sort函数用法与stable_sort函数
sort函数用于c++中,对给定区间所有元素进行排序,默认升序,也可以降序
头文件:#include< algorithm >
using namespace std;
语法:sort(start,end,cmp)
注意:第三个参数cmp升序情况下可以不写,降序情况需要多调用一个函数
参数:
(1)strat表示要排序的起始地址;
(2)end表示数组结束地址的下一位
(3)cmp用于规定排序方法,可以不填,默认升序
例如:
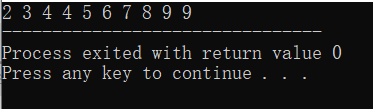
对a[10]数组升序排列
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{int a[10]={9,4,5,6,7,8,9,3,2,4};sort(a,a+10);for(int i=0;i<10;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);return 0;
}
运行结果:
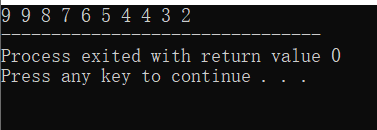
对a[10]数组降序排列(降序需要用到第三个参数cmp,多写一个函数)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b)
{return a>b;
}
int main()
{int a[10]={9,4,5,6,7,8,9,3,2,4};sort(a,a+10,cmp);for(int i=0;i<10;i++)printf("%d ",a[i]);return 0;
}
或者sort(a,a+10,greater< 类型 >( ));//头文件:#include< iostream >
运行结果:
假设自己定义了一个结构体node
typedef struct
{
int a;
int b;
double c;
}node;
node arr[100];
有一个node类型的数组node arr[100],想对它进行排序:先按a值升序排列,如果a值相同,再按b值降序排列,如果b还相同,就按c降序排列。就可以写一个比较函数:
以下是代码片段:
bool cmp(node x,node y)
{
if(x.a!=y.a) return x.a<y.a;
if(x.b!=y.b) return x.b>y.b;
return x.c>y.c;
}
stable_sort(稳定排序函数)
与sort的区别:sort更类似于快速排序的思想,而stable_sort用得是归并排序的思路
当数据都相同时,他不会打乱原有的顺序,所以更加稳定
例如:有两个相同的数A和B,在sort排序后B有可能会跑到A的前面,但是stable_sort则不会打乱原有顺序
