MySQL强化关键_019_索引优化
目 录
一、最左前缀原则
1.完全使用索引
2.部分使用索引
3.不使用索引
4.效率折损
(1)使用范围查找
(2)索引断开
二、索引失效场景
1. 索引列参与运算
2.索引列模糊查询以“%”开始
3.索引列是字符串类型,查询省略单引号
4.查询条件包含“or”,其中有未添加索引的字段
5.查询符合条件的记录在表中占比较大
三、指定索引
四、覆盖索引
1.说明
2.实例
五、前缀索引
六、单列索引与复合索引的选择
七、创建索引的原则
一、最左前缀原则
# 初始化
drop table if exists t_customer;
create table t_customer(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10),age int,gender char(2),email varchar(20)
);
insert into t_customer(name, age, gender, email) values('刘林', 21, '女', '2238953721@999.com'),('王刚', 23, '男', '1477123899@999.com'),('赵辉', 19, '男', '3287654466@999.com'),('何钰', 20, '女', '7981112520@999.com'),('周洋', 27, '男', '6287553412@999.com');create index index_tcustomer_nag on t_customer(name, age, gender);show index from t_customer;
若要索引生效,必须遵循最左前缀原则。即上述为 t_customer 创建了name,age,gender 联合索引,添加顺序如此。则在进行查询时,如果 where 条件中没有 name 字段参与,则复合索引失效。
条件中必须要有最左侧字段参与,这样复合索引才会生效。最具有唯一性的字段应该放在最左侧。
1.完全使用索引
explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰' and age = 20 and gender = '女';
2.部分使用索引
explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰' and age = 20;explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰';explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰' and gender = '女';


3.不使用索引
explain select * from t_customer where age = 20 and gender = '女';4.效率折损
(1)使用范围查找
使用了范围查找,若范围条件不添加等号,则范围条件右侧列不会使用索引。
如下实例,从【key_len】字段可以看出:第一条【gender】字段没有使用索引。而第二条完全使用了索引。
explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰' and age > 20 and gender = '女';explain select * from t_customer where name = '何钰' and age >= 20 and gender = '女';

(2)索引断开
条件中使用了索引最左侧字段,但是没有使用索引中的全部字段且间断使用,会使间断的字段不使用索引。
如下方第一条,条件中没有使用【age】字段,而导致间断,所以【gender】字段没有使用索引。而第二条完全使用了索引。


二、索引失效场景
# 初始化
drop table if exists t_emp;
create table t_emp(id int primary key auto_increment,name varchar(10),sal int,age char(2)
);
insert into t_emp(name, sal, age) values('刘强', 6000, 37),('川建国', 2000, 53),('郭珊珊', 9000, 27);create index index_temp_name on t_emp(name);
create index index_temp_sal on t_emp(sal);
create index index_temp_age on t_emp(age);show index from t_emp;
1. 索引列参与运算
explain select * from t_emp where sal * 10 > 50000;
2.索引列模糊查询以“%”开始
explain select * from t_emp where name like '%珊珊';
3.索引列是字符串类型,查询省略单引号
explain select * from t_mep where name = 郭珊珊;
4.查询条件包含“or”,其中有未添加索引的字段
-- 查看执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age = '53' or sal = 2000;-- 删除sal索引
alter table t_emp drop index index_temp_sal;-- 查看执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age = '53' or sal = 2000;

5.查询符合条件的记录在表中占比较大
# 新插入几条数据
insert into t_emp(name, sal, age) values('王琳', 1800, 20),('张昂', 3000, 23),('李冬雪', 4000, 33),('王子安', 6500, 47),('陆佳佳', 7000, 28),('王明', 1000, 26),('邱钰红', 2500, 31),('黄灿灿', 10000, 38);# 创建sal索引
create index index_temp_sal on t_emp(sal);# 查询计划
explain select * from t_emp where sal > 1500;explain select * from t_emp where sal > 8000;
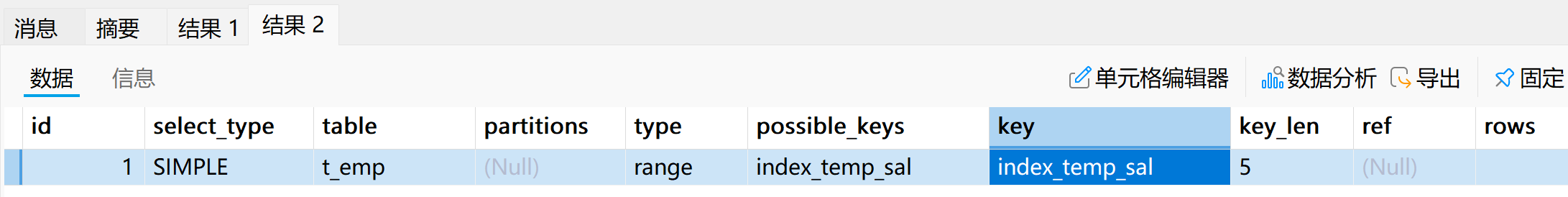
# 执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age is null;# 将age字段全部更新为null
update t_emp set age = null;# 执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age is null;
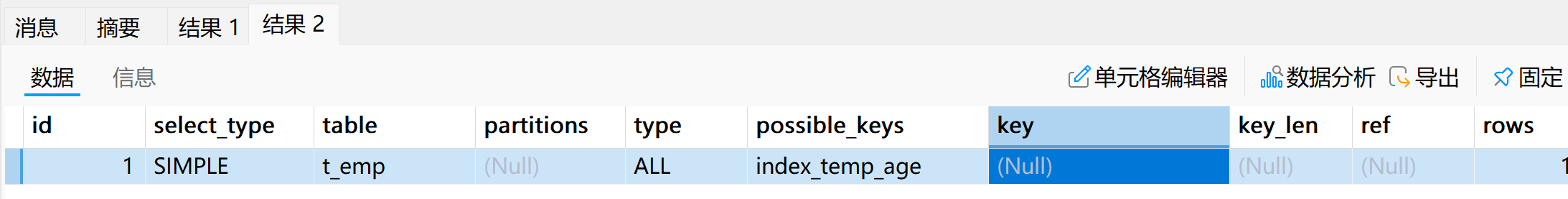
# 执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age is not null;# 将age字段全部更新为not null
update t_emp set age = 23;# 执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where age is not null;

三、指定索引
- 当一个字段上既有单列索引,也有复合索引,可以通过下述 SQL 语句指定索引:
- use index(索引名):建议使用该索引。MySQL 会根据实际效率考虑是否使用;
- ignore index(索引名):忽略该索引;
- force index(索引名):强制使用该索引。
# 查看索引
show index from t_emp;# 为 t_emp 添加一个复合索引
create index index_temp_nsa on t_emp(name, sal, age);# 查看索引
show index from t_emp;# 执行计划
explain select * from t_emp where name = '郭珊珊';
explain select * from t_emp use index(index_temp_nsa) where name = '郭珊珊';
explain select * from t_emp ignore index(index_temp_name) where name = '郭珊珊';
explain select * from t_emp force index(index_temp_nsa) where name = '郭珊珊';




四、覆盖索引
1.说明
select 后的字段,尽可能是索引所覆盖的字段,如此可以避免“回表”。
尽量避免使用【select * 】,因为其容易导致“回表”操作。
2.实例
t_user 表字段有: id,name,password,realname,birth,email。表中数据有600万条,请针对下述 SQL 给出优化方案。
select id, name, realname from t_user where name = '郭珊珊';建议给 name 和 realname 两个字段添加联合索引,减少回表操作,大大提升效率。
五、前缀索引
若一个字段类型是 varchar 或 text,直接对其创建索引会使索引体积较大。
那么,可以将字符串前几个字符截取下来当作索引,这种索引被称为前缀索引。
# 为t_emp表的name字段前两个字符创建索引
create index index_temp_subname on t_emp(name(2));# 截取字符数计算公式,其值越接近于1,越具有唯一性
select count(distinct substring(字段名, 1, 前几个字符)) / count(*) from 表名;select count(distinct substring(name, 1, 2)) / count(*) from t_emp;六、单列索引与复合索引的选择
当查询语句有多个条件,建议将这些列创建为复合索引,因为创建单列索引容易造成“回表”操作。
七、创建索引的原则
- 表中数据量庞大,通常超过百万;
- 经常出现在 where、order by、group by 后边的字段建议添加索引;
- 创建索引的字段具有较强的唯一性;
- 字段存储文本,内容较大,一定要创建前缀索引;
- 尽量使用复合索引,避免回表查询;
- 若一个字段中的数据不会为 null,建议建表时添加 not null 约束。如此优化器知道使用哪个索引列更有效;
- 不要创建太多的索引,因为对数据进行增删改时,索引需要重新排序;
- 如果较少查询,频繁增删改,不建议添加索引。

