Introduction to SQL

目录
SQL特点
编辑
Select-From-Where Statements
Meaning of Single-Relation Query
Operational Semantics
* In SELECT clauses
Complex Conditions in WHERE Clause
PATTERNS
NULL Values
Three-Valued Logic
Multirelation Queries
Aggregations
NULL’s Ignored in Aggregation
Grouping
HAVING Clauses
SQL特点
- SQL是一种结构化查询语言
- SQL语言包括DQL(数据查询)、DCL(数据控制)、DDL(数据定义)、DML(数据操纵)
- 因为关系模式中,实体与实体之间用关系表示联系,所以操作符比较简单,每种操作只需要一种操作符表示
- SQL语言的操作对象都是集合(查询、插入、修改、删除)
- SQL语言既是自含式语言,同时也是嵌入式语言
- 语言简洁
- 核心功能只有九个
Select-From-Where Statements
SELECT desired attributes
FROM one or more tables
WHERE condition about tuples of
the tables
Meaning of Single-Relation Query
-
Begin with the relation in the FROM clause.
-
Apply the selection indicated by the WHERE clause.
-
Apply the extended projection indicated by the SELECT clause
FROM确定数据源,WHERE进行数据的筛选,SELETE对属性进行投影
Operational Semantics
-
Think of a tuple variable visiting each tuple of the relation mentioned in FROM.
-
Check if the “current” tuple satisfies the WHERE clause.
-
If so, compute the attributes or expressions of the SELECT clause using the components of this tuple.
可以认为元组变量将访问所有FROM中涉及的关系,然后循环的检验是否满足WHERE中的条件,最后将满足条件的数据放到返回结果中,并且进行扩展投影
* In SELECT clauses
When there is one relation in the FROM clause, * in the SELECT clause stands for “all attributes of this relation.”
SELETE中既可以是属性也可以是常量
Complex Conditions in WHERE Clause
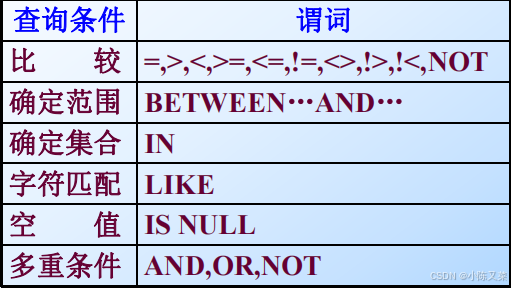
PATTERNS
-
A condition can compare a string to a pattern by: <Attribute> LIKE <pattern> or <Attribute> NOT LIKE <pattern>
-
Pattern is a quoted string with % = “any string”; _ = “any character. ”
-
% 0~任意多个字符
-
_ 任意单个字符
-
[] 集合范围内的任意单个字符
-
[^] 不在集合范围内的任意单个字符
-
[…-…] 前一字符至后一字符中的任一字符
-
ESCAPE 取消后面通配字符的通配作用(也就是说有时候需要使用到字符本身)
NULL Values
-
Tuples in SQL relations can have NULL as a value for one or more components.(SQL关系中允许元组有一种或多种属性是NULL)
-
Meaning depends on context. Two common cases:
Missing value : e.g., we know Joe’s Bar has some address, but we don’t know what it is.(缺省值)
Inapplicable : e.g., the value of attribute spouse for an unmarried person.(不适用值)
Three-Valued Logic
-
To understand how AND, OR, and NOT work in 3-valued logic, think of TRUE = 1, FALSE = 0, and UNKNOWN = ½.
-
AND = MIN; OR = MAX, NOT(x) = 1-x.
-
Example:
TRUE AND (FALSE OR NOT(UNKNOWN)) =
MIN(1, MAX(0, (1 - ½ ))) =
MIN(1, MAX(0, ½ )) = MIN(1, ½ ) = ½.
Multirelation Queries
-
Interesting queries often combine data from more than one relation.
-
We can address several relations in one query by listing them all in the FROM clause.
-
Distinguish attributes of the same name by “<relation>.<attribute>” .
Example: Joining Two Relations
Using relations Likes(drinker, beer) and Frequents(drinker, bar), find the beers liked by at least one person who frequents Joe’s Bar.
SELECT beer
ROM Likes, Frequents
WHERE bar = ’Joe’’s Bar’ AND
Frequents.drinker = Likes.drinker;Aggregations
-
SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX can be applied to a column in a SELECT clause to produce that aggregation on the column.
-
Also, COUNT(*) counts the number of tuples.

NULL’s Ignored in Aggregation
-
NULL never contributes to a sum, average, or count, and can never be the minimum or maximum of a column.
-
But if there are no non-NULL values in a column, then the result of the aggregation is NULL.
NULL值不参与聚合函数的运算
当表为空集时,返回结果为0
Grouping
- We may follow a SELECT-FROM-WHERE expression by GROUP BY and a list of attributes.(在select-from-where语句后面接GroupBy和一系列属性)
- The relation that results from the SELECT-FROM-WHERE is grouped according to the values of all those attributes, and any aggregation is
- applied only within each group.(select返回的结果将会被Group语句进行分组,并且groupby只在分组内应用)
select语句后面是可以接单属性的,当且仅当group后面接的属性
HAVING Clauses
- HAVING <condition> may follow a GROUP BY clause.
- If so, the condition applies to each group, and groups not satisfying the condition are eliminated.
注意:
WHERE:在分组前过滤行。
GROUP BY:对过滤后的行分组。
HAVING:对分组后的聚合结果过滤。
例题:


