android binder(二)应用层编程实例
一、binder驱动浅析

从上图看出,binder的通讯主要涉及三个步骤。
- 在 Binder Server 端定义好服务,然后向 ServiceManager 注册服务
- 在 Binder Client 中向 ServiceManager 获取到服务
- 发起远程调用,调用 Binder Server 中定义好的服务
整个流程都是建立在 Binder 驱动提供的跨进程调用能力之上,bingde驱动的实现比较复杂,现阶段我们先以黑盒的方式去了解它:
Binder 是一个 Linux 字符驱动,对外提供了以下函数供应用程序使用:
- open(),用于打开 binder 驱动,返回 Binder 驱动的文件描述符
- mmap(),用于在内核中申请一块内存,并完成应用层与内核层的虚拟地址映射
- ioctl,在应用层调用 ioctl 向内核层发送数据或者读取内核层发送到应用层的数据:
ioctl(文件描述符,ioctl命令,数据)文件描述符是在调用 open 时的返回值,ioctl 命令和第三个参数"数据"的类型是相关联的,具体如下:
| ioctl命令 | 数据类型 | 函数动作 |
|---|---|---|
| BINDER_WRITE_READ | struct binder_write_read | 应用层向内核层收发数据 |
| BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS | size_t | 设置最大线程数 |
| BINDER_SET_CONTEXT_MGR | int or flat_binder_object | 设置当前进程为ServiceManager |
| BINDER_THREAD_EXIT | int | 删除 binder 线程 |
| BINDER_VERSION | struct binder_version | 获取 binder 协议版本 |
二、安卓提供的封装
servicemanager - OpenGrok cross reference for /frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/

在 frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager 目录下的 binder.c 和 bctest.c 针对应用编写的需求,对open mmap ioctl 等基本操作做了封装,提供了以下几个函数:
- binder_open:用于初始化 binder 驱动
- binder_become_context_manager:设置当前进程为 ServiceManager
- svcmgr_lookup:用于向 ServiceManager 查找服务
- svcmgr_publish:用于向 ServiceManager 注册服务
- binder_call:用于发起远程过程调用
- binder_loop:进入循环,在循环中,获取和解析收到的 binder 数据
三、 ServiceManager 源码分析
- 打开 Binder 驱动
- 告知驱动自身为 service manager
- 循环处理
- 从驱动读取数据
- 解析数据并调用
- 处理service端的注册服务请求:其实就是在一个链表记录服务名
- 处理client获取服务请求:
- 在链表查询服务
- 返回 server 进程的 handle
service_manager.cbinder_open //打开 Binder 驱动binder_become_context_manager //告知驱动自身为 service managerbinder_loopbinder_parse //从驱动读取数据并解析svcmgr_handler//根据不同的命令,进入不同的处理流程do_add_service //添加服务do_find_service//获取服务四、编写自定义service代码
参考代码:bctest.c - OpenGrok cross reference for /frameworks/native/cmds/servicemanager/bctest.c
1、主流程:
- 打开binder驱动
- 注册服务
- 进入loop,等待client请求服务
2、消息处理流程
当 client 发起远程调用时,server 端会收到数据,并将这些数据传递给服务回调函数,这个回调函数需要我们自己来定义:也就是binder_loop(bs, test_server_handler)传入的test_server_handler函数。
3、服务处理流程:hello_service_handler
我们在注册服务的时候,传入了一个func handle, hello_service_handler。当收到client请求服务的时候,会进入这个函数进行处理。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>#include "binder.h"#define LOG_TAG "BinderServer"
#include <log/log.h>#define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO 1
#define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO 2void sayhello(void)
{static int cnt = 0;//fprintf(stderr, "say hello : %d\n", ++cnt);ALOGW("say hello : %d\n", ++cnt);
}int sayhello_to(char *name)
{static int cnt = 0;//fprintf(stderr, "say hello to %s : %d\n", name, ++cnt);ALOGW("say hello to %s : %d\n", name, ++cnt);return cnt;
}int hello_service_handler(struct binder_state *bs,struct binder_transaction_data_secctx *txn_secctx,struct binder_io *msg,struct binder_io *reply)
{struct binder_transaction_data *txn = &txn_secctx->transaction_data;/* 根据txn->code知道要调用哪一个函数* 如果需要参数, 可以从msg取出* 如果要返回结果, 可以把结果放入reply*//* sayhello* sayhello_to*/uint16_t *s;char name[512];size_t len;//uint32_t handle;uint32_t strict_policy;int i;// Equivalent to Parcel::enforceInterface(), reading the RPC// header with the strict mode policy mask and the interface name.// Note that we ignore the strict_policy and don't propagate it// further (since we do no outbound RPCs anyway).strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);switch(txn->code) {case HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO:sayhello();bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); /* no exception */return 0;case HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO:/* 从msg里取出字符串 */s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); //"IHelloService"s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len); // nameif (s == NULL) {return -1;}for (i = 0; i < len; i++)name[i] = s[i];name[i] = '\0';/* 处理 */i = sayhello_to(name);/* 把结果放入reply */bio_put_uint32(reply, 0); /* no exception */bio_put_uint32(reply, i);break;default:fprintf(stderr, "unknown code %d\n", txn->code);return -1;}return 0;
}int test_server_handler(struct binder_state *bs,struct binder_transaction_data_secctx *txn_secctx,struct binder_io *msg,struct binder_io *reply)
{struct binder_transaction_data *txn = &txn_secctx->transaction_data;int (*handler)(struct binder_state *bs,struct binder_transaction_data *txn,struct binder_io *msg,struct binder_io *reply);handler = (int (*)(struct binder_state *bs,struct binder_transaction_data *txn,struct binder_io *msg,struct binder_io *reply))txn->target.ptr;return handler(bs, txn, msg, reply);
}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{struct binder_state *bs;uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;uint32_t handle;int ret;//打开驱动bs = binder_open("/dev/binder", 128*1024);if (!bs) {fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver\n");return -1;}//添加服务ret = svcmgr_publish(bs, svcmgr, "hello", hello_service_handler);if (ret) {fprintf(stderr, "failed to publish hello service\n");return -1;}binder_loop(bs, test_server_handler);return 0;
}五、编写自定义client 代码
编写 Client 程序的主要流程如下:
- open binder 驱动
- 向service manager查询服务,获取到服务的句柄 handle
- 通过 handle 调用远程调用函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "binder.h"#define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO 1
#define HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO_TO 2int g_handle = 0;
struct binder_state *g_bs;void sayhello(void)
{unsigned iodata[512/4];struct binder_io msg, reply;/* 构造binder_io */bio_init(&msg, iodata, sizeof(iodata), 4);/* 放入参数 */bio_put_uint32(&msg, 0); // strict mode headerbio_put_string16_x(&msg, "IHelloService");/* 调用binder_call */if (binder_call(g_bs, &msg, &reply, g_handle, HELLO_SVR_CMD_SAYHELLO))return ;/* 从reply中解析出返回值 */binder_done(g_bs, &msg, &reply);}int main(int argc, char **argv)
{int fd;struct binder_state *bs;uint32_t svcmgr = BINDER_SERVICE_MANAGER;int ret;bs = binder_open("/dev/binder", 128*1024);if (!bs) {fprintf(stderr, "failed to open binder driver\n");return -1;}g_bs = bs;/* get service */g_handle = svcmgr_lookup(bs, svcmgr, "hello");if (!g_handle) {return -1;} //调用服务sayhello();}六、梳理(待整理)
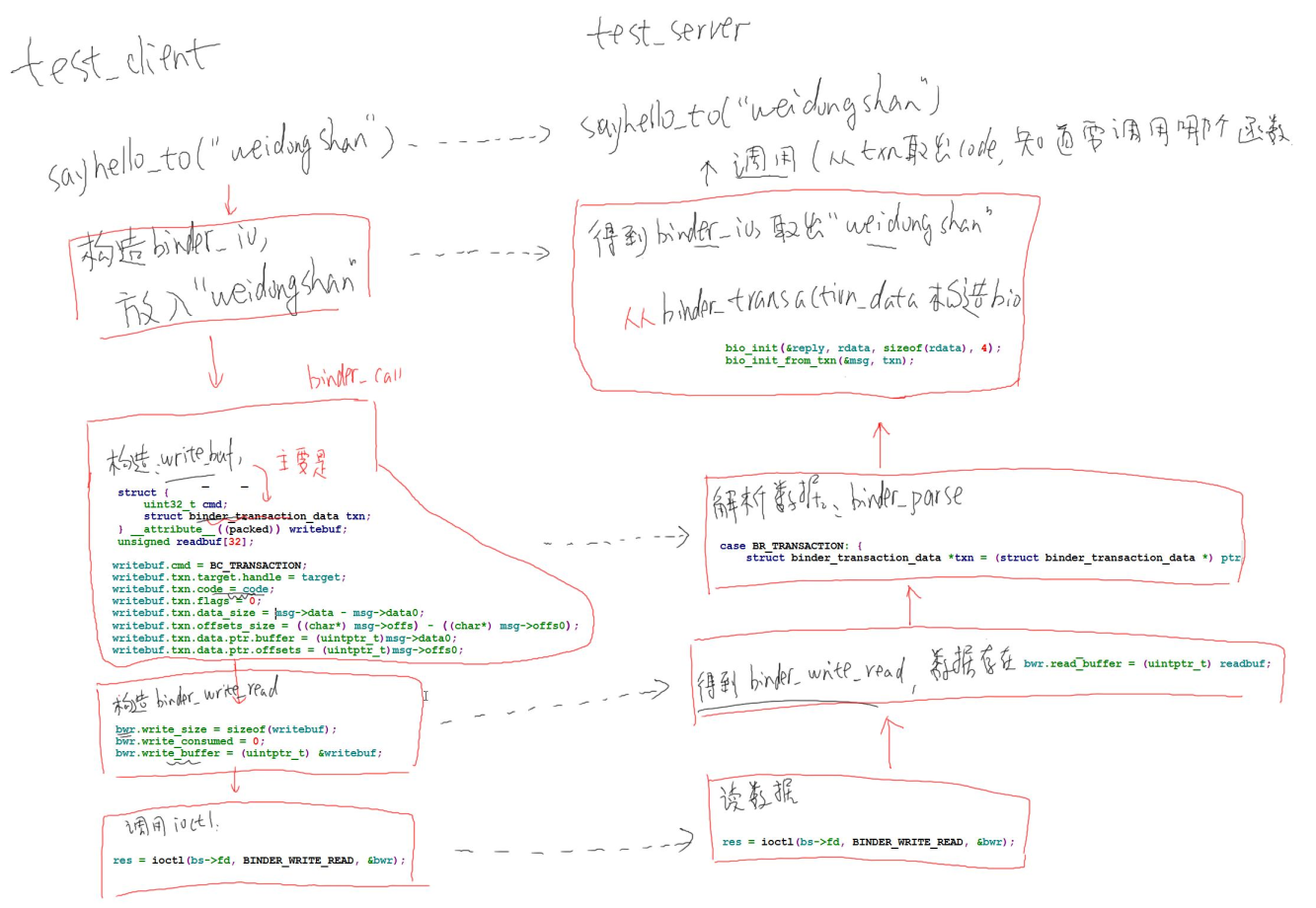
ref:
https://juejin.cn/post/7214342319347712057
Android系统--Binder系统具体框架分析(一) - lkq1220 - 博客园
https://juejin.cn/post/7210245482861264955
第5课第1节_Binder系统_C程序示例_框架分析_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
XRefAndroid - Support AOSP 15.0 AndroidXRef & OpenHarmony 5.0
【Android ServiceManager】从源码入手,剖析ServiceManager是如何处理客户端的请求的?_bnservicemanager 源码实现-CSDN博客
https://cs.android.com/android/platform/superproject/main
