Postgresql B-tree索引
索引结构
B-tree索引的索引行存在page中,在叶子page中,存储这索引键和指向表行的TID信息。
B-tree索引的重要特性:
- B树是平衡的,也就是说,每个叶子页面从根节点由相同数量的内部页面分隔。因此,搜索任何值都花费相同的时间。
- B树有多个分支,即每个页面(通常为8 KB)包含许多(数百个)TID。所以,B树的深度很小,只有非常大的表,才会高达4–5的深度。
- 索引中的数据以升序排序(页面之间和每个页面内部),并且同一级别的页面通过双向列表相互连接。因此,我们可以仅通过列表的一个方向或另一个方向获得有序数据集,而不必每次都返回到根。
下图是一个简单的整数为索引键的例子
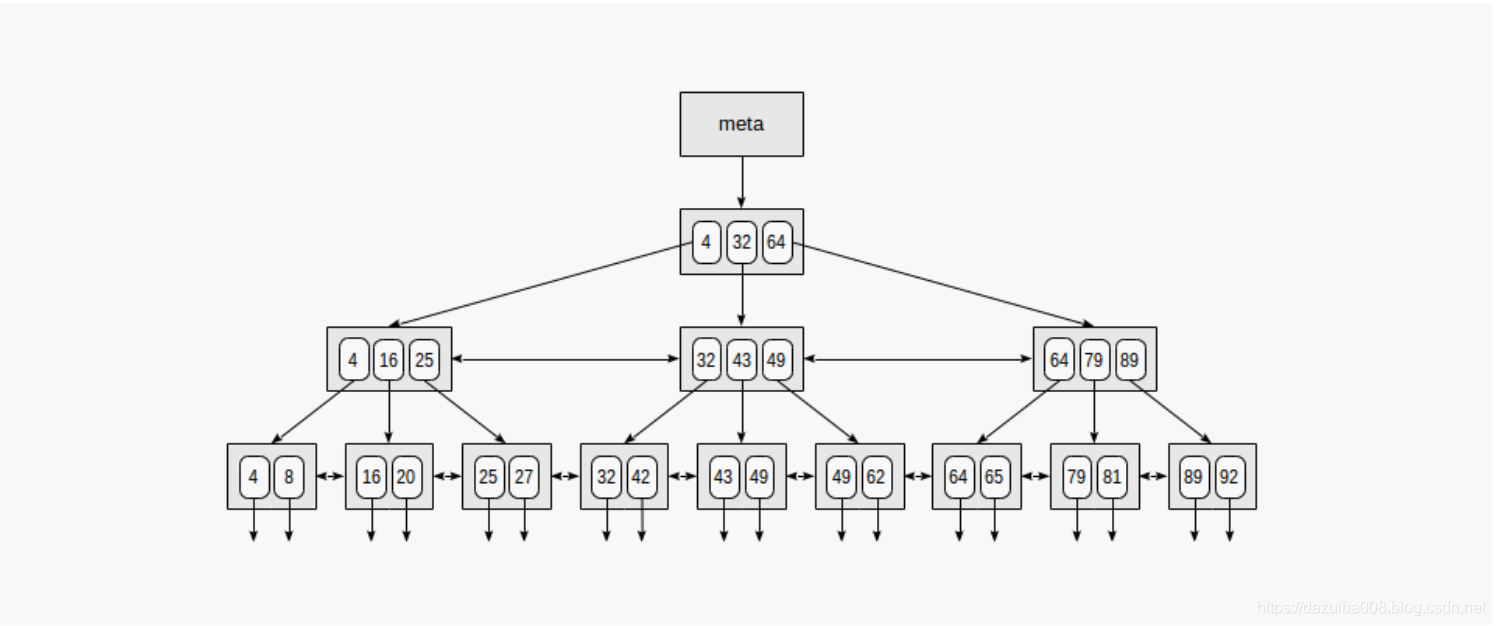
索引的第一页是meta页,它和索引的根节点关联。内部节点位于根下方,叶子页位于最底行。叶子节点向下的箭头表示从叶节点到表行(TID)的引用。
等值搜索
通过条件“索引字段=表达式”在树中搜索值。比如,搜索键值为49,过程如下
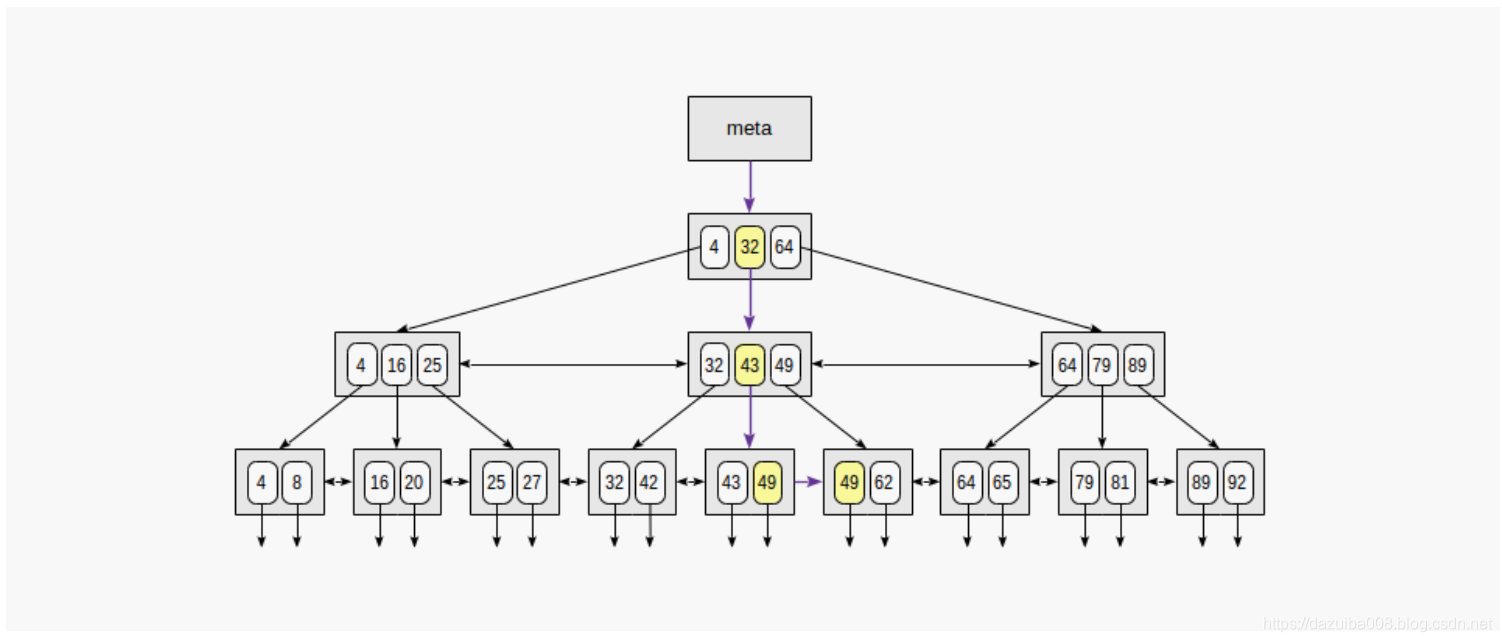
首先从根节点开始搜索,确定要降到下一层子节点。我们知道根节点(4、32、64)中的键,因此我们找出了子节点中的值范围。由于32≤49 <64,因此我们需要下降到第二个子节点。接下来,重复相同的过程,直到我们到达叶子节点,可以从该叶节点获得所需的TID。
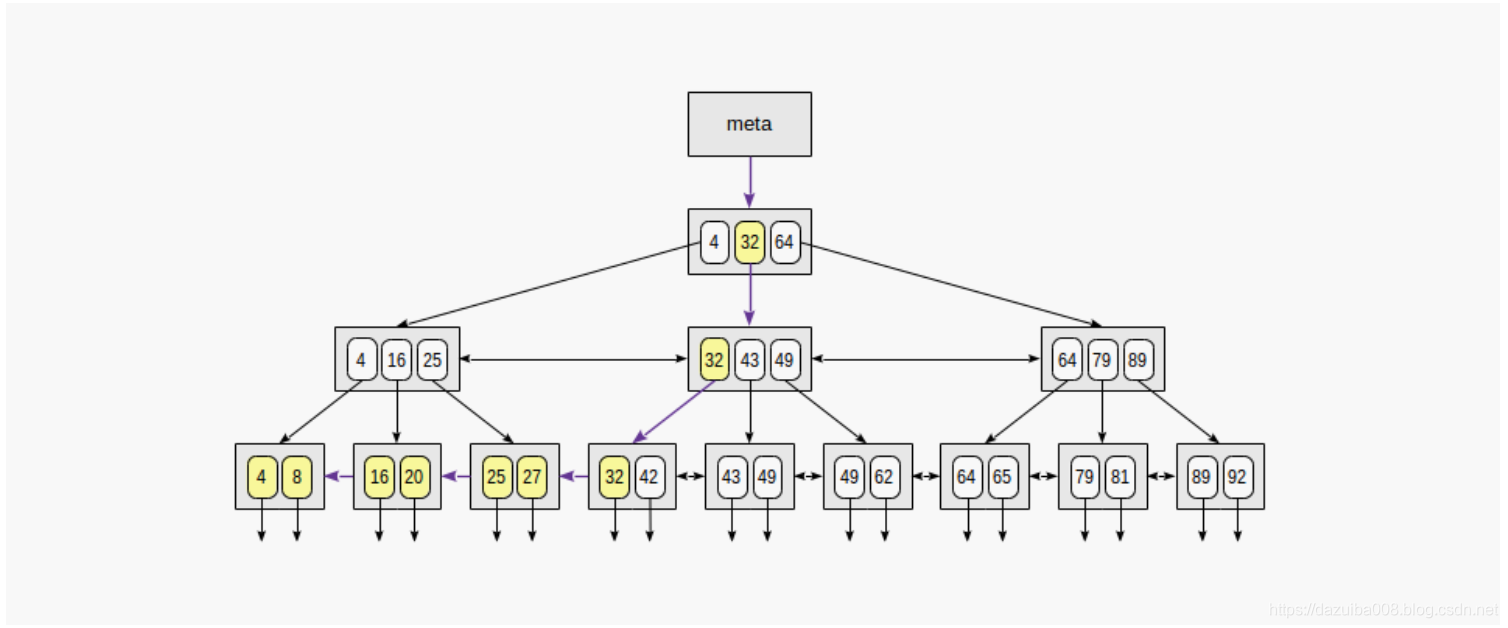
非等值搜索
当通过条件“ indexed-field≤expression”(或“ indexed-field≥expression”)进行搜索时,我们首先通过相等条件“ indexed-field = expression”在索引中找到一个值(如果有),然后按对应的方向遍历叶子页。
如下索引键n<=35的处理过程
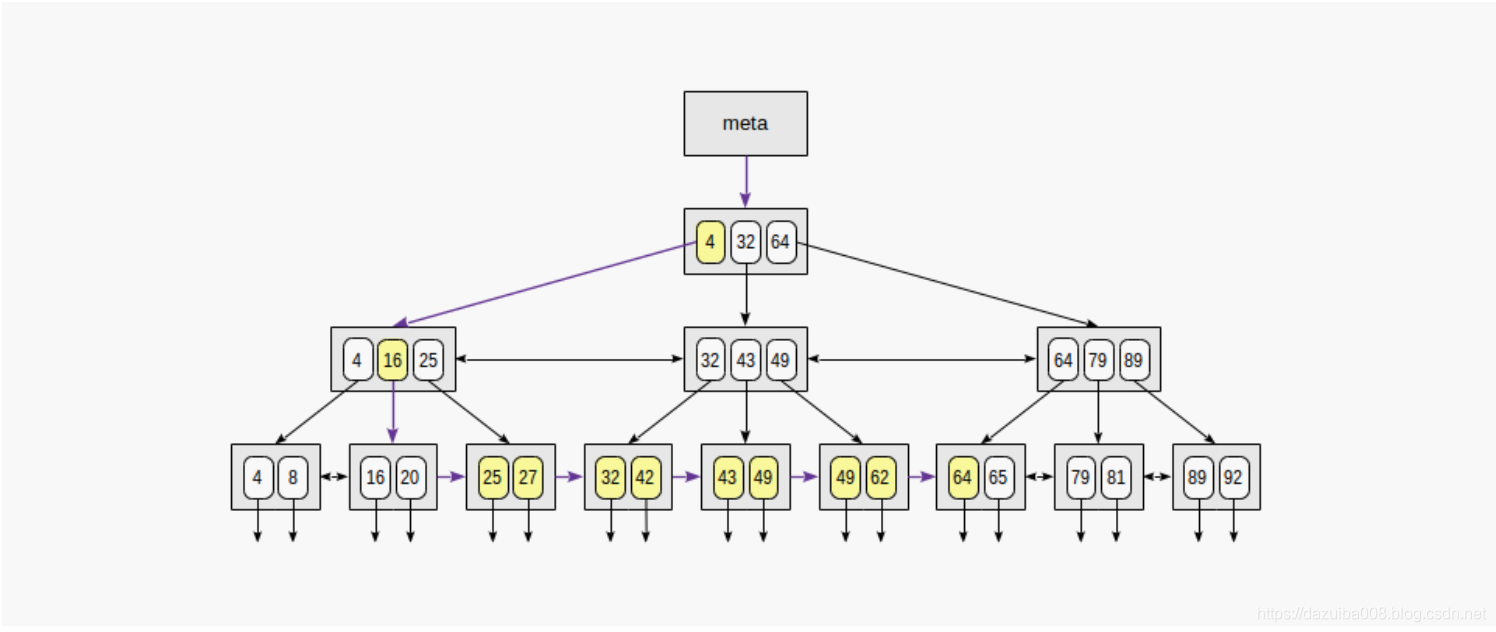
范围搜索
如:23 ≤ n ≤ 64 处理过程见下图
实际应用举例:
如下有9行飞行航班数据
demo=# select * from aircrafts;aircraft_code | model | range
---------------+---------------------+-------773 | Boeing 777-300 | 11100763 | Boeing 767-300 | 7900SU9 | Sukhoi SuperJet-100 | 3000320 | Airbus A320-200 | 5700321 | Airbus A321-200 | 5600319 | Airbus A319-100 | 6700733 | Boeing 737-300 | 4200CN1 | Cessna 208 Caravan | 1200CR2 | Bombardier CRJ-200 | 2700
(9 rows)在range创建B-tree索引
demo=# create index on aircrafts(range);
关闭全表扫描
demo=# set enable_seqscan = off;
等值查询执行计划
demo=# explain(costs off) select * from aircrafts where range = 3000;QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------Index Scan using aircrafts_range_idx on aircraftsIndex Cond: (range = 3000)
(2 rows)非等值查询的执行计划
demo=# explain(costs off) select * from aircrafts where range < 3000;QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------Index Scan using aircrafts_range_idx on aircraftsIndex Cond: (range < 3000)
(2 rows)范围查询的执行计划
demo=# explain(costs off) select * from aircrafts
where range between 3000 and 5000;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------Index Scan using aircrafts_range_idx on aircraftsIndex Cond: ((range >= 3000) AND (range <= 5000))
(2 rows)
排序使用索引
创建索引时,我们可以指定排序顺序。例如,我们可以通过这种方式特别按照航班范围创建索引:
demo=# create index on aircrafts(range desc);
在这种情况下,较大的值将出现在左侧的树中,而较小的值将出现在右侧。
表达式索引使用
demo=# create view aircrafts_v as
select model,casewhen range < 4000 then 1when range < 10000 then 2else 3end as class
from aircrafts;demo=# select * from aircrafts_v;model | class
---------------------+-------Boeing 777-300 | 3Boeing 767-300 | 2Sukhoi SuperJet-100 | 1Airbus A320-200 | 2Airbus A321-200 | 2Airbus A319-100 | 2Boeing 737-300 | 2Cessna 208 Caravan | 1Bombardier CRJ-200 | 1
(9 rows)
创建表达式索引
demo=# create index on aircrafts((case when range < 4000 then 1 when range < 10000 then 2 else 3 end),model);demo=# select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class, model;class | model
-------+---------------------1 | Bombardier CRJ-2001 | Cessna 208 Caravan1 | Sukhoi SuperJet-1002 | Airbus A319-1002 | Airbus A320-2002 | Airbus A321-2002 | Boeing 737-3002 | Boeing 767-3003 | Boeing 777-300
(9 rows)demo=# explain(costs off)
select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class, model;QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------Index Scan using aircrafts_case_model_idx on aircrafts
(1 row)可以降序使用索引,如下
demo=# select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class desc, model desc;class | model
-------+---------------------3 | Boeing 777-3002 | Boeing 767-3002 | Boeing 737-3002 | Airbus A321-2002 | Airbus A320-2002 | Airbus A319-1001 | Sukhoi SuperJet-1001 | Cessna 208 Caravan1 | Bombardier CRJ-200
(9 rows)demo=# explain(costs off)
select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class desc, model desc;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------Index Scan BACKWARD using aircrafts_case_model_idx on aircrafts
(1 row)
但是我们查询中如果一列是升序,一列是降序,那么无法使用该索引
demo=# explain(costs off)
select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class ASC, model DESC;QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------SortSort Key: (CASE ... END), aircrafts.model DESC-> Seq Scan on aircrafts
(3 rows)
创建对应的升序和降序的索引,才可以使用索引
demo=# create index aircrafts_case_asc_model_desc_idx on aircrafts((casewhen range < 4000 then 1when range < 10000 then 2else 3end) ASC,model DESC);demo=# explain(costs off)
select class, model from aircrafts_v order by class ASC, model DESC;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------Index Scan using aircrafts_case_asc_model_desc_idx on aircrafts
(1 row)
列的排序
使用多列索引时出现的另一个问题是索引中列出列的顺序。对于B树,此顺序非常重要:页面内的数据将按第一个字段排序,然后按第二个字段排序,依此类推。
如下图:
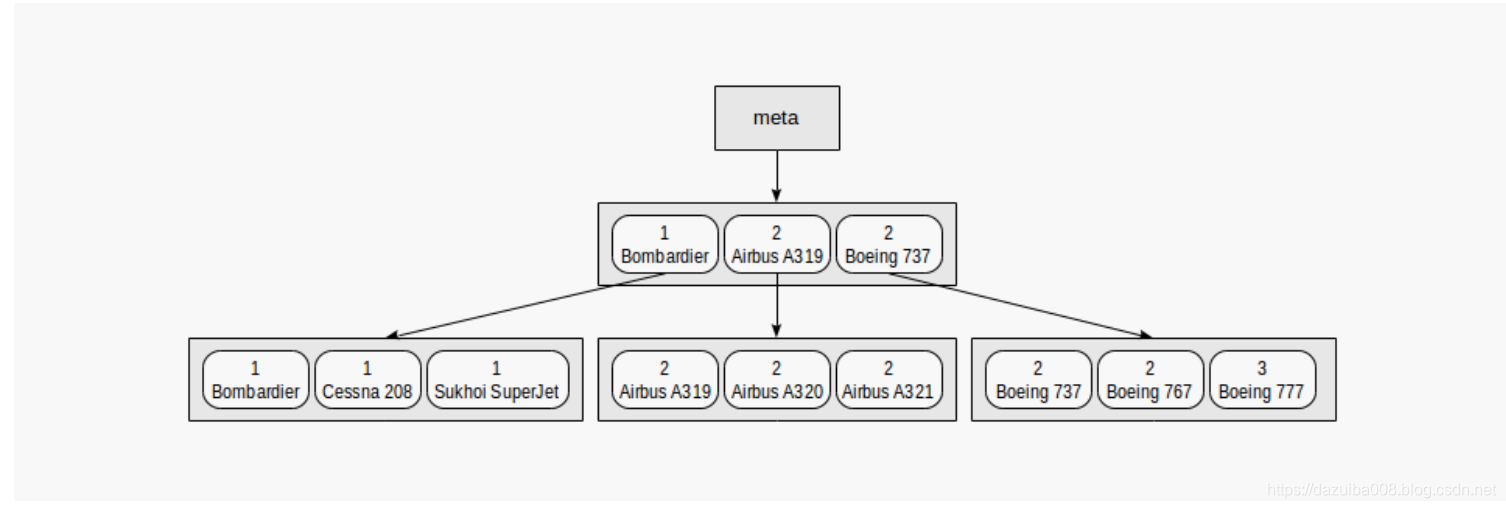
从该图可以清楚地看出,按谓词进行搜索,例如“ class = 3”(按第一个字段进行搜索)或“ class = 3 and model =‘Boeing 777-300’”(按两个字段进行搜索)将非常有效。
但是我们查询条件中如果只有"model = 'Boeing 777-300"的时候,也是从根节点开始扫描,但是不知道需要下降到下一层的那个节点,所以下面的节点都需要扫描。
创建以下索引
demo=# create index on aircrafts(model,(case when range < 4000 then 1 when range < 10000 then 2 else 3 end));
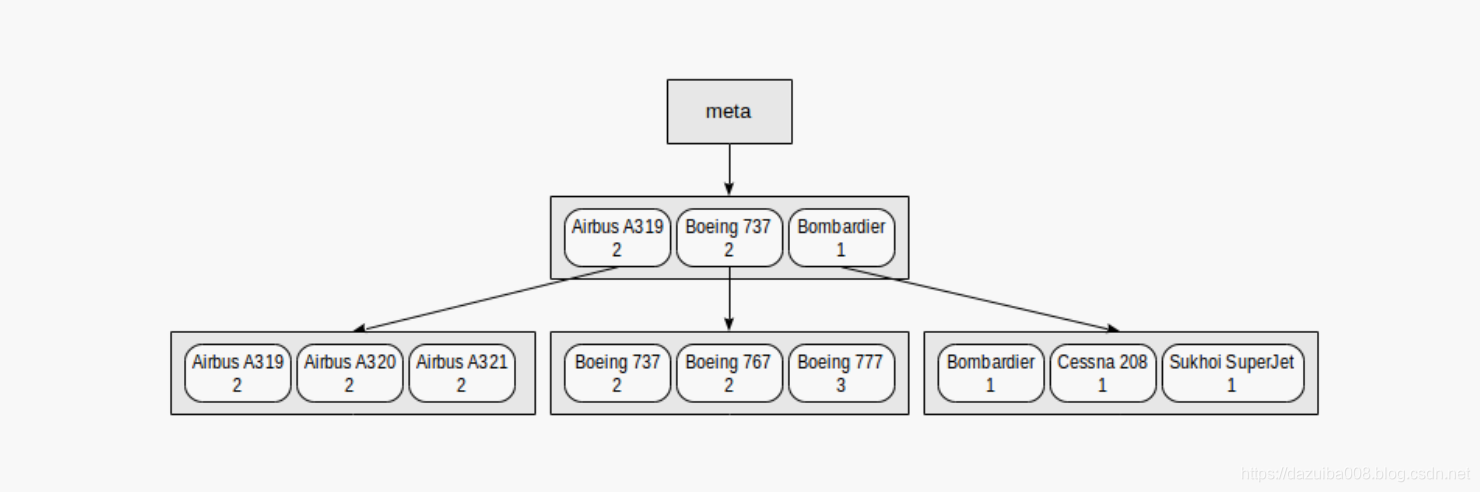
通过条件"model = ‘Boeing 777-300’"查询将会使用该索引,"class = 3"将不会使用,以上描述的就是前导列可以使用索引,没有前导列不能使用索引。
NULLs处理
B-tree索引支持IS NULL和IS NOT NULL,如下查询
demo=# create index on flights(actual_arrival);demo=# explain(costs off) select * from flights where actual_arrival is null;QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------Bitmap Heap Scan on flightsRecheck Cond: (actual_arrival IS NULL)-> Bitmap Index Scan on flights_actual_arrival_idxIndex Cond: (actual_arrival IS NULL)
(4 rows)
NULL位于索引的某一端,具体取决于创建索引的方式(NULLS FIRST或NULLS LAST)。如果SELECT命令在其ORDER BY子句中指定的NULL顺序与为构建索引指定的顺序相同(NULLS FIRST或NULLS LAST),则可以使用索引。
demo=# explain(costs off)
select * from flights order by actual_arrival NULLS LAST;QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------Index Scan using flights_actual_arrival_idx on flights
(1 row)
如果顺序不同,则无法使用索引
demo=# explain(costs off)
select * from flights order by actual_arrival NULLS FIRST;QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------SortSort Key: actual_arrival NULLS FIRST-> Seq Scan on flights
(3 rows)要想使用,则必须创建顺序一致的索引
demo=# create index flights_nulls_first_idx on flights(actual_arrival NULLS FIRST);demo=# explain(costs off)
select * from flights order by actual_arrival NULLS FIRST;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------Index Scan using flights_nulls_first_idx on flights
(1 row)原因是因为null和任何值比较,都是未定义的
demo=# \pset null NULLdemo=# select null < 42;?column?
----------NULL
(1 row)
B-tree的一些属性如下:
amname | name | pg_indexam_has_property
--------+---------------+-------------------------btree | can_order | tbtree | can_unique | tbtree | can_multi_col | tbtree | can_exclude | tname | pg_index_has_property
---------------+-----------------------clusterable | tindex_scan | tbitmap_scan | tbackward_scan | tname | pg_index_column_has_property
--------------------+------------------------------asc | tdesc | fnulls_first | fnulls_last | torderable | tdistance_orderable | freturnable | tsearch_array | tsearch_nulls | t
索引列之外的行可以使用index only scan
如下表结构,book_ref是主键也是外键
demo=# \d bookingsTable "bookings.bookings"Column | Type | Modifiers
--------------+--------------------------+-----------book_ref | character(6) | not nullbook_date | timestamp with time zone | not nulltotal_amount | numeric(10,2) | not null
Indexes:"bookings_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (book_ref)
Referenced by:TABLE "tickets" CONSTRAINT "tickets_book_ref_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (book_ref) REFERENCES bookings(book_ref)创建一个include book_date的索引
demo=# create unique index bookings_pkey2 on bookings(book_ref) INCLUDE (book_date);替换原来的索引
demo=# begin;demo=# alter table bookings drop constraint bookings_pkey cascade;demo=# alter table bookings add primary key using index bookings_pkey2;demo=# alter table tickets add foreign key (book_ref) references bookings (book_ref);demo=# commit;demo=# \d bookingsTable "bookings.bookings"Column | Type | Modifiers
--------------+--------------------------+-----------book_ref | character(6) | not nullbook_date | timestamp with time zone | not nulltotal_amount | numeric(10,2) | not null
Indexes:"bookings_pkey2" PRIMARY KEY, btree (book_ref) INCLUDE (book_date)
Referenced by:TABLE "tickets" CONSTRAINT "tickets_book_ref_fkey" FOREIGN KEY (book_ref) REFERENCES bookings(book_ref)可见select字段里面包含book_ref, book_date两个字段,但是依然可以走index only scan
demo=# explain(costs off)
select book_ref, book_date from bookings where book_ref = '059FC4';QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------Index Only Scan using bookings_pkey2 on bookingsIndex Cond: (book_ref = '059FC4'::bpchar)
(2 rows)
注意:只有B-tree支持include,include不支持表达式。
B-tree可以包含哪些操作
例如:布尔型和整型包含以下操作
postgres=# select amop.amopopr::regoperator as opfamily_operator,amop.amopstrategy
from pg_am am,pg_opfamily opf,pg_amop amop
where opf.opfmethod = am.oid
and amop.amopfamily = opf.oid
and am.amname = 'btree'
and opf.opfname = 'bool_ops'
order by amopstrategy;opfamily_operator | amopstrategy
---------------------+-------------- <(boolean,boolean) | 1<=(boolean,boolean) | 2=(boolean,boolean) | 3>=(boolean,boolean) | 4>(boolean,boolean) | 5
(5 rows) postgres=# select amop.amopopr::regoperator as opfamily_operator
from pg_am am,pg_opfamily opf,pg_amop amop
where opf.opfmethod = am.oid
and amop.amopfamily = opf.oid
and am.amname = 'btree'
and opf.opfname = 'integer_ops'
and amop.amopstrategy = 1
order by opfamily_operator;opfamily_operator
---------------------- <(integer,bigint)<(smallint,smallint)<(integer,integer)<(bigint,bigint)<(bigint,integer)<(smallint,integer)<(integer,smallint)<(smallint,bigint)<(bigint,smallint)
(9 rows)
新数据类型支持B-tree
创建复合类型和相关表,插入数据
postgres=# create type complex as (re float, im float);
postgres=# create table numbers(x complex);postgres=# insert into numbers values ((0.0, 10.0)), ((1.0, 3.0)), ((1.0, 1.0));postgres=# select * from numbers order by x;x
--------(0,10)(1,1)(1,3)
(3 rows)
默认情况下,对于复合类型,排序是按组件进行的:首先比较第一个字段,然后比较第二个字段,依此类推,与逐个字符比较文本字符串的方式大致相同。但是我们可以定义不同的顺序。例如,复合类型可被视为向量,并按系数(长度)排序,该系数被计算为坐标平方和的平方根。为了定义这样的顺序,让我们创建一个函数来计算:
postgres=# create function modulus(a complex) returns float as $$select sqrt(a.re*a.re + a.im*a.im);
$$ immutable language sql;postgres=# create function complex_lt(a complex, b complex) returns boolean as $$select modulus(a) < modulus(b);
$$ immutable language sql;postgres=# create function complex_le(a complex, b complex) returns boolean as $$select modulus(a) <= modulus(b);
$$ immutable language sql;postgres=# create function complex_eq(a complex, b complex) returns boolean as $$select modulus(a) = modulus(b);
$$ immutable language sql;postgres=# create function complex_ge(a complex, b complex) returns boolean as $$select modulus(a) >= modulus(b);
$$ immutable language sql;postgres=# create function complex_gt(a complex, b complex) returns boolean as $$select modulus(a) > modulus(b);
$$ immutable language sql;
创建运算符:
postgres=# create operator #<#(leftarg=complex, rightarg=complex, procedure=complex_lt);postgres=# create operator #<=#(leftarg=complex, rightarg=complex, procedure=complex_le);postgres=# create operator #=#(leftarg=complex, rightarg=complex, procedure=complex_eq);postgres=# create operator #>=#(leftarg=complex, rightarg=complex, procedure=complex_ge);postgres=# create operator #>#(leftarg=complex, rightarg=complex, procedure=complex_gt);
进行数值比较
postgres=# select (1.0,1.0)::complex #<# (1.0,3.0)::complex;?column?
----------t
(1 row)
postgres=# create function complex_cmp(a complex, b complex) returns integer as $$select case when modulus(a) < modulus(b) then -1when modulus(a) > modulus(b) then 1 else 0end;
$$ language sql;postgres=# create operator class complex_ops
default for type complex
using btree asoperator 1 #<#,operator 2 #<=#,operator 3 #=#,operator 4 #>=#,operator 5 #>#,function 1 complex_cmp(complex,complex);postgres=# select * from numbers order by x;x
--------(1,1)(1,3)(0,10)
(3 rows)postgres=# select amp.amprocnum,amp.amproc,amp.amproclefttype::regtype,amp.amprocrighttype::regtype
from pg_opfamily opf,pg_am am,pg_amproc amp
where opf.opfname = 'complex_ops'
and opf.opfmethod = am.oid
and am.amname = 'btree'
and amp.amprocfamily = opf.oid;amprocnum | amproc | amproclefttype | amprocrighttype
-----------+-------------+----------------+-----------------1 | complex_cmp | complex | complex
(1 row)
可以使用pageinspect查看B-tree索引的内部结构
可以看到有2个level,不包含root节点
demo=# create extension pageinspect;
Index metapage:demo=# select * from bt_metap('ticket_flights_pkey');magic | version | root | level | fastroot | fastlevel
--------+---------+------+-------+----------+-----------340322 | 2 | 164 | 2 | 164 | 2
(1 row)
块164的统计信息
demo=# select type, live_items, dead_items, avg_item_size, page_size, free_size
from bt_page_stats('ticket_flights_pkey',164);type | live_items | dead_items | avg_item_size | page_size | free_size
------+------------+------------+---------------+-----------+-----------r | 33 | 0 | 31 | 8192 | 6984
(1 row)
块中数据查看
demo=# select itemoffset, ctid, itemlen, left(data,56) as data
from bt_page_items('ticket_flights_pkey',164) limit 5;itemoffset | ctid | itemlen | data
------------+---------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------1 | (3,1) | 8 |2 | (163,1) | 32 | 1d 30 30 30 35 34 33 32 33 30 35 37 37 31 00 00 ff 5f 003 | (323,1) | 32 | 1d 30 30 30 35 34 33 32 34 32 33 36 36 32 00 00 4f 78 004 | (482,1) | 32 | 1d 30 30 30 35 34 33 32 35 33 30 38 39 33 00 00 4d 1e 005 | (641,1) | 32 | 1d 30 30 30 35 34 33 32 36 35 35 37 38 35 00 00 2b 09 00
(5 rows)
