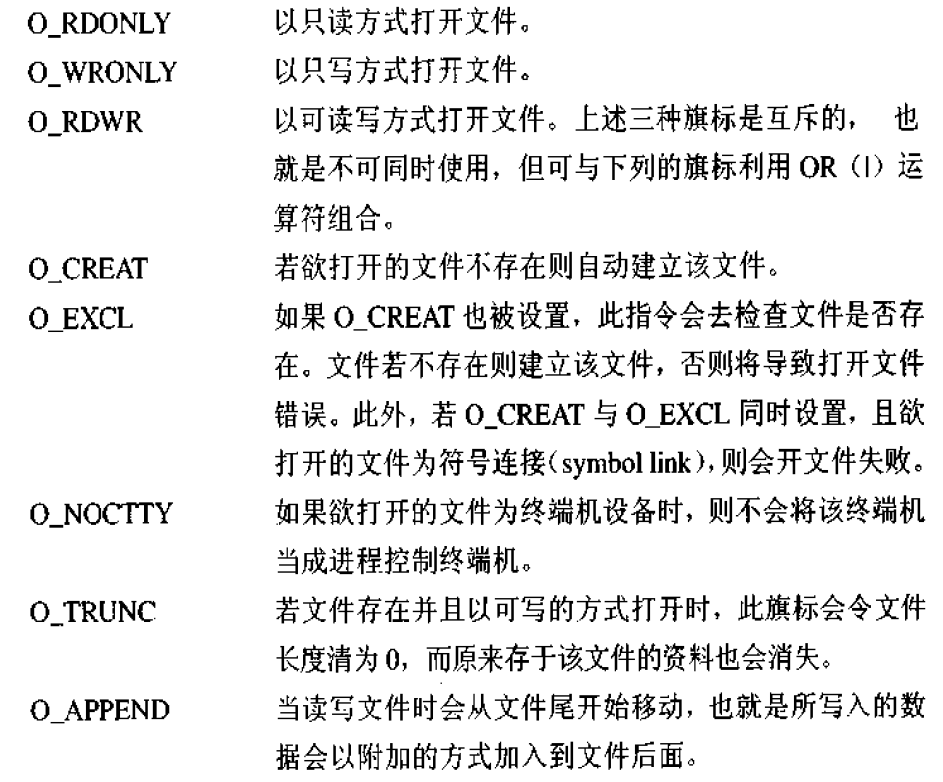
flags必须是以下之一:
- O_EDONLY 以只读方式打开
- O_WRONLY 以只写方式打开
- O_RDWR 以可读可写方式打开文件
mode_t mode 权限
返回值:成功返回文件描述符,失败返回-1
close(文件描述符)
open的注意事项
多次open同一文件、实现共享操作时、制定O_APPEND可以防止数据相互覆盖的发生
原因:不同程序的读写位置是不一样,(两个终端同时访问一个文件,文件读写位置是不一样的,会造成数据覆盖)
2. write
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count)
fd:往哪个文件去写
buf:把什么数据写进去(地址)
count:写多少个字节
返回值:返回写进去的字节数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){printf("please put in .txt\n"); }# if 0//creat("hello.txt",S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);//creat(argv[1], 0655);int fd = creat(argc[1], S_IRWXU | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH);if (fd == -1){printf("error!");}#endifint fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0655);if (fd == -1){perror("open file error!");exit(1);}printf("open file success! = %d\n", fd);char buffer[1024];strcpy(buffer, "hello world");int w_len = write(fd, buffer, strlen(buffer));if (w_len == -1){perror("write data error!");exit(1);}printf("write data len = %d\n", w_len);close(fd);return 0;
}
3.read
ssize_t read(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count)
fd:往哪个文件去读
buf:把读出的数据写进去(地址)
count:读多少个字节
返回:实际读到的字节数
跟write很像
问题产生:无法读到数据
当时程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){printf("please put in .txt\n"); }# if 0//creat("hello.txt",S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);//creat(argv[1], 0655);int fd = creat(argc[1], S_IRWXU | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH);if (fd == -1){printf("error!");}#endifint fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0655);if (fd == -1){perror("open file error!");exit(1);}printf("open file success! = %d\n", fd);char buffer[1024];strcpy(buffer, "hello world");int w_len = write(fd, buffer, strlen(buffer));if (w_len == -1){perror("write data error!");exit(1);}printf("write data len = %d\n", w_len);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));int r_len = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);if (r_len == -1)//r_len == 0 read file end{perror("read data error!");exit(1);}printf("read data :%s\n", buffer);close(fd);return 0;
}
当时结果
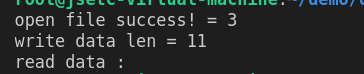
没有读到数据
原因分析
读文件:是从读写指针往后读的
4.Iseek
移动文件读写指针
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence)
off_t是有符号型
offset是向前,还是向后(负是向前)
whence先将文件指针固定到什么位置
SEEK_SET 将文件指针固定到开始位置
SEEK_CUR 将文件指针固定到现在位置
SEEK_END 将文件指针固定到末尾位置
返回值,距离文件头的长度
int file_len = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{if(argc != 2){printf("please put in .txt\n"); }# if 0//creat("hello.txt",S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);//creat(argv[1], 0655);int fd = creat(argc[1], S_IRWXU | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH);if (fd == -1){printf("error!");}#endifint fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0655);if (fd == -1){perror("open file error!");exit(1);}printf("open file success! = %d\n", fd);char buffer[1024];strcpy(buffer, "hello world");int w_len = write(fd, buffer, strlen(buffer));if (w_len == -1){perror("write data error!");exit(1);}printf("write data len = %d\n", w_len);memset(buffer, 0, sizeof(buffer));//lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);lseek(fd, -w_len,SEEK_CUR);int r_len = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);if (r_len == -1)//r_len == 0 read file end{perror("read data error!");exit(1);}else if(r_len == 0){printf("read file end\n");}printf("read data :%s\n", buffer);close(fd);return 0;
}
附 man1、2、3的解释
man 1:表示查看Linux命令
man 2:表示查看系统调用函数
man 3:表示查看标准C库函数
